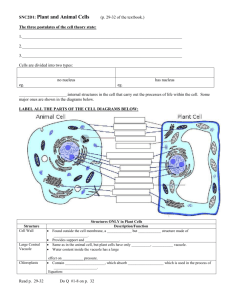
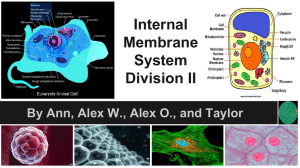
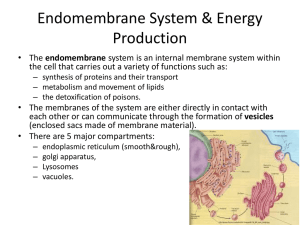
Cell Organelles
advertisement

Lysosomes • A sac of hydrolytic enzymes – – – – made in the rough ER & modified in the golgi Acidic in nature Special inner membrane that resists auto (self) digestion Can carry out intracellular digestion via phagocytosis (enfolding of membrane around an object) of membrane bound food vacuoles • Digestion products (simple sugars, amino acids, & other monomers) pass back to the cytosol via exocytosis Vacuoles • Food storage structures in plants, protist, and fungal cells. • Contain hydrolytic enzymes much like lysosomes • Can be specialized in different animals to perform specific functions – Contractile vacuole • protists use this structure to maintain salinity by adding and removing water – Central vacuole • found in mature plants – enclosed in a specialized membrane called a tonoplast – can be used to store molecules, ions, waste, pigments, or anything needed for growth – plays a major growth role • transform energy from their environment to be used by the host organism. They Mitochondria produce their own energy, are mobile, and divide (bud) to create new structures. – found in all Eukaryotes • Transferred from the maternal egg – site of cellular respiration • produces ATP through reactions in the mitochondrial membranes – the # of mitochondria present is based on the cell's (organism's) need for energy – has a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane called cristae – contains its own DNA & ribosomes Chloroplasts • Converts energy from the sun to into chemical energy – contain the green pigment chlorophyll • function in the photosynthetic production of sugar – consists of many flattened sacks called thalokoids (stacks are called granum) – fluid outside is called the stroma • contains the DNA & ribosomes Peroxisomes • Structures is much like lysosomes. – Produce peroxide (H2O2) for the breakdown of fatty acids by oxidation for use in the mitochondria. – Also found in the liver as sites of detoxification. – Glycoxysomes are specialized structures in plant seeds that convert fatty acids to sugar used as a source of energy • Cannot self replicate - product of lipids from the ER, proteins from the cytosol, & lipids made in the peroxisomes – they may split (bud) once the necessary parts are assembled and the size is sufficient Microfilaments • Threadlike structures that form a support structure for the cell and are used in movement – Composed of Actin • a double twisted rod • Muscle motor unit – long actin filaments bridged with myosin, a protein that "walks" the fiber causing contraction • Pseudopodia (fake foot) – actin network that converts the solution into gel in ameoboid organisms • Cytoplasmic streaming – a process in large plant cells where cytoplasm is directed to other parts of the cell to speed delivery of needed materials • Hollow tubes made of tubulin (globular protein) Microtubules – Centrosomes • located near the nucleus in plants • grow tubules outward resisting compression forces – Centrioles • a set of 9 tubes set in a ring • Help organize replication in animals – Flagella & Cilia • 9 + 2 arrangement • propel using a whip-like motion in flagella & oar-like motion in cilia