Unit 6 Test Review
advertisement

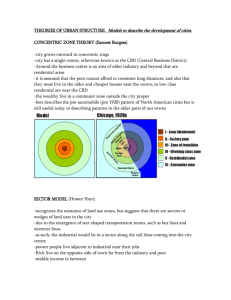
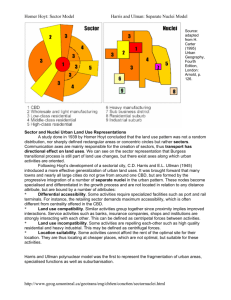
Unit 6 Test Review Industrialization & Urbanization Name of each model? • A – Concentric Zone – Burgess • B – Sector Model – Hoyt • C – Multiple Nuclei – Ullman & Harris What theory? • It is shown to be a widely dispersed, multi-centered metropolis consisting of increasingly independent zones, each focused on its own suburban downtown; the only exception is the shrunken central area, which is focused on the Central Business District (CBD). Urban Realms • Muller & Hartshorn What model? What does read represent? Yellow? Walter Christaller’s Central Place Theory • City – specialized goods • Hamlet or Village – common goods Industrialized zone from Britain, through Eurasia, to Japan is called what? Urban Banana In Burgess & Hoyt models, what are the areas? • • • • • 1– 2– 3– 4– 5– CBD Factories/Industry Working Class Housing Middle Class Housing Commuter Zone / High Class Housing How is Hoyt’s model different from Burgess? Areas develop in multiple zones; “other side of the tracks” is seen How is CBD the same for Burgess and Hoyt? Both in center How is CBD different in Ullman & Harris model? Not as centralized, and creation of edge cities make it less important Can you label the model? Parts of Multiple Nuclei Model 3 2 1 3 4 3 6 9 5 1 – CBD 2 – Wholesale/Light Manuf. 3 – Low income housing 4 – Medium income housing 5 – High income housing 6 – Heavy manufacturing 7 – Outerlying BD (EDGE city) 8 – Residential suburb 9 – Industrial suburb 7 8 Name of Harold Hotelling model, and what was he analyzing? Variable Revenue Analysis • Locational Interdependence 3 Things that led to suburbanization? • Increased service jobs & standard of living • Affordable cars • Interstate Highway System ______ is to Borchert’s 2nd stage as _____ is to the added 5th stage. Borchert’s Epoch Period – Communication & Transportation • 1st – Sail-wagon – low technology • 2nd – Iron Horse – steam-powered locomotive; spreading rails • 3rd – Steel – Rail – full impact of trains • 4th – Auto-Air-Amenity – gasw pwered engine • 5th – High Technology – expansion of service & information industries (telecommuting / Skype) Transportation and Proximity to market are what type of factors? Situational Factors • Situation to market Factors that are concerned with cost of production – labor, factory, capital, land, etc? Site Factors Less crime is benefit of gentrification or suburbanization? Suburbanization • More people – more crime – always Benefits of Suburbanization? • • • • Less Crime Better Education More Space (land/yards) Less Traffic Benefits of Gentrification? • • • • • City Life (amenities) Heterogeneous (diverse) population Cheaper Houses Unique Architecture Closer to work – no/less commute Benefits of SEZs, FTZs, and EPZs? • • • • • Less regulatory laws (ex. Labor laws) Subsidized rents No/Low tax zones Few environmental laws Paid for infrastructure (factories already built) ___is to Christaller as ___ is to Weber • Christaller – Central Place Theory • Weber – Least Cost Theory 3 Factors of Weber’s Theory • Minimize Labor costs • Minimize Transportation costs • Maximize Economies of Agglomeration What urban model has a “spine” down the middle? Latin American Urban Model Name of Latin American Model? Griffin – Ford Model What do European urban areas and the Latin American model have in common? • High class homes surround CBD, unlike in U.S. where affluent homes are in the suburbs Test Prep Advice • This was just a sampling of topics – make sure you also know all parts of your Study Guide that we went over in class (1-66) and study the notes online for additional help.