Carbohydrades power point
advertisement

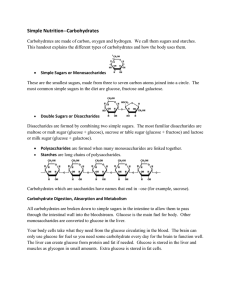
AnWhat organic compound that is are Carbohydrates the body’s main source of energy. They are found mainly in plants There are two groups of carbohydrate – simple and Sugar makes up simple carbohydrates is another word for saccharides. - it Monosaccharides – single sugars which are the building block of other sugars. Glucose is a simple sugar often which builds all carbohydrates - Fructose is a simple sugar found in fruits Galactose is not found free in nature but is always bound to something else Disaccharides – sugars made up of two monosacchrides bonded together. Sucrose – a common monosacchride made up of glucose and fructose. Lactose – is found in milk of glucose and galactose. made up Maltose – found in cereals and sprouting grains made up of two molecules of glucose. Complex Carbohydrates Starch and Fiber Starch is made up of chains of sugar molecules called polysaccharides. Examples of Complex Carbs = dry beans, peas, lentils, potatoes, corn, rice, pasta, and breads Fiber is what gives plants their structure. Bran – the most concentrated form of fiber forms the outer layer of grains. Fiber also is useful by carrying excess cholesterol out of the body. A n important function of fiber is to move food through the digestive tract. Carbohydrates in the Body Carbohydrates provide fuel for the body Glucose is called blood sugar Hydrolysis of Sugars – in the small intestine compounds are split into smaller parts by the addition of water. This releases glucose to be used for energy. Example: Sucrose + Water = Glucose + Fructose Enzymes with water act on the sugar to break it down. The pancreas monitors the flow of glucose to the cells. The pancreas secretes insulin- a messenger that signals the cells to accept the surge of nutrients including glucose. Diabetes A condition where the body can not regulate blood glucose levels. Type I = the pancreas secretes little or no insulin. ( Common among child diabetes) Type II = insulin is produced but not enough or can not be used effectively. (Most common) Both types can cause high blood glucose levels which strains and damages the heart and kidneys Sugar Substitutes Sucralose is an artificial sweetener that is a chlorinated sucrose derivative. Because the body cannot recognize the chlorinated carbohydrate, it is not absorbed by the body so does not add calories to you. It does not break down when heated so is good for baking. Aspartame – is an amino acid-based sweetener often used in diet pop. It does not promote tooth decay nor does it have an aftertaste. Starches as Thickening Agents