UNIT 3 PART 4 DEVELOPMENT
advertisement

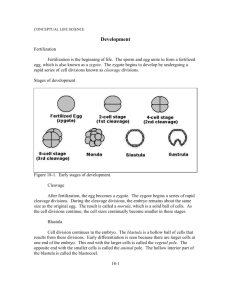
UNIT 3 PART 4: EMBRYOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENT • In the early stages of development the organism is called an embryo. • The basic processes of development are always the same in animals. • Development involves cleavage, growth, and differentiation. 1 Fertilization • Fertilization occurs when the sperm nucleus fuses with the egg nucleus. • A fertilization membrane forms around the egg once a sperm has entered to prevent other sperm from entering. 2 Cleavage • After fertilization the zygote starts to divide by a special type of mitosis called cleavage to form an embryo. • During cleavage cells divide like in mitosis, but there is no growth between divisions. • The cells get smaller with each division. 3 2 & 4 Cell Embryo • The first division results in a 2 celled embryo. • Each cell in the embryo then divides to form 4 cells. • Notice that all the cells are still inside the fertilization membrane. 4 8 & 16 Cell Embryo • The cells continue to divide and form 8 and 16 cell stages. • Note that all structures are the same size as the original unfertilized egg; the cells produced by cleavage have not grown. 5 • After several rounds of cleavage, a solid ball of cells, called a morula, is formed. Morula • The cells on the inside have trouble getting water & oxygen and getting rid of wastes. 6 Blastula • The cells on the inside of the morula push their way out and form a hollow ball called a blastula. • Cells still get smaller with each round of cleavage. • The hollow space inside is called the blastocoel. blastocoel 7 Gastrula • A gastrula forms when one side of the blastula surface pushes in at a point called the blastopore. • This forms a tube that will become the lining of the digestive system. • The blastopore is the future anus of the embryo. Blastopore 8 Late Gastrula ectoderm • By the end of the gastrula stage, the cells start to grow between divisions. mesoderm • A third layer of cells begins to grow between the inner and outer layers forming three primary germ layers. • The cells in these germ layers will differentiate to become different endoderm types of cells. 9 DIFFERENTIATION • All embryos form from one cell, the zygote, by the process of mitosis. • This means that all the embryo’s cells are alike - they all have all the same genes. • As development progresses groups of cells will become different and make tissues which form the different organs. • These tissues and organs are different because one type of cell uses different genes than another. Example: stomach cells use different genes than eye cells. 10 The Primary Germ Layers • Ectoderm: – Cells on the outside – Forms the skin and & nervous system Mesoderm • Endoderm: – Cells on the inside lining the tube – Forms the ling of the digestive system • Mesoderm: – Cells that form between these layers – Forms the muscles, bones, and organs Mesoderm 11 Review • How does the zygote change after fertilization? • Label the cleavage stages on the right. • What is the blastopore? • What is ectoderm & what does it form? • What is endoderm & what does it form? • What is mesoderm & what does it form? 12 Starfish Development Composite 13