Medical Math 2
advertisement

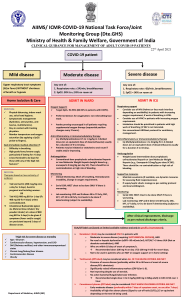
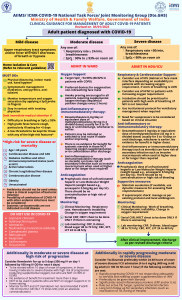
Medical Math Operations and Formulas Metric Abbreviations for Weight Kilogram kg Gram gm Milligram mg Microgram mcg Metric Equivalencies for Weight 1 kilogram= 1000 g 1gram= 1000 mg 1 milligram= 1000 mcg • • Household 1 cup • 1 tablespoon T (tbs) • 1 teaspoon t (tsp) • drop gtt • pound lb Abbreviation / C Metric / 240 cc Apothecary 15 cc or 15 ml 5 cc depends on size of the drop 2.2 lb = 1 kg 1 lb. = 16 oz • The formula method: D x Q =X H • D - dosage desired or ordered H - what is on hand (available) Q - unit of measure that contains the available dose. When using solid products (tablets, capsules) Q is always 1 and can be eliminated. Q varies when using liquid measures. X - the unknown dosage you need to administer Units • Calculating dosages in units (insulin, heparin, pitocin, vitamins, some antibiotics) • Example: Ordered: Heparin 8000 units subcutaneous q12h Available: Heparin 10,000 units per ml How much will you administer? • Formula: 8000 units X 1 ml = 0.8 ml 10,000 units Calculations based on body weight • The first step is to convert the patient’s body weight into kg. The formula is 2.2 lb. = 1 kg. • The second step is to calculate the medication dose. • a. Calculate the daily dose • b. Divide the daily dose by the number of doses to be administered. • c. Use either the ratio-proportion or formula method to calculate the number of tablets/capsules or volume to be administered with each dose Temperature Conversion °C = (°F-32) 5/9 or 0.5556 °F = (°C) 9/5 or 1.8 + 32