Chapter 1 PowerPoint
advertisement

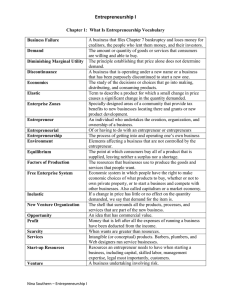
Going Into Business for Yourself What is Entrepreneurship? What is Entrepreneurship? Entrepreneur is an individual who undertakes the creation, organization and ownership of a business. Venture - A business enterprise involving some risk in expectation of gain. What is Economics? Economics is the study of how people choose to allocate scarce resources to fulfill their unlimited wants. Economics has a great influence on entrepreneurship. 3 Fundamental Questions asked of the economic system What goods and services should be produced and how much in quantity should be produced? How should goods and services be produced? For whom should goods and services be produced? The Free Enterprise System In a free enterprise system (also called capitalism or a market economy), people choose what products to buy, what property to own, and can choose to start a business and compete with other businesses on their own. The price of a product is determined by the marketplace. Most Democratic nations have this type of enterprise system. Profit Motive Profit - money that is left after all expenses of running a business have been deducted from the income. Competition Provides consumers with choice In a free enterprise system, competition forces companies to improve quality and become more efficient. Leads to surplus, which leads to lower prices. Risk of failure encourages the production of quality products that meet the needs of consumers Market Structures Perfect competition – the goods or service being sold is nearly identical. • Numerous buyers and sellers with no single buyer or seller capable of affecting price. Monopolistic competition – many sellers produce similar but differentiated products. • Retail stores, fast food, gas stations Monopoly and Oligopoly A Monopoly is when a business is the sole supplier of a particular good or service and they are given the total control over price. • National Grid, Amtrak Oligopoly is a market in which control over the supply of a commodity is in the hands of a small number of larger companies who have dominated the industry. • Ex. Tobacco Industry, Automobile Industry, Softdrink industry, Basketball sneakers Oligopolies Company US Brands Market Share Philip Morris Marlboro, Virginia Slims, Benson & Hedges, Merit, Parliament, Alpine, Cambridge 49.9% R.J. Reynolds Camel, Doral, Winston, Salem, Vantage, More, Monarch 22.9% BAT/Brown & Williams GPC, Kool, Viceroy, Raleigh, Barclay, Lucky Strike 10% Lorrillard Newport, Kent, True, Old Gold, Max, Style, Crowns 8.2% Liggett & Myers L&M, Lark, Chesterfield, Eve 2.3% Company Basketball Superstar Market Share Nike Michael Jordon (Now)LeBron James 60% Adidas Tracy McGrady 20% Reebok Allen Iverson 15% What resources does it take for a business to produce a good and service? Factors of Production • Land – geographic territory, air, trees, minerals and crude oil • Labor – Human efforts • Capital – money, equipment, tools • Entrepreneurship – ideas and decisions of business owner Scarcity occurs when demand exceeds supply Supply and Demand Demand – quantity of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to buy. Supply – goods and services that producers are willing and able to provide. Equilibrium is the point at which consumers buy all of a product that is supplied. Theory of Supply and Demand Heavy demand + Short Supply = price increase. Heavy supply + Short Demand = Price decrease. Prices tend to stabilize at the level where demand equals supply • Equilibrium point Supply/Demand Elastic demand – a change in price creates a change in demand • Butter Inelastic demand – a change in price has little effect on demand for product. • Milk ECONOMIC INDICATORS Employment rate Consumer confidence GDP ( Gross Domestic Product) – • the total market value of goods and services produced by workers and capital within a country during a given period. Business Cycle Economy is growing rapidly = inflation Economy is slowing down = deflation. Start-Up Process – 5 Key Components Entrepreneur – driving force of start up process. Environment • Enterprise Zone – specially designated areas of a community that provide tax benefits to new businesses locating there. Opportunity Start-Up Resources New Venture Organizations New Business Failure A business failure is a business that has stopped operating with a loss to creditors. Discontinuance is when a business is operating under a new name Supply Curve Original Supply Decrease in supply Shift to the left Price Increase in supply Shift to the right Quantity Demand Curve Original Demand Price Decrease in demand Shift to the left Increase in demand Shift to the right Quantity How to read a graph! Apple Juice Market Original Demand Original Supply 10.00 9.00 8.00 New E.P. 7.00 6.00 Price Original E. P. 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 1 2 3 4 Quantity 5 6 7