Carbohydrates

The energy you use comes from the carbohydrates in food
Your body changes carbohydrates into glucose– a form you can use for immediate energy
Your body also stores some glucose in muscles and liver for later use
An organic compound that is the body’s main source of energy
Its name breaks down into tow of the main elements in the structure– Carbon (C) and
Hydrogen (H)
Carbohydrates also contain oxygen (O)
Empirical Formula: C n
H
2n
O n
We will look at these structures more later
They are found mainly as foods from plant sources such as:
Fruits
Vegetables
Grain products
Peas
They are produced by plants through the process of photosynthesis
Plants absorb energy from the sun, water through the roots and carbon dioxide from the air
A chemical reaction occurs which produces oxygen and glucose
CO
2
+ H
2
O + energy = O
2
+ C
6
H
12
O
6
Glucose is the basic sugar molecule from which all other carbohydrates are built
Plants can convert sugar into other sugars, starches, and fiber
Glucose will convert to sugar first then to starch as plants mature
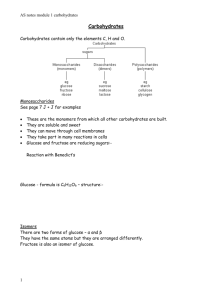
Carbohydrate
Disaccharides
Simple
Monosacharides
Fiber
Complex
Starch
Simple carbohydrates are one or two sugars in very small molecules
Complex carbohydrates are starches and fiber– large molecules made of many simple carbohydrates
Sugars exist in various crystalline structures
Contain –OH groups called hydroxyl groups
A hydroxyl group is a combination of hydrogen and oxygen atoms, containing one atom of each
Sugars are given the name saccharide
A saccharide is a sugar or substance made from sugar
Two types of simple sugar saccharides
Monosaccharide
disaccharide
Single molecule of sugar
Three examples:
Glucose- the “building blocks” of all sugars
Fructose- found in fruits and tree sap
Galactose- Not found free in nature, but bonded to something else; found in yogurt and aged cheese
Made of two monosaccharides bonded together
Three examples:
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
Table Sugar
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
Cereals & Grains
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Milk
Polymers form when many single sugars join together chemically
Include: Starch & Cellulose
Bonded together through glycosidic covalent bonds
Storage molecule in plants
Provides the majority of food calories consumed by people worldwide
Plants store energy in amylopectin
Animals store energy in the muscles and liver as glycogen
For long term storage, animals convert the food calories from carbohydrates to fat
Humans store fat in adipose tissue
Found in plant cell walls and is the most abundant carbohydrate on Earth
Source of dietary fiber
Cannot be digested by animals