Advanced Adult Intravenous Calculations
advertisement

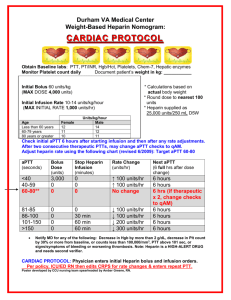
Advanced Adult Intravenous Calculations Chapter 16 Revised KBurger1108 IV Heparin • Anticoagulant – prevention of clot formation • High alert medication • All heparin orders, dosage, vial, amount and calculations should be checked by another nurse • Available in various dosage strengths • See figure 16-1 page 406 in Pickar 2 Heparin Flow Rate • Set up a ratio-proportion with: - supply dosage strength [units per ml] - ordered infusion dose [units/hr per units/ml] • Example: Order: 500 mL D5W with Heparin 25,000 units to infuse @ 850 units / hr 25,000units = 500 mL 25,000X = 425,000 25,000 25,000 850units/hr X mL/hr = 17 mL/hr 3 Heparin Flow Rates Try these… 1. The doctor orders heparin to infuse at 800 unit per hour. The pre-mixed intravenous solution available is 250mL D5W with 25000 units heparin added. Calculate the infusion rate for delivery with an infusion pump. 8 mL / hr 2. The doctor orders heparin to infuse at 750 unit per hour. The pre-mixed intravenous solution available is 500mL D5W with 25000 units heparin added. Calculate the infusion rate for delivery with an infusion pump. 15 mL / hr 4 See p.408 Pickar Standard Weight-Based Heparin Protocol 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Weight in kilograms. Required for order to be processed ______kg Heparin 25,000 units in 250mL 1/2NS. Bolus dosage strength 1000units/mL. APTT q6hrs or 6 hrs after rate change; daily for 2 consecutive therapeutic APTTs. CBC initially and repeat every ______day[s] Obtain APTT and PT/INR on day one prior to initiation of therapy Guaiac stool initially then every _____day[s] until heparin d/c Neuro checks every _____hrs while on heparin Discontinue APTT and CBC once heparin is discontinued Notify physician of any bleeding problems Bolus with 80 units/kg. Start drip at 18 units/kg/hr 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. If APTT is less than 35 seconds If APTT is 36-44 seconds If APTT is 45-75 seconds If APTT is 76-90 seconds If APTT is greater than 90 seconds 1. 2. 3. Rebolus with 80units/kg and increase rate by 4 units/kg/hr Rebolus with 40units/kg and increase rate by 2 units/kg/hr Continue current rate Decrease rate by 2 units/kg/hr Hold heparin for 1 hour and decrease rate by 3 units/kg/hr 5 Using the Heparin Protocol • Patient weight = 110 lbs Convert to kilograms = 50 kg • Calculate the heparin bolus Protocol states: Bolus with 80 units/kg 80 units X 50 kg = 4000 units • Calculate the bolus in milliliters Protocol states: Bolus dosage strength 1000 units/mL 1000 Units 1 mL = 4000 Units X mL = 4 mL 6 Using the Heparin Protocol • Calculate the starting infusion rate Protocol states: Start drip at 18 units/kg/hr Multiply by pt weight of 50 kg: 18units X 50 kg = 900units/hr Protocol states: Heparin 25,000 Units in 250 mL of ½ NS. 25000 Units = 900 Units/hr 250 mL X mL/hr X = 9 mL/hr • Adjust infusion rate according to APTT results. Follow protocol guidelines. Examples: Client has APTT of: Rebolus with 40units/kg/hr & increase rate by 2 units/kg/hr 40 70 Continue current rate 88 Decrease rate by 2units/kg/hr 7 IV Flow Rate Ordered “Per Minute” • Critical Care IV calculations • Determine electronic IV infusion rate (mL per hour) for IV medications ordered per minute (such as mg per min) • Step 1: Calculate dosage in mL per min • Step 2: Calculate flow rate in mL per hour 8 2000 mg EXAMPLE: Ordered lidocaine 2g IV in 500 mL D5W @ 2 mg/min Step 1 Calculate ml/min: 2000mg = 2mg/min 500mL X mL/min X = 0.5mL/min Step 2 Calculate ml/hr: 0.5mL 1 min = X mL/hr 60 min/hr X = 30ml//hr 9 IV Flow Rate Ordered by Kilogram per minute • Calculate electronic IV infusion rate (mL per hour) for IV medications ordered by weight per minute (such as mg per kg per min): Step 1- Calculate desired dosage per minute Step 2- Calculate desired dosage in mL per minute Step 3- Calculate flow rate in mL per hour 10 EXAMPLE: 250mL of D5W with 225 mg of 0.003 mg dobutamine to infuse @ 3mcg/kg/min. Client weighs 50 kg Step 1- Calculate desired dosage per minute 0.003mg X 50 kg = 0.15mg/minute Step 2- Calculate desired dosage in mL per minute 225mg = 0.15mg/min 250mL X mL/min X = 0.17 ml/min Step 3- Calculate flow rate in mL per hour 0.17mL = X mL/hr 1 min 60min/hr X = 10ml/hr 11 Titrating IV Drugs • • • • Mostly seen in Critical care and/or OB Started with bolus Then increased to produce desired effect Started at lowest dosage and increased or decreased as needed • Examples: Dopamine, Pitocin 12 Example: RL 1000mL with Magnesium Sulfate 20g. Start with bolus of 4g for 30 min, then maintain continuous infusion @ 2g/hr. Step 1:Calculate bolus in g/mL: 20g = 1000mL 4g X mL X = 200mL should infuse over 30 min Step 2:Calculate bolus in mL/hr 200mL = 30 min XmL/hr 60 min/hr X = 400mL/hr Step 3:Calculate continuous infusion rate by repeating steps 1 and 2 using 2 g instead of 4g. 13