Atoms
advertisement

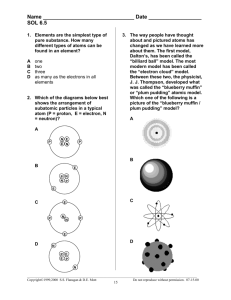
S.MORRIS 2006 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZ6zR 0vu7cU&feature=related Bill Nye the Science Guy The word atom is derived from the Greek word atom which means indivisible. (uncuttable) The Greeks concluded that matter could be broken down into particles too small to be seen. These particles were called atoms The Atom Atoms are made up of 3 types of particles electrons , protons and neutrons . Electrons are tiny, very light particles that have a negative electrical charge (-). Protons are much larger and have a positive charge (+). Neutrons are large and heavy like protons, however neutrons have no electrical charge. (Neutral) The Atom ATOMIC STRUCTURE He 2 4 Atomic number the number of protons in an atom Atomic mass the number of protons and neutrons in an atom number of electrons = number of protons Atomic mass = protons + neutrons Atomic number = the number of protons The number of protons = The number of electrons. The Atom Give the symbol and number of protons in one atom of: Li, 3 Lithium __________________ Br, 35 Bromine __________________ Iron __________________ Fe, 26 Cu, 29 Copper __________________ Checking on the Atom Give the symbol and number of electrons in a neutral atom of: Uranium __________________ U, 92 Cl, 17 Chlorine __________________ B, 5 Boron __________________ I, 53 Iodine __________________ Checking on the Atom Give the symbol and number of neutrons in a neutral atom of: Carbon __________________ C, 12 - 6 = 6 neutrons Cu, 64 - 29 = 35 neutrons Copper __________________ Fluorine __________________ F, 19 - 9 = 10 neutrons Mg, 24 - 12 = 12 neutrons Magnesium __________________ Atomic mass = protons + neutrons Checking on the Atom 1913 Niels Bohr Bohr claimed electrons move in paths around the nucleus. They are very small without much mass. History of the Atom Model of the atom pictures the electrons moving around the nucleus in a region called an electron cloud. The electron cloud is a cloud of varying density surrounding the nucleus. The varying density shows where an electron is more or less likely to be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels have additional electron clouds of different shapes that also show where those electrons are likely to be. What is the Electron Cloud Model? http://regentsprep.org/Regents/physics/phys05/catomodel/cloud.htm Do you know what these are called? Electron Orbital What is the Electron Cloud Model? Electrons can spin in any direction; scientists cannot tell exactly where an electron is at a given moment or where it is going. They can calculate the probability that an electron will be found in a given space. This is quantum mechanics. The distance from the nucleus that the electron spins is called its energy shell, energy level, or orbital. Orbital Electrons are arranged in Energy Levels or shells around the nucleus of an atom. The first shell can hold The second shell can hold The third shell can hold The fourth level can hold The fifth level can hold The sixth level can hold The seventh level can hold Atomic Structure 2 electrons 8 electrons 8 electrons 18 electrons 32 electrons 50 electrons 72 electrons ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION With electronic configuration elements are represented numerically by the number of electrons in their shells and number of shells. For example; Nitrogen 2 in 1st shell 5 in 2nd shell configuration = 2 , 5 2 + 5 = 7 N 7 14 ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION Write the electronic configuration for the following elements; a) Ca 20 b) Na 40 2,8,8,2 d) Cl 17 35 2,8,7 11 23 c) 2,8,1 e) Si 14 28 2,8,4 O 8 16 2,6 f) B 5 11 2,3 DOT & CROSS DIAGRAMS X X X N X X X X N 7 14 Nitrogen With Dot & Cross diagrams elements and compounds are represented by Dots or Crosses to show electrons, and circles to show the shells. Dot and Cross Diagrams Draw the Dot & Cross diagrams for the following elements; X 8 17 X a) O b) Cl 35 X 16 X X X X X X X X X Cl X X X X X O X X X X X X X X X SUMMARY 1. The Atomic Number of an atom = number of protons in the nucleus. 2. The Atomic Mass of an atom = number of Protons + Neutrons in the nucleus. 3. The number of Protons = Number of Electrons. 4. Electrons orbit the nucleus in shells. 5. Each shell can only carry a set number of electrons. Elements Compounds Mixtures Composition of Matter Elements: Made of only one type of atom. All atoms are identical. ◦ Atom: building block of an element - Molecule: two or more atoms chemically bonded together. Examples: oxygen, nitrogen, iron Composition of Matter Compounds: made from atoms of two or more elements that are chemically combined. ◦ Examples: water (H2O), table salt(NaCl) Mixtures: made up of two or more substances that are not chemically combined. Easily separated. ◦ Examples: soil, ocean water, air Homogeneous mixture: means that mixture is evenly spread out, and no differences can be detected. Ex: water, vinegar Heterogeneous mixture: means that material in mixture is not evenly spread out and differences can be detected. Ex:soil, chocolate chip cookie This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.