Name: Period: Anatomy and Physiology Blood Blood has several

Name:
Anatomy and Physiology
Blood
Blood has several functions, according to its components: red blood cells (rbc’s) carry
Period:
_________________________________, white blood cells (wbc’s) protect against/fight
_________________________________, and platelets promote _________________________________.
• Blood within an adult human is ~______________________ liters.
• Whole blood is heavier and more viscous than ____________________________________.
• A _______________________________________ (HCT) is the percentage of blood cell volume (generally
45%).
• The majority of cells are rbc’s, then wbc’s, and platelets (considered fragments in the blood).
• 55% of blood is ______________________________________________, a watery substance mixed with
amino acids, macromolecules, electrolytes, vitamins, hormones & wastes. This results in a straw
colored fluid.
• The percentage of blood volume varies: body size, [fluid] and [electrolyte], and amount of adipose (fat).
• Blood components can be separated by centrifuging them:
• __________________________________________ is the lightest (and rests atop the rest), the
________________________________________coat is the middle layer of cells containing wbc’s
and platelets while the bottom-most layer contains the rbc’s.
Blood Plasma:
• ______________________________, straw colored fluid
• liquid portion of blood
• contains ~90% _______________________________________ & a mix of dissolved chemicals
(macromolecules, vitamins, electrolytes & wastes)
• proteins are the most abundant of the dissolved substances in plasma
There are 3 groups of proteins: albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen.
• ______________________________________________: smallest but majority of the plasma proteins (by weight); regulate the movement of water controlling blood
______________________________________________ & controlling
_______________________________________________________________________
• globulins: ________________________________________________ lipids &fat soluble vitamins; 3
types: alpha, beta
• fibrinogen: __________________________________________- but least of plasma proteins; functions in
blood coagulation (clumping)
Name:
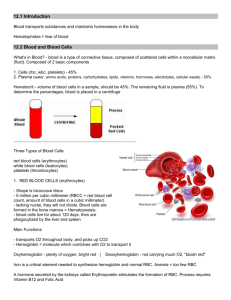
Red Blood Cells:
Period:
• a.k.a. ____________________________________________________________________
• concave disks (look like donuts with no hole).
• Contains a protein, ____________________________________________(~1/3 of the rbc) which is the
reason rbc’s are red
• When O
2
binds with hemoglobin, blood is bright red; when rbc’s are O
2
deficient, blood is dark (but
STILL _______________________________).
• The average life span of a rbc is ~____________________________ days; however, the blood cell count
is stable.
• One test performed on blood is a red blood cell count (a.k.a
______________________________________ or RCC).
• Used in discovering illness: change in # of rbc’s affects the amount of O
2
being carried; therefore, affecting the health of an individual.
• Rbc’s are broken down by macrophages in the ________________________________________ &
___________________________________________________.
• When rbc’s are broken down, ________________________________________(an iron-containing
compound from hemoglobin) is released.
• Rbc production is controlled by a ___________________________________________ feedback
mechanism: erythropoietin (a hormone) regulates rbc formation.
• When O
2
is deficient, the kidneys & liver release erythropoietin to make rbc’s.
• Rbc production requires: vitamin ______________________________, folic acid, and
______________________________________________.
• __________________________________________is a condition in which there are too few rbc’s or too
little hemoglobin. This condition results in __________________________________________ or lack of
energy. Many women have this condition due to menstruation or pregnancy.
White Blood Cells:
• a.k.a. ____________________________________________________________
• __________________________________________________ against disease, fight infection
• include 5 types which differ in size, cytoplasm, nuclei shape & staining characteristics.
Name: Period:
• These are broken into 2 groups: ______________________________________________ (leukocytes with
granular cytoplasm) and ____________________________________________________ (leukocytes
without a granular cytoplasm).
Granulocytes
• are ___________________________________ the size of a rbc
• contain granular cytoplasm
• are produced in the red bone marrow
• life span is ~________________________________ hours
• include: Neutrophils, Basophils, and Eosinophils
Neutrophils
• Contain fine cytoplasmic granules
• ~_____________________________% of wbc’s in an adult blood sample.
• contain lysosomes which perform __________________________________________ (ingest small
particles); generally die b/c of the amount of toxins ingested
Eosinophils
• uniformly sized cytoplasmic granules
• ~____________________________% of wbc’s circulating.
• kill specific ____________________________________, control
_________________________________________reactions & inflammation & are weakly phagocytic
Basophils
• irregularly shaped cytoplasmic granules
• _______________________________% of circulating wbc’s.
• _______________________________________blood clots by releasing heparin (a blood thinner) and
play a major role in allergic reactions by releasing _____________________________________________
(increases blood flow to injured tissues)
Agranulocytes
• no cytoplasmic granules
• include 2 types of wbc’s: Monocytes & Lymphocytes
Monocytes
• life span ~________________________________________________________
• nuclei vary in shape
Name: Period:
• _________________________________________________ of wbc’s (2-3X larger than
rbc’s)
• account for ~_______________________________% circulating wbc’s
• produced in the red bone marrow
• contain lysosomes which perform
____________________________________________________________, engulfing large
particles. Generally die b/c of the amount of toxic material ingested
Lymphocytes
• life span ~______________________________________________
• nuclei is large & round
• slightly larger than rbc’s
• ~___________________________________% of circulating wbc’s
• produced in the red bone marrow & lymphatic system organs
• produce ________________________________________________ providing immunity.
Brief Summary
• There are 5 types of White Blood cells in circulation.
• From the majority of cells to the least amount of cells in circulation:
________________________________________ (N) Lymphocytes (L)
________________________________________ (M) Eosinophils (E) Basophils (B)
• An acronym: Never Let My Eggs Break!
White Blood Cells:
• A white blood cell count (_________________________) is a diagnostic test that measures the amount
of wbc’s in a sample of blood.
• Generally, a differential WBCC (________________________) is performed. This is a test that provides
the %ages of wbc’s (types of leukocytes in a sample of blood).
• Wbc’s are able to leave the blood & move by _______________________________________ motion
(self-propulsion)
Blood Platelets:
• a.k.a. ____________________________________________________
• considered cell fragments (incomplete cells)
• formed in the red bone marrow from
_________________________________________________(shatters like a plate, forming platelets)
• lack nuclei (cannot produce proteins or divide)
Name:
• life span ~___________________________ days
• aid in _____________________________________ formation
Hematopoiesis:
Period:
• This is a.k.a. ____________________________________________________________
• Occurs in ______________________________________ bone marrow
• ___________________________________________________ (hormone) controls rbc production.
• ___________________________________________________ (hormone) controls thrombocyte
production.
• ___________________________________________________&
______________________________________________________________________ (CSFs) control wbc
production.
Hemostasis
• This is the _______________________________________________ of bleeding.
• When a blood vessel (bv) is cut, blood flows. Almost immediately, a bv spasm, a.k.a. a
_________________________________________________, occurs. This is the constriction of a bv by
the smooth muscles contracting, slowing blood flow.
• This occurs in 3 steps: vascular ______________________________________, platelet plug formation,
and _____________________________________________________.
• A platelet ______________________________________________ is a clump of platelets that stick to
the collagen in connective tissue (that has been cut) and to each other.
• This generally controls blood loss (in small breaks). Otherwise, a clot must form to stop bleeding.
Blood Coagulation
• This causes a blood clot and is the result of _______________________________________ factors
(biochemicals that help or inhibit the formation of a clot).
• In normal bodies, ____________________________________________________ do not allow blood to
clot.
• However, when a clot forms (called formation), fibrinogen forms
________________________________________________________(insoluble threads of protein).
• A blood clot forms from a series of events: prothrombin (a normal component of plasma produced in the
liver) is converted to _____________________________________________ in the presence of Ca++.
• Thrombin then triggers a series of reactions that convert fibrinogen into fibrin, causing a blood
clot.
Name: Period:
• Fibrin causes a meshwork of threads that trap platelets & blood cells, forming a mass that stops blood
flow.
• Fibrin threads are eventually dissolved and the injury is
____________________________________________________________.
• This is how bruises (hematomas) are healed. _______________________________________ are caused
by blood leaks within a damaged tissue.
• If a clot has filled a large area (large blood vessels), it is usually surgically removed.
• Blood clots can form abnormally: this is called a
____________________________________________________________.
• If the clot dislodges from the bv, it is called an
____________________________________________________. Emboli may block blood flow in another
bv and may be fatal.
• Coronary thrombosis is a blood clot forming in the heart while a cerebral thrombosis is a blood clot
forming in the brain.
• These kill the tissues in the area, called an _________________________________________________, and can be fatal.
• Infarctions can result in heart attacks and strokes.
• A pulmonary embolism is a traveling embolus that blocks a bv of the
__________________________________________________.
• Treatment of these are usually plasminogen activators that break up clots.
Blood Groups
• Agglutination: after a transfusion of blood, a clump of rbc’s form. This is a result of
__________________________________________________ (surface molecules on rbc’s) and
__________________________________________________ (proteins within the plasma).
• There are 2 groups of antigens: ABO group and Rh group.
ABO group
• This is the presence or absence of antigens on the surface of
____________________________________________________________________.
• These antigens are _______________________, _____________________________, or
A and B.
• These are a direct result of the person’s blood type, which is
________________________________________________________.
Name: Period:
• If a person has antigen A, then he has type A blood; if a person has antigen B, then he has type B blood; if a person has both antigens A and B, then that person has type AB blood; if a person lacks antigens,
then the person has type O blood.
• If the person has type A blood, they have anti-B; this means that the have antibodies against antigen B.
What is the significance of this? A person with type A blood cannot receive type AB or type B blood
receive type A or type O blood.
Blood Type Antigen
A A
B
AB
O
B
A & B none
Antibody anti-B anti-A none anti-A &B
Transfuse
A; O
B; O
A; B; AB; O
O
Rh Blood Group
• This was named after the Rhesus monkey. These are __________________________________________
(factors) in human blood (as well as monkey blood).
• These antigens are inherited as well.
• When blood types are said to be Rh ___________________________________________ (Rh-), there are
___________________________ Rh antigens while if the blood type is said to be Rh positive (Rh+),
there is at least 1 type of Rh antigen.
• Look up in text or online! Know the following: ALL types of anemia, leukemia, thrombus, embolus, thrombocytopenia, petechiae, and hemophilia.