Short Stories - My Teacher Pages
advertisement

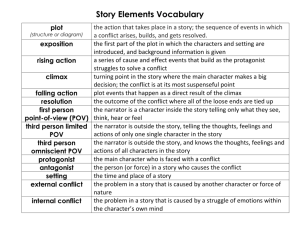
Short Stories Characteristics of Short Stories Limited in length Limited to one main event and the development of one character Ex: Napoleon Dynomite vs. Breakfast Club Plot Sequence of incidents or actions in a story. Whatever the characters do, or whatever happens to them, constitutes plot. Finding Nemo Plot http://www.glencoe.com/sec/literature/co urse/course1/unit/shortstory.shtml Plot The most important element in plot is conflict. External or internal conflict A story often ends when conflict is resolved but this is not always the case… Plot Structure Plot is the literary element that describes the structure of a story. It shows the a causal arrangement of events and actions within a story. Types of Linear Plots Plots can be told in Chronological order Flashback In media res (in the middle of things) when the story starts in the middle of the action without exposition Pyramid Plot Structure The most basic and traditional form of plot is pyramidshaped. This structure has been described in more detail by Aristotle and by Gustav Freytag. Aristotle’s Unified Plot The basic triangle-shaped plot structure was described by Aristotle in 350 BCE. Aristotle used the beginning, middle, and end structure to describe a story that moved along a linear path, following a chain of cause and effect as it works toward the solution of a conflict or crisis. Freytag’s Plot Structure Freytag modified Aristotle’s system by adding a rising action (or complication) and a falling action to the structure. Freytag used the five-part design shown above to describe a story’s plot. Modified Plot Structure Freytag’s Pyramid is often modified so that it extends slightly before and after the primary rising and falling action. You might think of this part of the chart as similar to the warm-up and cool-down for the story. Plot Components Climax: the turning point, the most intense moment—either mentally or in action Rising Action: the series of conflicts and crisis in the story that lead to the climax Falling Action: all of the action which follows the climax Exposition: the start of the story, the situation before the action starts Resolution: the conclusion, the tying together of all of the threads Conflict Conflict is the dramatic struggle between two forces in a story. Without conflict, there is no plot. Types of Conflict Interpersonal Conflict Human vs Human Human vs Nature Human vs Society Internal Conflict Human vs Self Leiningen Versus the Ants Suspense in the story will result from a person in conflict in nature. Neighbor Rosicky: Characterizations How do you arrive to an opinion about a person you don’t know very well? List the words that come to mind for the following series of photos… (Don’t think about it to much, just your gut reaction) Stereotyping What can appearance reveal about a person? Would it help you if you could know the person’s thoughts? This is how you establish character in fiction. Pay attention to how Rosicky’s character is revealed. Neighbor Rosicky: Characterization We create opinions based on: – The way someone looks – Someone’s dress – Someone’s background – Stereotypes Pay attention to the “first impressions” we get from Rosicky, and how these evolve. A symbol is anything that hints at something else, usually something abstract, such as an idea or belief. A literary symbol is an object, a person, a situation, or an action that has a literal meaning in a story but suggests or represents other meanings. Define: Ex: A general symbol is universal in its meaning. Even if the symbol were removed from a work of literature, it would still suggest a larger meaning. – Ex: While the sea symbolizes the universal voyage from life to death in The Odyssey, it retains this association independent from literature. The "sea" is a general symbol. – Ex: In poetry, a "rose" often is not only a flower, but also a general symbol for romantic love. A specific symbol is not universal in its meaning. It acquires a specific meaning based on how it relates to the content of a novel, poem, etc. The symbol's significance exists only within the context created by the author. – Ex: A hunting cap in The Catcher in the Rye has no universal meaning, but within the novel it is worn backwards and symbolizes a looking back at childhood. – Ex: A pair of eyes on a billboard in the Great Gatsby has no universal meaning, but within the story symbolizes the eyes of God watching humanity. Tips about Symbols: – • The story itself must furnish a clue that a detail is to be taken symbolically. Symbols nearly always signal their existence by emphasis, repetition, or position. – The meaning of a literary symbol must be established and supported by the entire context of To be called a symbol, an item must suggest a meaning different in kind from its literal meaning; a symbol is something more than its class or type. A symbol may have more than one meaning. This does not mean that the symbol can mean anything you want it to because possible meanings are always controlled by the context. To identify a symbol, note if an object seems to: – appear repeatedly – have an unusually vivid quality – be described with language conveying much emphasis – have more significance than its literal reality would suggest Carefully examine how the symbol functions in relation to the story. Ask yourself what idea is represented by the symbol. Classification may reveal opposite relationships, such as symbols of good and evil, life and death. Or symbols may fall into isolated categories, such as destruction, innocence, or sexuality. Determine how much depth a particular symbol has and classify its possible meanings. While you may focus on only one major symbol, you may be able to divide it into two specific meanings and two general meanings. Remember: A symbol has a literal meaning in a story but suggests or represents other meanings. – Not all symbolism is obvious; often it is subtle and indirect. – American Beauty: Symbolism In the clip American Beauty what kind of descriptions are used to describe the plastic bag? What does the plastic bag mean to the male character? Based on the description of the plastic bag and what the plastic bag appears to mean to the male character, what would you predict that the bag symbolizes throughout the film? General vs. Specific Symbolism A general symbol is universal in its meaning. Even if the symbol were removed from a work of literature, it would still suggest a larger meaning A specific symbol is not universal in its meaning. It acquires a specific meaning based on how it relates to the content of a novel, poem, etc. The symbol's significance exists only within the context created by the author. Definition: – Catcher in the Rye: Backwards hat means to “look back on child hood” – Great Gatsby : Eyes on a billboard, but within the story symbolizes the eyes of God watching humanity. – Odyssey: Sea symbolizes the universal voyage from life to death. – Ashes: The weather symbolizes the events within life: dark clouds, sunshine, ect. Neighbor Rosicky: Symbolism The new child of Polly & Rudolph: The cemetery behind Rosicky’s house: Rosicky’s land: Marigolds: Symbolism Marigolds: The stone throwing: The Gift of the Magi: Symbolism Read “The Gift of the Magi” under class links. Identify symbols that you see throughout. The Gift of the Magi: Symbolism Identify two symbols in the story and what they represent. Answer the comprehension questions located on the assignment calendar for today. When completed print and put in in-bin. Marigolds: Memories Think about the memories that you have that others remember differently than you. “Coming of Age” story – Breakfast Club – My Girl – The Wonder Years Turning point Marigolds: Making Inferences About Character Consider how they and others you know have changed over time. In good fiction characters are complex and make mistakes. As you read Marigolds you should be making inferences about Lizabeth’s character as a young person and an adult. Marigolds: Writing Write an essay about childhood mischief in which you participated. Was it harmless or cruel? Were you influenced by peers? How did you feel then? How do you feel now about the experience? OR Write an essay about a childhood memory. It could be happy or sad memory, but it should be one that is vivid to you even now. How did you feel then? How do you feel now about the experience. Due 10/7 (Thursday) The Beginning of Greif: Symbols Kevin shaves head – The Beginning of Grief: Writing In a brief essay (approximately 200-250 words), discuss Corporal Punishment. State your position and support it with both opinion and fact. You may need to research this topic to include facts. The Rifles of the Regiment: Stock Characters Stock characters are characters that tend to be types rather than individuals. – Private Detectives – Southern Belle – Girl next door – Cowboy – Marine Sergeant The Rifles of the Regiment: Background Weeks after other British troops have been evacuated from France during WWII, Colonel Heathergalls leads his regiment, the Loyal Rifles, across France to the coast. Colonel insists all rifles be taken. Point of View Point of view is simply the vantage point from which the story is told. Omniscient means “all knowing”. In this case there is no identifiable narrator. The omniscient narrator knows all the thoughts and feelings of all the characters . Omniscient Narrator Example Once upon a time there was a girl named Cinderellla. Cinderella got her name because she was forced to work as a servant and sleep near the cinders. Cinderella was treated cruelly by her wicked stepmother, who was jealous of the girl’s good looks and sweet temper because her own daughters were ugly and mean. Limited Third-person point of view Story is narrated by someone who stands outside the story, but who sees everything from the limited vantage point of only one character. All attention is focused on one person. We do not know much of what other characters outside this one are thinking or feeling. Limited-Third-Person POV example One upon a time there was a girl name Cinderella, who was treated cruelly by her stepmother. Cinderella often wept bitterly in her ashy corner. Nightmares haunted her, and she feared that darkened scullery when the rats came out and played about her feet. At times, she wondered if her goodness would ever be rewarded, First-Person point of view This is when the writer lets one character tell the story. This narrator can be a hero or heroine of the story, or a minor character is observing the action. This narrator would speak using “I”. As an audience we only know what the narrator reports to us. First Person POV example I had spent sixteen years sitting in the cinders of my kitchen. My stepmother must have hated me, because she made me do the dirty work. I could not understand the reasons for her feelings, for I had always treated her with respect. I slept in the ashes, and was tortured by nightmares and fear of rats. To analyze the POV ask these questions. Who is the narrator of the story? Is this narrator a character in the story, or does the narrator stand outside the story? Does the narrator know about all the action and characters in the story or is it limited to one character? How does the point of view affect my reaction to the story’s characters and events? Setting Setting: time, place of its action. Setting includes: – Time of day (evening) – What surroundings are like (dreary & melancholy) Setting creates atmosphere in a story Contents of the Dead Man’s Pocket What two settings exists in the story? How does Finney set up a contrast between them? How does he make you feel about each setting? BLOG IT! The Rockpile The Rockpile is an important symbol in the story. It stands for something in itself and for a broader meaning as well. How does the rock pile emphasize the threatening nature of the setting? How does it also reveal the helplessness of the characters in the story? BLOG IT! POE DAY! Poe Background Edgar Allan Poe (1809-1849) was an American author best known for his dark and ominous short stories and poems. Poe experienced tragedy in his life. He was born into poverty; his father was an alcoholic who left when Edgar was young; his mother died of tuberculosis; his foster mother and his wife died; he lived and died in poverty. Ideas that come to mind regarding The Pit and the Pendulum, The Raven, and The Tell-Tale Heart may include horror stories, terror, fear, death, darkness, murder, obsession, insanity, sadness, loss, guilt, torture, and the unknown. The Masque of the Red Death Atmosphere: overall mood or feeling established. This is often produced by description of setting. While reading pull out at least 3 lines that demonstrate how Poe creates an “atmosphere” and what that atmosphere is within the story. Poe Film Poe Research On Mrs. F’s Webpage – Class Links for Sites – Resources for WS Point of View Point of view is simply the vantage point from which the story is told. Omniscient means “all knowing”. In this case there is no identifiable narrator. The omniscient narrator knows all the thoughts and feelings of all the characters . Omniscient Narrator Example Once upon a time there was a girl named Cinderellla. Cinderella got her name because she was forced to work as a servant and sleep near the cinders. Cinderella was treated cruelly by her wicked stepmother, who was jealous of the girl’s good looks and sweet temper because her own daughters were ugly and mean. Limited Third-person point of view Story is narrated by someone who stands outside the story, but who sees everything from the limited vantage point of only one character. All attention is focused on one person. We do not know much of what other characters outside this one are thinking or feeling. Limited-Third-Person POV example One upon a time there was a girl name Cinderella, who was treated cruelly by her stepmother. Cinderella often wept bitterly in her ashy corner. Nightmares haunted her, and she feared that darkened scullery when the rats came out and played about her feet. At times, she wondered if her goodness would ever be rewarded. First-Person point of view This is when the writer lets one character tell the story. This narrator can be a hero or heroine of the story, or a minor character observing the action. This narrator would speak using “I”. As an audience we only know what the narrator reports to us. First Person POV example I had spent sixteen years sitting in the cinders of my kitchen. My stepmother must have hated me, because she made me do the dirty work. I could not understand the reasons for her feelings, for I had always treated her with respect. I slept in the ashes, and was tortured by nightmares and fear of rats. To analyze the POV ask these questions. Who is the narrator of the story? Is this narrator a character in the story, or does the narrator stand outside the story? Does the narrator know about all the action and characters in the story or is it limited to one character? How does the point of view affect my reaction to the story’s characters and events? The Quiet Man ____________ narrator. How does this contribute to the story? BrainPop! “Blues Ain’t No Mockin Bird” Point of View: 5 minute write: – Describe a parade from the POV of a threeyear-old. Keep in Mind: –Knee level of adult, –Vocabulary –Interests ect. “Blues Ain’t No Mockin Bird”: Essential Question You should be able to identify and analyze characterization and POV in “Blues Ain’t No Mockin’ Bird” “Blues Ain’t No Mockin’ Bird” Blog Class Blog: Privacy Rights Respond to question @ 2 peers. Writing a Bill project! Essential Question How do both the mood & tone of a story help the author achieve it’s purpose? Mood = EMOTIONS! Tone Content What is tone? Purpose of tone Elements to make the tone How to identify tone? What is Tone? Tone: the implied attitude of a writer toward the subject and characters of a work. ATTITUDE CHARACTERS AUTHOR Tone may be happy, sad, formal, informal, ironic, playful, serious, angry, naive condescending, or many other possible attitudes TONE EXAMPLE Finally, one of the girls pointed to the grass and giggled. "Meow!" A cat sat on the edge of the field and licked its paw. They did indeed have company. The girls ran over to the cat and pet his belly. They laughed and the cat sauntered back to the field. TONE Example The tone of this passage is happy/contentment as there was a successful, happy resolution to the problem. Elements to make the tone Elements contribute to make the tone The speaker The author’s language The theme The author or/and the characters Tips to identify tone Tone must be inferred through the use of descriptive words. You can recognize the tone/attitude by the language/word choices the author uses. His language will reveal his perspective/opinion Note: Be careful to separate mood from tone. The tone shows you an author's opinion, while mood is the feeling and atmosphere of the text Essential Question How do both the mood & tone of a story help the author achieve it’s purpose? BrainPop: Mood & Tone Class Blog “A Pair of Silk Stockings” Character Motivation The overall aim is for you to analyze character and motivation in “A Pair of Silk Stockings”. What is character motivation? – The reason a character thinks, feels, acts. – What do you know about court cases and motivation of crimes? “A Pair of Silk Stockings” cont. Examine the motivation for Mrs. Sommer’s actions. Analyze: how does third-person point of view helps create sympathy toward a person engaged in self-centered “extravagance”? Irony: Verbal Irony: – Examples: clear as mud” "as much fun as a root canal. Situational Irony - Situational irony results from recognizing the oddness or unfairness of a given situation, be it positive or negative. – Examples: Bill Gates win’s a computer contest Dramatic Irony :when the words and actions of the characters of a work of literature have a different meaning for the reader than they do for the characters. Examples: “The Quiet Man” Shawn Kelvin who wants to avoid conflict, is a prize fighter. Big Liam of course doesn’t know this. Alanis Morissette: Isn't it ironic “The Bet” & Irony Analyze the Irony of the situation in “The Bet”. Glogster – Find websites, movie clips, written examples, or photo of irony. – Label these examples as situation, verbal or dramatic on your poster. – Visually appealing, creative. Irony Review Objective: – Locate the use of both Irony and Satire in “Harrison Begeron”. – What is Irony? Glogster Projects Alanis Morissette: “Isn’t It Ironic” lyrics Harrison Bergeron: Brainstorm (2 or 3 minutes): – What is the definition of equality? – Do you think the world would be improved if all humans were equal in every way? – What problems would this cause in school, sports, work, and other areas of life? Films and Cartoons Definition of Satire…. A literary work that ridicules its subject through the use of techniques such as exaggeration, reversal, incongruity, and/or parody in order to make a comment or criticism about it. I know Kung Fu Clip Matrick Original Clip Matric Original Clip 2 Exaggeration - To enlarge, increase, or represent something beyond normal bounds so that it becomes ridiculous and its faults can be seen - Example: Princess Fiona fights and successfully defeats Robin Hood and all of his Merry Men without any help and without any weapons. - Comment on Society: The traditional story of the knight rescuing the damsel-in-distress is not a realistic depiction of the roles filled by men and women in modern society. - Reversal To present the opposite of the normal order (e.g., the order of events, hierarchical order). Matrix Shrek Reversal Example: The roles of the hero and the damsel in distress have been reversed. In this clip, it is Princess Fiona, the rescuee, who fights and defeats the foe. Incongruity To present things that are out of place or are absurd in relation to its surroundings. Example: Princess Fiona uses her ponytail to deliver a knockout punch to one of the Merry Men. While frozen in a mid-air martial arts kick, Princess Fiona pauses to fix her disheveled hair before knocking out two of the Merry Men. Parody To imitate the techniques and/or style of some person, place, or thing. Matrix Parodies Criticism about Society? The traditional story of the knight rescuing the damsel-in-distress is not a realistic depiction of the roles filled by men and women in modern society. Example: Current Hollywood action movies like The Matrix have become ridiculous because they are too focused on special effects. “Harrison Bergeron”: Satire Pre-reading Pay careful attention to the attitudes expressed toward creativity, originality, and the arts. Consider how the author Vonnegut feels about creativity & imagination. – If it uses Satire it must be making a statement 2 step process: Locate Satire What is that Satire saying about society? The Piece of Yarn 5 minute write: – Do you think people are generally suspicious of one another? – Do people tend to assume the worst about others? – Do they prefer to believe the worst? – Objective: Analyze Characters, motive, irony in “A Piece of Yarn”. Love Objective: Analyze tone in “Love” 5 minute write: – Describe an object in the classroom as though it were a beloved treasure of great sentimental value. – Describe that same object as if it were a piece of junk. The Alligator War Objective: identify symbolism, the moral or lesson, and the allegoric characteristics. 5 minute write: – What is a fable? – What lessons are drawn from fables that you know? Study Guide Due at End of Class! Quiz Tomorrow Shaving Objective: Analyze character, motive, theme, & symbols. 5 minute think: – List characteristics that describe a man or woman as a hero. Literary Themes Commonly found in creative writing What is a theme? • Themes can be found everywhere: literature, stories, art, movies etc… • The theme of a fable is its moral. • The theme of a parable is its teaching. • The theme of a piece of literature is its view about life and how people behave. Theme & Meaning Theme is the… • underlying meaning of the story, • a universal truth, • a significant statement the story is making about society, human nature, or the human condition. Theme = idea The theme of a literary work is its underlying central idea or the generalization it communicates about life. Theme...the meaning of life? The theme expresses the author's opinion or raises a question about human nature or the meaning of human experience. At times the author's theme may not confirm or agree with your own beliefs. Even then, if skillfully written, the work will still have a theme that illuminates some aspects of true human experience. The author's task is to communicate on a common ground with the reader. Although the particulars of your experience may be different from the details of the story, the general underlying truths behind the story may be just the connection that both you and the writer are seeking. An understanding of theme is dependent upon one's previous experience of life and literature. At the same time, theme in literature can enlarge one's understanding of life. Be aware that the theme never completely explains the story. It is simply one of the elements that make up the whole. Some short stories have secondary themes as well. Common Literary Themes (Themes repeated in many works) 1. The quest for immortality “Stranger, stop and cast an eye. As you are now, so once was I. As I am now, so you shall be, Prepare for death and follow me.” 2. The individual’s relationship and obligation to society. Sometimes called “man vs. society” 3. The individual’s inward journey to understand himself or herself/identity. Sometimes called “man vs. self” 4. The individual’s relationship and obligation to the natural world. Sometimes called “man vs. nature” 5. How justice and injustice are decided 6. The individual as hero; what it means to be a hero or anti-hero. 7. What it means to be a “survivor.” 8. The individual’s experience of alienation and despair 9. The artist’s relationship and obligation to society. 10. aka: What tomorrow’s world “The Future” holds for us … 11. Love: Topics/Effects • Marriage Logical-sensible love • Romance Self-centered love • Platonic or companionate love Game-Playing • Altruistic love • Love of Country • Admiration • Possessiveness • Intense dependency Unrequited love Godly love Familial love Infatuation Erotic love Jealousy 12. Role of Institutions Sometimes called “man vs. the institution” Creativity provides many possibilities • Think about these themes—what would you add as an important theme often expressed in creative writing? • What theme would you most like to explore? Through the Tunnel Objective: Understand the concept of theme. 5 minute think: Give an example of a static & dynamic character. Chee’s Daughter Can you think of anyone personally or in society that puts their personal comfort above others welfare? What kind of person does it take to do something like that? Analyze both setting and theme. Blog! The Handsomest Drowned Man in the World What might it take to give a small desolate village a happier, more fruitful existence? – Vast sums of money? – An inspirational leader? Story Presentation: March 1st Choose a classic novel to approved by Mrs. F. You are to present this story by BREIFLY summarizing, but mainly touching on how the character, plot, setting, point of view, irony, symbolism, and theme of your novel. This requires a careful reading of the text, and thoughtful analysis. Presentations will be made, and should be between 4-7 minutes in length. Rubrics will be posted online, and used for grading. You must all prepared on the same day to present March 1st You must have some form of a visual aid. All technical problems must be worked out IN ADVANCE, and any equipment needed must be addressed ahead of time.