Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
advertisement

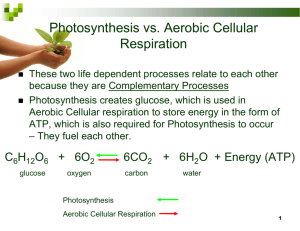
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Energy Use in Living Organisms Step 1 Convert sunlight energy into chemical food energy Ends in Glucose Step 2 Convert chemical food energy into chemical energy that the cell can use Ends in ATP Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Ribose Three phosphate groups Adenine Energy Cycle • ATP is a charged battery for cell • Made during cellular respiration • Used up to complete activities for cell • Energy in ATP is stored in high energy bonds between phosphate groups ATP • ADP is a used battery for cell • one phosphate has been removed • Phosphate must be added back on to recharge battery ADP ATP and ADP What do Plants do? Plants do step 1 with chloroplasts Plants do step 2 with mitochondria Because plants make their own food and then eat it, they are called autotrophs What do Animals do? Only do step 2 with mitochondria Because animals must eat food that others have made, they are called heterotrophs Step 1: Photosynthesis Convert sunlight energy into glucose Chloroplast performs photosynthesis Plants, algae, some bacteria, and some protists all perform photosynthesis Overall reaction 6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Occurs in two stages Light dependent reactions Light independent reactions Chloroplast Found only in Plant cells Thylakoid- coin-shape structure containing chlorophyll and proteins; also called photosystems Grana- stacks of thylakoids Stroma- fluid inside chloroplast (similar to cytoplasm) Light Dependent Reactions Energy from sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in the thylakoid membrane Water is split into oxygen (given off as waste), H+, and electrons Electrons go through a series of proteins in the membrane called the electron transport chain Electrons provide energy for hydrogen protein pumps to pump H+ into the thylakoid More sunlight energy is absorbed Electrons are added to NADP+ to create NADPH Hydrogen ion diffuse through another membrane protein The diffusion fuels the production of ATP by the enzyme ATP synthase Light Dependent Reactions Light Independent Reactions Occurs in the stroma Also called the Calvin cycle Is a series of reactions controlled by enzymes The ATP and NADPH made during the light dependent reactions are used to fuel the reactions CO2 provides the carbon used to make the sugars Simple sugars (primarily glucose) are made during the cycle Light Independent Reactions Factors that Affect Photosynthesis Water Water shortages can slow or stop photosynthesis Plants in dry climates Waxy coating Thin leaves (needles on cactus) Temperature Low temps slow or stop photosynthesis Enzymes do not work well at low temps Factors that Affect Photosynthesis (cont) Light Intensity/Amount Increase in light, increase in photosynthesis until at maximum level Plants still perform photosynthesis in periods without light Density of Other Plants Crowded plants complete for light and resources Reduces photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Convert glucose into ATP Mitochondria performs cellular respiration All organisms Process is called aerobic because it requires oxygen Overall reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O Mitochondria Found in animals and plants Outer and Inner membrane Cristae- folding of inner membrane Matrix- area inside of inner membrane Glycolysis Occurs in cytoplasm of cell Anaerobic (oxygen not needed) 2 ATP’s are used to start the process Glucose (a 6 carbon sugar) is broken into two three carbon sugars 4 ATP’s, 2 NADH’s, and 2 pyruvates are made What comes next? With oxygen Other processes of cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria Without oxygen Fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm Krebs Cycle Occurs in the matrix Pyruvate is broken into a 2 carbon molecule producing 2 NADH and CO2 Coenzyme A attaches to the 2 carbon molecule and enters the Krebs cycle It is converted into citric acid Citric acid is broken down through a series of steps producing 3 more NADH’s. one ATP, one FADH2, and two more CO2’s Two turns of the cycle are needed to process the 2 pyruvates from glycolysis Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Occurs along the inner membrane of the mitochondria Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are used Electrons fuel hydrogen protein pumps which pump H+ out of the matrix H+ diffuses through a membrane protein and fuels ATP production by ATP synthase Oxygen picks up the electrons and H+ to form water Summary of Cellular Respiration Fermentation Occurs when oxygen in unavailable In humans occurs as lactic acid fermentaion (some yeast and plants do alcohol fermentation) Pyruvates are converted to lactic acid and NAD+ is formed No more ATP are produced Comparison Ps Rs Function Make food for plants Make energy for ALL organisms Location in cell Chloroplast Mitochondria Uses what? Water, CO2, Sunlight Oxygen, Food/Glucose Makes what? Oxygen, Food/glucose Water, CO2, Energy/ATP