Mrs Ingrams Mitosis quiz power point review
advertisement

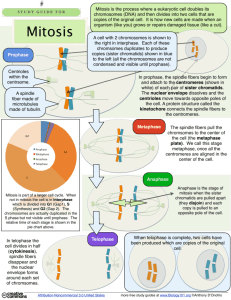
What is the definition of Mitosis? What is the definition of Mitosis? Nuclear Division What is the cell cycle? What is the cell cycle? Cell Growth and Division What is Chromatin? What is Chromatin? (Thin Thread Like) Stretched out, unwound DNA found inside the nucleus during Interphase Looks like spaghetti USEABLE DNA!!! What is a Chromosome? What is a Chromosome? Coiled up DNA (condensed) version of chromatin; easier for moving DNA during Mitosis Coiling up of Chromosomes happens during PROPHASE What is the Centromere? What is the Centromere? Holds Sister Chromatids together Where spindle fibers grab chromatids to pull apart Think: Centro = center mere = middle of chromatids What are Sister Chromatids? What are Sister Chromatid? Two identical strands of a chromosome that are attached What are the Centrioles? What are the Centrioles? Organelle in ANIMAL CELLS that creates the spindle fibers “Centrioles go to the poles” during Metaphase What are Spindle Fibers? What are Spindle Fibers? Fibers that act like the “Muscles” of the cell and move the chromosomes Name the 4 phases of the Cell Cycle Name the 4 phases of the Cell Cycle G1 Phase S Phase G2 Phase M Phase Think: Cell Cycle has the “S” sound and it has the “S Phase” What happens in the G1 Phase (Gap 1)? What happens in the G1 Phase (Gap 1)? Growth Phase When cell gets bigger and makes lots of proteins and does its job 1st part of Interphase What happens in the S Phase? What happens in the S Phase? “Synthesis” Phase Makes a copy of the DNA Single strand →Double strand 2nd part of Interphase What happens in the G2 (Gap 2) Phase? What happens in the G2 (Gap2)Phase? “Growth 2” Phase Cell is getting ready to divide; Making organelles and proteins 3rd part of Interphase What happens in the M Phase? What happens in the M Phase? Mitosis (PMAT) and Cytokinesis What is the longest phase of the Cell Cycle? What is the longest phase of the Cell Cycle? Includes: G1, S, G2 Cells are in this phase more than any other phase Interphase Name the phases of Mitosis (Nuclear division) Name the phases of Mitosis (Nuclear division) Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase “PMAT” Name each phase of these phases and put in the correct order Name each phase of these phases And put in the correct order #2 Metaphase #4 Telophase #3 Anaphase #1 Prophase When is the chromatin coiling (visible) under the microscope? (phase) When is the chromatin coiling (visible) under the microscope? (phase) Prophase What happens in Prophase? What happens in Prophase? “Prepare” Longest phase of Mitosis!!! 1. Chromosomes coil up to make easier to move 2. Nuclear envelope (membrane) dissolves 3. Centrioles make spindle fibers to help move chromosomes What happens in Metaphase? What happens in Metaphase? “Middle” Chromosomes are lined up in the middle of the cell Spindle fibers are attached to sister chromatids and Centrioles go to the poles What happens in Anaphase? What happens in Anaphase? “Apart” Sister Chromatids get pulled apart by spindle fibers What happens in Telophase? What happens in Telophase? “Tidy Up” (Reverse of Prophase) 1. Uncoiling of chromosomes 2. Nuclear envelope reforms 3. Spindle fibers go away 4. Cytokenesis What is this called? When cytoplasm and membrane pinch in and divides into two cells ??????? What is this called? When cytoplasm and membrane pinch in and divides into two cells Cytokenesis – not a phase; it is at end of Telophase. Think: “Cyto-Kut-Nesis” Cytoplasm gets cut in 2 Cytokenesis in Animal Cells What structure appears? Cytokenesis in Animal Cells What structure appears? Creates a CLEAVAGE FURROW (Think: Animals have fur) Cytokenesis in Plant Cells What structure appears? Cytokenesis in Plant Cells What structure appears? Creates a hard CELL PLATE New cell wall between 2 new plant cells (Think: Plant and Plate) What are the two new DNA identical cells made in cell division called? What are the two new identical cells made in cell division called? 1 cell divides into 2 new cells 2 Daughter Cells What regulates the cell cycle? What regulates the cell cycle? CYCLINS Explain the difference between Internal Regulators and External Regulators Explain the difference between internal regulators and external regulators Internal regulators are proteins that respond to events inside the cell to tell it when to go to the next phase of cell cycle. G1→S→G2→M Prophase→Metaphase→Anaphase→Telophase External regulators are proteins that respond to events outside the cell and tell the cell to speed up division then slow down to normal again. EXAMPLE: Cut in the skin or broken bone What is the mass called when cells are growing out of control? Abnormal Cells What is the mass called when cells are growing out of control? TUMOR What is the condition called when cells have lost their ability to control their growth? What is the condition called when cells have lost their ability to control their growth? FAST NONE