Virus Replication Power Point
advertisement
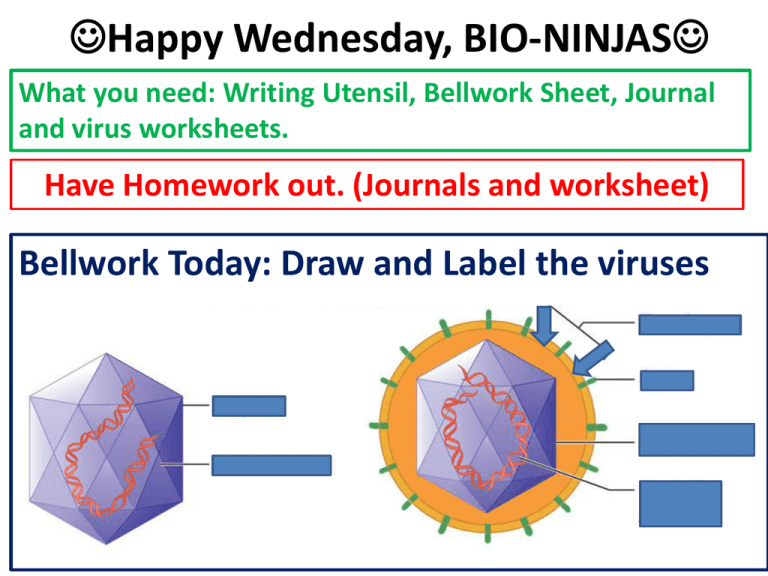
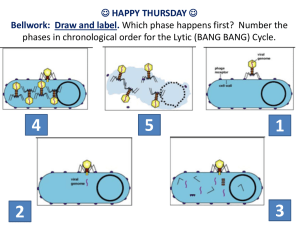
Happy Wednesday, BIO-NINJAS What you need: Writing Utensil, Bellwork Sheet, Journal and virus worksheets. Have Homework out. (Journals and worksheet) Bellwork Today: Draw and Label the viruses On your Vocab sheet: Highlight or mark these words then glue into your journal HOST CELL GENETIC MATERIAL VIRUSES RETROVIRUS IMMUNIZATION LYTIC LYSOGENIC HIV BACTERIOPHAGE CAPSID PATHOGEN PARASITE Vocab Quiz tomorrow over these words You have 4 minutes to glue in your: Lysogenic Sheet and Lytic sheet. 4 minutes Set up today’s page in your journal… • Date: 2-3-15 • Title: Viral Reproduction • Essential Question: What takes place when a virus reproduces? YES - Cornell notes, please! • • • • • BIO.4C The student will: compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction describe the role of viruses in causing diseases such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and influenza. When a virus invades… Viruses have both living and nonliving characteristics. Living Non-Living Reproduce Quickly Need a host cell to function They have DNA/RNA Not made of cells They can Mutate Do Not Grow/Develop Do not Metabolize/use energy Do not react to the environment 1. Lysogenic Cycle Take a look at your “Lysogenic” sheet. • Without me telling you anything, what do you think is happening in the diagram? *remember what you learned yesterday about virus structure 1. Lysogenic Cycle • Viruses “hide” for a while inside host cells before becoming active • Example = HIV 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Steps to the Lysogenic Cycle: Virus attaches to cell Virus injects DNA/RNA Virus DNA/RNA Integrates and Waits (months or years) in cell DNA Virus DNA removes from cell DNA Becomes active (starts lytic cycle) Cell undergoes “lysis” (bursts) - Viruses Lysogenic Cycle Ways to remember… • Lysogenic is a Looooooong word • LYS-ogenic---> sounds like “lies” around or “lays low” Lysogenic Example: HIV • Enveloped virus • Retroviruses transcribe RNA to DNA. • Two viral strands of RNA found in core surrounded by protein capsid. AIDS • White blood count drops below 200 person is considered to have advanced HIV disease • Most deaths occur with a white blood count less than 50 • AZT = medicine used to treat HIV/AIDS – Blocks “reverse trascriptase” Lytic Cycle Take a look at your “Lytic” sheet. • Without me telling you anything, what do you think is happening in the diagram? *remember what you just learned about virus replication Lytic Cycle •Lysis- to cut or to burst •Active viruses enter cells and immediately begin to multiply, leading to the quick death of the invaded cells. Steps to the lytic cycle: 1. Attach to cell 2. Inject DNA/RNA 3. Produce (replicate) virus parts 4. Assemble new virons 5. Cell undergoes “Lysis”- viruses are released to infect other cells - Viruses Lytic Cycle Ways to remember • Lytic = the shorter word, therefore shorter cycle • Lytic = Bang Bang (kill you dead) • Lytic sounds like you got “lit up” Lytic Example: Influenza • Enveloped virus with a segmented RNA • Symptoms appear within days/weeks • Infects a wide range of animals other than humans • Undergoes extensive mutations • Causes the flu Spread of influenza virus Today’s Activity: Sage and Scribe Happy Friday Comic Strip Lytic or Lysogenic? DISEASE VIRUSES AIDS HIV Wart Herpes Simplex Virus Flu Measles Cancer Influenza Morbillivirus Hepatitis B Dengue Fever .