13.2 Human Body Systems
advertisement

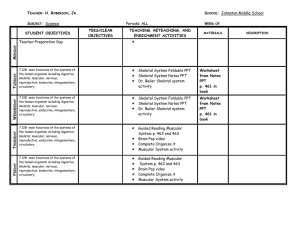
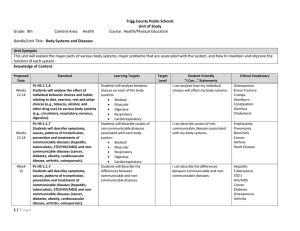
13.2 Human Body Systems 11 Body Systems ( We won’t cover all of them) • Although the body can be divided into 11 different organ systems, all of the systems are interconnected with each other • 11 Systems: Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous, Circulatory, Respiratory, Excretory, Digestive, Endocrine, Reproductive, Immune Integumentary system ( skin) • 2 layers: epidermis and dermis • Functions: temperature regulation, vitamin production, protection, senses • Hair- keratin, sebaceous glands to lubricate/ protect Skeletal system • Functions- support, protection, blood cell formation, reservoir for minerals, movement • Axial system- skull, vertebrate, ribs, sternum • Appendicular- shoulders, arms, hips, legs • Compact bone- dense, tough, strong • Spongy bone- lightweight • Osteocyte- living bone cells Muscular system • 3 types of muscle tissue: – smooth: no striations, one nucleus per cell – skeletal: many nuclei, striations – cardiac: one nucleus per cell, striations Nervous system • Neuron- nerve cell consisting of 3 parts: dendrite, cell body, axon • Neurotransmitter- chemical that transfers electrical impulse from one cell to another • Synapse- gap between neurons and other cells Circulatory system • • • • • • • • Functions: transport, temperature control 4 chambered heart: 2 atria, 2 ventricles Closed circuit, double loop Red blood cell- carries oxygen White blood cell- fights infection Artery- carries blood away from heart Vein – Carries blood towards heart Capillary- smallest blood vessel where exchange of gases and nutrients, into cells, occur Respiratory System • Air enters through mouth, past larynx ( voice box/ adam’s apple), trachea, L and R Bronchi, then to alveoli • Alveoli are the site of gas exchange ( oxygen and carbon dioxide) • Diaphragm- special muscle in mammals that, along with rib muscles, cause movement of air in and out of lungs Excretory System • Kidneys filter waste from blood • Waste then moves to bladder and awaits signal to empty Digestive System • Mechanical digestion- chewing • Chemical digestion- chemicals ( enzymes) are added to speed up chemical breakdown of food • Peristalsis- muscular movement of food through digestive system • Path: esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine We didn’t cover all of them!