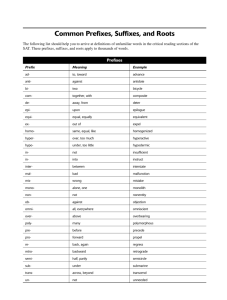
Combining Forms & Suffixes
advertisement

BASIC MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Presented by: Penny Osmon, BA, CPC Wisconsin Medical Society Copyright 2007 Objectives • Reviewing body systems and related medical terms • Understanding how medical terms are formed including combining forms, prefixes and suffixes • Learning to define, spell and pronounce medical terms according to the component word parts • Forming a foundation that allows continuing expansion of medicla terminology skills What We Will Cover Today! • • • • • • • • Basic Medical Word Structure Gastrointestinal System Respiratory System Cardiovascular System Urinary System Reproductive System Nervous System, Special Senses Integumentary System STOP! I will now test your knowledge Word Root • Foundation or core • All medical words contain one or more • Conveys fundamental meaning Example: HEPAT/ITIS "HEPAT" (liver) is the word root. SUFFIX • Medical terms may/may not contain a suffix • Attached to the end of a word root • Alters or modifies the meaning Example: HEPAT/ITIS "-ITIS" (inflammation) is the suffix. PREFIX • Attached to the beginning • Influences the meaning • Not all medical terms contain a prefix Example: SUB/HEPAT/IC "SUB-" (under) is the prefix. ("-IC" is the suffix for pertaining to, subhepatic means pertaining to under the liver.) COMBINING VOWEL • • • • • • Usually an “O” Links two word roots or a word root and a suffix Eases pronunciation Not all medical terms contain combining vowels Has no meaning of its own A word root which a vowel is attached is called a combining form RULES • When connecting two word roots, a combining vowel is usually used even when vowels are present at the junction oste/o/arthr/itis • When connecting a word root and a suffix, a combining vowel is usually not used if the suffix begins with a vowel - hepat/ic BREAKDOWN • Medical terms include pertinent word parts, not all the time • Breakdown can sometimes be misleading • Knowing the breakdown will help with the learning process • Breakdown alone will not always give you the entire meaning of the term • Useful tool for identifying procedure, anatomical site or condition EXAMPLES • LEUK/EMIA - literally means blood condition of white; actual meaning is large increase in the number of cancerous abnormal white blood cells • AUT/O/PSY - literally means process of viewing self; actual meaning is exam of dead body (with one’s own eyes) to determine cause of death Analyzing and Defining Medical terms are usually read “backwards” or suffix first Examples: HYPO GASTR IC Pertaining to below the stomach NEURO LOGY Study of Nerves SUFFIXES Pertaining To -AC -AL -AR -ARY -EAL -IAC -IC -ICAL -INE -IOR -OSE -OUS -TIC • • • • • • Hypogastric Peritoneal Cellac Pulmonary Infectious Diagnose SUFFIXES Abnormal -OSIS -IASIS • Cholelithiasis • Endometriosis SUFFIXES One Who -OR -ER • Doctor • Professor • Explorer SUFFIXES Specializes In -IST • • • • Cardiologist Proctologist Neurologist Allergist SUFFIXES Pain -ALGIA • Cephalalgia Headache SUFFIXES Hernia -CELE • • Cystocele Varicocele SUFFIXES Surgical Puncture -CENTESIS • Thoracentesis SUFFIXES Pain • -DYNIA • Gastrodynia • Mastodynia SUFFIXES Stretching -ECTASIA • Gastrectasia SUFFIXES To Cut or Remove -ECTOMY • Gastrectomy • Appendectomy • Tonsillectomy SUFFIXES Vomiting -EMESIS • Hyperemesis SUFFIXES Blood Condition -EMIA • Anemia • Leukemia SUFFIXES Recording or Tracing -GRAM • Radiogram SUFFIXES Process of Recording • Radiography -GRAPHY • Cardiography SUFFIXES Inflammation of Heat Redness Swelling Warmth -ITIS • Gastritis • Appendicitis • Tonsillitis SUFFIXES Process -ION • Incision SUFFIXES Study of Science of -LOGY • • • • Gastrology Hematology Cardiology Neurology SUFFIXES Tumor Benign Malignant – OMA • • • • Gastroma Lymphoma Melanoma Sarcoma SUFFIXES To View -OPSY • Biopsy SUFFIXES Disease of -PATHY • Hepatopathy • Neuropathy • Cardiopathy SUFFIXES Drooping Sagging -PTOSIS • Nephroptosis SUFFIXES Surgical Repair -PLASTY • Rhinoplasty • Bronchoplasty SUFFIXES Severe Bleeding Bursting -RRHAGIA -RRHAGE • Hemorrhage • Menorrhagia • Meningorrhagia SUFFIXES Suturing - RRHAPHY • Gastrorrhaphy SUFFIXES Instrument for Visual Exam -SCOPE • Gastroscope • Proctoscope • Bronchoscope SUFFIXES Visual Examination -SCOPY • Gastroscopy • Laparoscopy • Bronchoscopy SUFFIXES Sudden Muscle Contraction -SPASM • Pylorospasm • Bronchiospasm • Vasospasm SUFFIXES Stopping Controlling -STASIS • Hemostasis SUFFIXES Tightening Stricture -STENOSIS • • • • Pyloristenosis Aortostenosis Pulmonarystenosis Valvularstenosis SUFFIXES Artificial or Surgical • Gastrostomy Opening New Opening -STOMY SUFFIXES Instrument to Cut -TOME • Osteotome SUFFIXES To Cut Into -TOMY • Gastrotomy • Laparotomy SUFFIXES Structure -UM • Epigastrium • Hypogastrium PREFIXES Negative Prefix No, Not, Without A AN- • • • • Afebrile Amnesia Anemia Anesthesia PREFIXES Away From AB- • Abnormal • Aberration • Abortion PREFIXES Before ANTE- • • • • Antepartum Anterior Antecedent Anteversion PREFIXES Against ANTI- • Antibiotic • Antidepressant • Antidiuretic PREFIXES Through Complete DIA- • Diameter • Diagnosis • Diaphoretic PREFIXES Difficult DYS- • • • • Dysesthesia Dysopia Dysmenorrhea Dysphagia PREFIXES In, Within EN ENDO- • Endoscope • Encephalitis • Endotracheal PREFIXES Above EPI- • Epiglottis • Epidermis • Epistaxis PREFIXES Out EX EXO- • Excretion • Exopathy • Exfoliate PREFIXES Half HEMI- • Hemiplegia • Hemicolectomy • Hemisphere PREFIXES Excessive Above HYPER- • Hyperactive • Hyperglycemia • Hyperesthesia PREFIXES Below Deficient HYPO- • Hypoactive • Hypodermic • Hypokalemia PREFIXES Into IN- • Incision • Index • Inflammation PREFIXES Between INTER- • • • • Intercostal Interfemoral Intermission Interval PREFIXES Within INTRA- • • • • Intraabdominal Intracranial Intracostal Intramammary PREFIXES Surrounding Around Periphery PERI- • Peritoneum • Peritonsillar • Peristalsis PREFIXES Increased Many Much POLY- • Polycythemia • Polyarthritis • Polygraph PREFIXES After Behind in Time or Place POST- • Postnatal • Postoperative • Postmortem PREFIXES Before PRO- • Procedure • Procreation • Prophylaxis PREFIXES Back Again RE- • Reduplication • Reduction • Resection PREFIXES Behind Backwards RETRO- • Retroaction • Retroversion • Retropharynx PREFIXES Across TRANS- • Transabdominal • Transference • Transfusion COMBINING FORMS ADEN/o Gland • • • • Adenoma Adenosclerosis Adenotomy Adenodynia COMBINING FORMS • ARTHR/O Joint • • • • Arthritis Arthroscopy Arthroplasty Arthrocentesis COMBINING FORMS • CARCIN/O Cancer • • • • Carcinoma Carcinogen Carcinostatic Carcinolysis COMBINING FORMS • CYST/O Fluid filled Sac Bladder • Cystic • Cystitis COMBINING FORMS • CYT/O Cell • Cytology • Cytogenic • Cytonecrosis COMBINING FORMS • ERYTHR/O Red • • • • Erythrocytosis Erythrophobia Erythropsia Erythroderma COMBINING FORMS • GEN/O Causing Caused by • Carcinogenic • Cytogenic COMBINING FORMS • • HEM/O HEMAT/O Blood • Hematology • Hemocytology COMBINING FORMS • IATR/O Relating to treatment Relating to physicians Relating to medicine • Iatrogenic • Pediatrics COMBINING FORMS • LEUK/O White • Leukemia • Leukocytosis COMBINING FORMS • PATH/O Disease • Pathology • Pathologist COMBINING FORMS • PED/O Child • Pediatrics • Pediatrician COMBINING FORMS • PHAG/O To Eat • Dysphagia • Aphagia COMBINING FORMS • SECT/O To Cut • Section COMBINING FORMS • THROMB/O Clot • Thrombosis • Thrombocytopenia COMBINING FORMS • VISCER/O Internal Organ • Visceral • Visceromegaly Internal Organ VISCER/O Disease PATH/O Cell CYT/O Cancer CARCIN/O Joint ARTHR/O Blood Hemo/o Hemat/o Arthritis ARTHR/ITIS WR S Hepatitis HEPAT/ITIS WR S Subhepatic SUB/HEPAT/IC P WR S Intravenous INTRA/VEN/OUS P WR S Arthropathy ARTHR/O/PATHY WR V S Osteitis OSTE/ITIS WR S GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Alimentary Tract • Digestive System – – Abbreviated GI System or GI Tract This system has three functions • • • Digestion Absorption Elimination GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Organs of the Digestive Tract – – – – – – – Mouth Pharynx or Throat Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Anus GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Accessory Organs – – – – – Salivary Glands Liver Bile Ducts Gallbladder Pancreas GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Other Structures – Peritoneum – Appendix – Abdomen GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Additional Terms – – Bile or Biliary Peristalsis GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Combining Forms OR/O PHARYNG/O ESOPHAG/O GASTR/O PYLOR/O ILE/O, ENTER/O DUODEN/O JEJUN/O ILE/O Mouth or Oral Cavity Pharynx or Throat Esophagus Stomach Pyloric sphincter Small Intestine Duodenum Jejunum Ileum GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Combining Forms COL/O; COLON/O CEC/O APPENDIC/O APPEND/O SIGMOID/O RECT/O AN/O PROCT/O Colon, Large Intestine Cecum Appendix Sigmoid Colon Rectum Anus Rectum & Anus GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM • Combining Forms HEPAT/O CHOL/E, BIL/I CHOLEDOCH/O CHOLECYST/O PANCREAT/O VISCER/O Liver Bile Bile Ducts Gallbladder Pancreas Viscera (any internal organ) GI - Combining Forms • Combining Forms BUCC/O CELI/O LAPAR/O GLOSS/O LINGU/O Cheek Abdomen/belly Laparotomy Tongue Lingual Buccal Celiac Hemiglossectomy GI Combining Forms & Suffixes • • • • • • LITHI/O OMENT/O PERITONE/O SIALADEN/O SIAL/O SIAL Stones Omentum Peritoneum Salivary Gland Salivary; Saliva Cholelithiasis Omentectomy Peritoneal Sialism #1 A partial or complete excision of the tongue is? Hemiglossectomy #2 A plastic surgical repair of the esophagus? Esophagoplasty #3 A surgical removal of part of all of the stomach? Gastrectomy #4 The establishment of a permanent passage between the stomach and jejunum? Gastrojejunostomy #5 The visual examination of the rectum and sigmoid colon? Proctosigmoidoscopy #6 A plastic surgical repair of the small intestines? Enteroplasty #7 The surgical creation of a permanent opening into the jejunum? Jejunostomy #8 A surgical repair of the anus or rectum? Proctoplasty Anoplasty #9 The surgical repair of a bile duct? Choledochoplasty #10 Pertaining to under the tongue? Subglossal Sublingual Cholecystectomy Procedure Surgical removal of the gallbladder Hemicolectomy Procedure Removal of ½ or part of the colon Pancreatoma Diagnosis Tumor of the Pancreas Choledocholithiasis Diagnosis Abnormal condition of stones in the bile duct Diverticulectomy Procedure Removal of Diverticula Esophagogastoduodenoscopy Procedure Visual exam of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • Provides oxygen to all body cells through blood • Exchanges oxygen for carbon dioxide • Eliminates carbon dioxide from the body Organs of the Respiratory System EIGHT ORGANS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM • • • • • • • • Nose Pharynx Larynx Trachea Bronchus Lungs Diaphragm Mediastinum Additional Terms Respiratory System • Apex (apices) • Base • Hilum • Lobes • Pleura Top portion of lung Lower portion of lung Midline/bronchi enter lungs Division of lungs Membrane sac that surrounds each lung Respiratory System Combining Forms • NAS/O • • • • • • • RHIN/O SINUS/O PHARYNG/O TONSILL/O ADENOID/O LARYNG/O EPIGLOTT/O Nose Nose Sinus Pharynx Tonsil Adenoid Larynx Epiglottis Respiratory System Combining Forms • TRACHE/O • • • • BRONCH/O BRONCH/I BRONCHIOL/I ALVEOL/O Trachea Bronchus Bronchiole Alveolus Respiratory System Combining Forms • • • • • • CYAN/O OX/O LOB/O PECTOR/O THORAC/O PHREN/O Blue Oxygen Lobe Chest Thoracic Diaphragm Cyanosis Anoxia Lobectomy Pectoral Phrenic Respiratory System Combining Forms & Suffixes • PLEUR/O • • • • -PNEA PNEUM/O PNEUMON/O PULMON/O • -PTYSIS Pleura Breathing Lung Pleuritis Dyspnea Pneumorrhagia Pneumonitis Pulmonary Spitting Hemoptysis #1 The digestive tract is also known as the GI or Alimentary Tract System. #2 The combining form for stomach is Gastr/o. #3 The space between the lungs is called the Mediastinum. #4 The combining form “rhin/o” means Nose. #5 The combining form for lung is Pneumo, Pneumon, Pulmon #6 The suffix –pnea means breathing. #7 The medical term for inflammation of the stomach and intestines is gastroenteritis. #8 The definition of the suffix – algia is pain. #9 The membrane surrounding each lung is called the pleura. #10 The abbreviation NPO means nothing by mouth. Thoracentesis Procedure A puncture of the chest. Endotracheal Intubation Procedure Inserting a tube into the trachea. Tracheostomy Procedure Creating a new opening in the trachea. Hypoxia Diagnosis Low or deficient oxygen levels. Rhinoplasty Procedure Surgical repair of the nose (nose job). Question 6 What is the difference between a tracheotomy and tracheostomy? Stomy = new opening Tomy = incision/cut into CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM • Circulatory System • Continually moves blood throughout the body in order to provide oxygen, hormones and nutrients to the body tissue • Removes waste material Parts of the Cardiovascular System Heart Muscular Organ Circulates blood through body Two upper chambers and two lower chambers Cardiovascular - Valves • Tricuspid Valve • Bicuspid Valve • Semilunar Valves Three Layers of Heart • Pericardium • Myocardium • Endocardium Cardiovascular Blood Vessels • Tube-like structures • Carry blood through the body • Average adult has over 60,000 miles of blood vessels in their body Cardiovascular Arteries • Carry blood away from heart • Exception: Pulmonary Artery Arterioles Aorta Cardiovascular Veins • Carry blood back to the heart • Exception: Pulmonary Vein Venules Vena Cava Cardiovascular Capillaries • Connect arterioles with venules This is where the actual exchange of nutrients and waste occurs (good and bad) Walls only one cell thick Cardiovascular Blood • Composed of plasma and formed elements Plasma Cells – Erythrocytes – Leukocytes – Platelets (thrombocytes) Cardiovascular System Terms • • • • • • • • Pacemaker Coronary Arteries Septum Pericardium Systole Diastole Coagulation Platelets Cardiovascular Combining Forms • • • • CARDI/O ATRI/O VALVUL/O VENTRICUL/O Heart Right or Left Atrium Any Valve Right or Left Ventricle Cardiovascular Combining Forms • • • • • • AORT/O ARTERI/O ARTER/O ARTERIOL/O VENUL/O VEN/O; PHLEB/O Aorta Artery Arteriole Venule Vein Cardiovascular; Combining Forms, Prefixes & Suffixes • • • • • • ANGI/O VAS/O -SCLEROSIS BRADY-CYTE ERYTHR/O Blood Vessel Angiogram Vasospasm Hardening Arteriosclerosis Slow Bradycardia Cell Thrombocyte Red Erythrocytes Cardiovascular; Combining Forms, Prefixes & Suffixes • • • • • • • LEUK/O White MY/O Muscle -MEGALY Enlargement ATHER/O Plaque TACHYFast CHOLESTEROL/O ANEURYSM/O Leukocytes Cardiomyopathy Cardiomegaly Atherosclerosis Tachycardia Cholesterol Aneurysm LYMPHATIC SYSTEM • Removal of excessive waste products • Lymph vessels found throughout the body • • • • Lymphatic System Parts Lymph Lymph Nodes Spleen Thymus Gland Lymphatic System Combining Forms • • • • • • LYMPH/O LYMPHADEN/O TONSILL/O ADENOID/O THYM/O SPLEN/O Lymph Lymph node Tonsil Adenoid Thymus Spleen 1. Lymph Node C – Acts as a filter to keep bacteria from the blood 2. Aorta F – Largest artery in the body 3. Plasma G – Liquid portion of the blood 4. Vena Cava Largest vein in the body 5. Leukocyte I – White blood cell 6. Heart J - Pumps blood throughout the body. 7. Spleen H – Largest lymphatic organ in the body. 8. Erythrocyte A – Red blood cell 9. Vein E – Carries blood back to the heart 10. Artery D – Carries blood away from the heart Hypercholesterolemia Diagnosis Blood condition of excessive cholesterol. Aneurysmectomy Procedure Surgical removal of an aneurysm Splenomegaly Diagnosis Enlargement of the spleen Coronary Angiography Procedure A recording of the blood vessels in the heart Procedure that uses ultrasound to assess the structures of the heart Echocardiography Procedure that graphically records the electrical impluses of the heart on a strip of paper Electrocardiogrphy Surgical puncture of the pericardium to remove fluid for testing in order to determine the causative organism of pericarditis Diagnostic Pericardiocentesis Mitral stenosis MS Series of tests that establish diagnosis and the extent of myocardial infarction by checking the release of cardiac enzymes into the blood Cardiac Enzyme Studies Radiographic study to identify and locate thrombi in the veins of the legs Phlebography Measures the efficiency of the heart when subjected to a predetermined exercise Stress/Exercise Testing Myocardial Infarction MI URINARY SYSTEM • Filters waste material from the blood and eliminates it from the body • Kidneys Nephron Glomerulus Renal Pelvis • Ureters • Urinary Bladder • Urethra • Urine Urinary System Terms • Dialysis • Diuresis • Micturition • Urinalysis Urinary System Combining Forms • • • • • • • REN/O, NEPHR/O PYEL/O URETER/O CYST/O, VESIC/O TRIGON/O URETHR/O MEAT/O Kidney Renal Pelvis Ureter Bladder Trigone Urethra Meatus Urinary System Combining Forms & Suffixes • • • • • UR/O -URIA DIPS/O GLYC/O GLUC/O Urination Dysuria Thirst Sugar Polydipsia Glycosuria Urinary System Combining Forms & Suffixes • • • • NOCT/O OLIG/O BACTERI/O LITH/O Night Scanty Bacteria Stone Nocturia Oliguria Bacteriuria Ureterolithiasis Kidney REN/O NEPHR/O Bladder, Sac CYST/O VESIC/O Ureter URETER/O Renal Pelvis PYEL/O Urethra URETHR/O Meatus MEAT/O Stone LITH/O Urination UR/O Sugar GLYC/O GLUC/O Intravenous Pyleogram Procedure Tracing of the renal pelvis Meatal Stenosis Diagnosis Tightening of the Meatus Urethroplasty Procedure Surgical repair of the urethra Nephrolithotomy Procedure Cut into the kidney for stone removal REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM • Produces cells and hormones • Fertilization of sex cells • Development and birth of offspring Female Reproductive System Internal Organs • Ovaries Ovum Graafian Follicles • Fallopian tubes or uterine tubes • Uterus Endometrium Cervix • Vagina Hymen • Rectouterine Pouch Female Reproductive System Glands • Bartholin’s Glands • Mammary Glands Female Reproductive System External Structures • Vulva (external genitals) • Perineum Female Reproduction Combining Forms • • • • • • • • OOPHOR/O; OVARI/O SALPING/O HYSTER/O; UTER/O METRI/O; METR/O CERVIC/O COLP/O; VAGIN/O EPISI/O; VULV/O MAMM/O; MAST/O Ovary Fallopian Tube Uterus Cervix Vagina Vulva Breast Female Reproduction Combining Forms Prefixes & Suffixes • • • • • MEN/O Menstruation Menorrhagia CULD/O Cul-de-sac Culdocentesis LACT/O Milk Lactation -ARCHE Beginning Menarche MULTI- Many Multiparous Female Reproduction Combining Forms, Prefixes & Suffixes • • • • • • • NULLI- None Nulliparous PRIMI- First Primigravida -RRHEA Flow, Discharge Menorrhea -TOCIA Labor, Birth Dystocia -SALPINX Fallopian Tube O/O; OV/O Egg OVUL/O Ovulation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Mamm/o Mast/o Vagin/o Hyster/o Oophor/o Episi/o Salping/o Colp/o 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Breast Breast Vagina Uterus Ovary Vulva Fallopian Tubes Vagina Male Reproductive System • Produces sperm • Secretes the hormone testosterone Male Reproductive System Seven Organs • • • • • • • Testis or Testicle Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Scrotum Penis Semen Male Reproductive System Combining Forms • • • • • • • SCROT/O ORCHI/O; TEST/O VESICUL/O VAS/O URETHR/O PROSTAT/O BALAN/O Scrotum Testicle, Testes Seminal Vesicles Vas Deferens Urethra Prostate Penis STD’s - Sexually Transmitted Diseases • 3 types - not all inclusive Bacterial – Chlamydia – Gonorrhea – Syphilis Viral – Genital Herpes – AIDS Other – Trichomoniasis Prostate PROSTAT/O Testicle ORCHI/O TEST/O Penis BALAN/O Seminal Vesicles VESICUL/O Vas Deferens VAS/O Urethra URETHR/O Prostatectomy Procedure Surgical removal of the prostate Amenorrhea Diagnosis Without menstrual flow Endometritis Diagnosis Inflammation of the uterus Oophorectomy Procedure Surgical removal of an ovary Vasectomy Procedure Surgical removal of the vas deferens NERVOUS SYSTEM • • • • Communication Integration Control of body functions Recognition of sensory stimuli Central Nervous System Organs • Brain – Cerebrum or Forebrain • Ventricles – Midbrain and Interbrain • Thalamus • Hypothalamus – Hindbrain • Cerebellum – Brain Stem – Pons – Medulla Oblongata • • Spinal Cord Meninges Peripheral Nervous System Organs • Nerve – Cranial Nerves – Spinal Nerves • Ganglion Central Nervous System Combining Forms • CEREBR/O • ENCEPHAL/O • MYEL/O Brain Spinal Cord Bone Marrow Peripheral Nervous System Combining Form • NEUR/O Nerve SPECIALIZED SENSE ORGANS • • • • • • • OCUL/O Eye OPT/O OPHTHALM/O OPTIC/O AUR/O OT/O AURICUL/O Ear Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Disease of the retina due to diabetes. Neuroencephalomyelopathy Diagnosis Disease of the nerves, brain and spinal cord Blepharitis Diagnosis Inflammation of the eyelid Blepharoconjunctivitis Diagnosis Inflammation of the eyelid and lining of the eye #5 Tympanoplasty and Myringoplasty are BOTH surgical repairs of the ear drum INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM • • • • Protection Formation Regulation Collection Integumentary System • Skin Epidermis – Keratin – Melanin Corium or Dermis – Sweat Glands – Sebaceous Glands Subcutaneous – Thick tissue Integrementary eference: CPT Coding Made Easy, A Technical Guide, Kotoski, Gabrielle, Asp Publishers, Gaithersburg, MD,1999. Integumentary System • Accessory structures of the skin Hair Nails Integumentary System Combining Forms • • • • • • • • • DERM/O DERMAT/O CUTANE/O TRICH/O PIL/O ONYCH/O UNGU/O SEB/O HIDR/O Skin Hair Nails Sebum or Oil Sweat or Sweat Glands Integumentary System • • • • • MELAN/O Black Melanoma ERYTHEM/O Redness Erythematous LIP/O Fat Lipoma CAUS/O Burning Causalgia ERYTHEMAT/O HIDR/O Sweat DERM/O Skin ONYCH/O Nail TRICH/O Hair DERMAT/O Skin SEB/O Oil/Sebum UNGU/O Nail CUTANE/O Skin Inflammation of the skin DERMATITIS Pain in the skin DERMATALGIA DERMATODYNIA One who specializes in studying skin disease DERMATOLOGIST Pertaining to skin repair or skin grafting DERMATOPLASTY The branch of medicine concerned with the study of the skin DERMATOLOGY Abnormality of the skin DERMATITIS THANK YOU!!! Questions may be directed to: Penny Osmon, BA, CPC (608) 442-3781 Pennyo@wismed.org