Nile Civilizations Section 1
advertisement

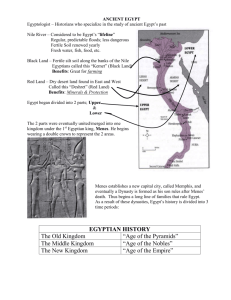
Nile Civilizations Section 1 Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Kingdom of Egypt Preview • Starting Points Map: The Nile Valley • Main Idea / Reading Focus • Geography and Early Egypt • The Old Kingdom • The Middle Kingdom • The New Kingdom • Map: The New Kingdom • Faces of History: Hatshepsut Nile Civilizations Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Section 1 Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Kingdom of Egypt Main Idea Egypt was one of the most stable and long-lasting civilizations of the ancient world. Reading Focus • How did geography influence Egypt’s early history? • What achievements were made in the Old Kingdom? • What happened during the Middle Kingdom? • What was Egypt like during the New Kingdom? Nile Civilizations Section 1 Geography and Early Egypt • The Nile – Most important physical feature in Egypt – 4,000 miles long; flows through the Sahara Desert • Without the Nile’s waters, no one could live there. Geography of Egypt • The Nile flooded every year – Predictable floodwaters with spring rains – Left rich, black silt • Narrow band of fertile soil • Became home of Egyptian civilization Section 1 Nile Civilizations Geographical Features Delta • Egypt’s most fertile soil in Nile Delta Cataracts • Nile afforded protection itself • Silt deposits at mouth of river • Flowed through cataracts to the south • Black Land of rich arable soil • Currents and waterfalls made sailing impossible • Red Land unlivable but afforded protection • Not an easy invasion route Nile Civilizations Two Kingdoms • First farming villages as early as 5000 BC • Northern Kingdom, Lower Egypt – Mild climate; cobra goddess worshipped • Southern Kingdom, Upper Egypt – Warmer climate; prayed to a vulture goddess Unification • Two kingdoms unified around 3100 BC • Upper Egypt ruler Menes conquered north – Founded capital city of Memphis – Adopted both symbols, the snake and the vulture • First of 31 dynasties Section 1 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Draw Conclusions How did geography affect where the early Egyptians lived? Answer(s): They lived in a narrow strip of fertile land where they could raise crops. It was surrounded by inhospitable desert, which would not easily support life. Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Old Kingdom Many of the institutions for which the Egyptian civilization is known were created during the period which began around 2650 BC. The Pyramids Building Pyramids • Most famous symbols of Egypt • Took great planning and skill • Largest located near Giza • Ordered when kings took the throne • Built as tombs for rulers – Hollow chamber for burial • Built from the inside out – Treasures buried with them • Not built by slaves – Deadly traps within • Design changed to smooth-sided over time – Peasants required to work one month per year – Professional craftspeople like architects, artists Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Pharaohs • The head of the government was the king • Became known as pharaoh (“great house”) • Had great power because he was believed to be a god • Egypt a theocracy, a state ruled by religious figures Egyptian Bureaucracy • Pharaoh could not rule Egypt alone • Aided by bureaucracy, many of whom were pharaoh’s relatives • Most powerful official was the vizier • Hundreds of lesser officials kept Egypt running smoothly Section 1 Nile Civilizations Summarize What Egyptian institutions were developed during the Old Kingdom? Answer(s): a government headed by the pharaoh, highly structured bureaucracy Section 1 Nile Civilizations The Middle Kingdom Old Kingdom collapsed around 2100 BC Warfare, economic strife for almost 200 years • New dynasty began Middle Kingdom 2055 BC – Strong leadership brought stability – Trade with surrounding lands encouraged • Trade routes not always safe – Fortresses built along the Nile – The Hyksos invaded, conquered around 1650 BC Section 1 Nile Civilizations Summarize How did the Middle Kingdom rise and fall? Answer(s): new dynasty came to power after almost 200 years of chaos; brought stability and economic prosperity; Middle Kingdom fell when Egypt was invaded by the Hyksos, who conquered Lower Egypt Section 1 Nile Civilizations The New Kingdom Hyksos ruled almost 100 years • Not harsh, but resented • Defeated by nobles from Thebes who became new rulers of Egypt First permanent army Securing Egypt • Egypt could not rely on geography for protection • Desert and sea not enough • Had to build powerful military Created an empire • Traditional foot soldiers • Egypt to rule beyond Nile Valley • Archers and charioteers • Headed south into Nubia • Adopted weapons from Hyksos • Also campaigns east into Asia Nile Civilizations Section 1 Nile Civilizations Section 1 The Reign of Hatshepsut • Hatshepsut best known for encouraging trade • Only woman pharaoh – Wanted to be treated like any other pharaoh – Dressed like a man, statues of her as a man Monotheism in Egypt • Amenhotep IV, 1353 – Worshipped only one god, Aten – Banned worship of all other gods • Built temple to Aten at Akhetaten • The next pharaoh restored worship of traditional gods Nile Civilizations Section 1 Section 1 Nile Civilizations Ramses the Great Egypt expanded empire • Fought campaigns in Nubia and Syria • A new foe around 1250 BC • Hittites invaded from Mesopotamia Confrontation with Hittites • Ramses the Great led army • Accounts of battle vary, but two armies signed truce • Ramses married Hittite princess and conflict ended Ramses’ rule • Reign marked with extravagant splendor • Built more temples and monuments than other pharaohs • Many political and artistic achievements Section 1 Nile Civilizations Egypt’s Decline • Ramses’ successors faced challenges to authority • Major invasions of Egypt – Sea Peoples devastated empires – Ended Hittite Empire, weakened Egypt’s control of Syria • Egypt broke into small states – Many foreign rulers over next 700 years – Libyans, Assyrians, Persians, Greeks – Finally fell to Rome Section 1 Nile Civilizations Sequence How did Egypt grow and change during the New Kingdom? Answer(s): built strong military, created own empire, increased trade