Semester Exam Review- Part I
advertisement

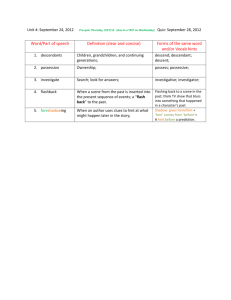
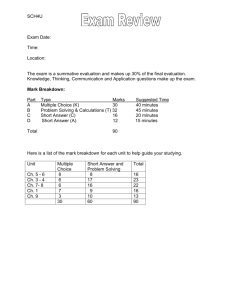
Semester Exam Review- Part I: Important Concepts and Questions ANSWER 1. As we learn and discover new things, old theories are 1. Answers will vary but can include: challenged and new theories are formed. What Retesting an old idea with new data contributes to new theories being formed? (Hint: Basing conclusions on tested Page 15 and notes from Unit 1) observations Reading about other scientists’ theories and discoveries Discovering a new planet with ancient water formations 2. Scientific knowledge comes from a 2. Answers will vary but students should variety of sources. Explain. discuss how science should be open to new Hint: Page 15, notes from Unit 1 ideas as new discoveries are being made. 3. Havannah decided to do a science 3. Scientific experiments should be written so fair project detailing how cities impact that others may replicate. New ideas or the alligator population. Why is it theories build upon prior research. important that Havannah take good notes and complete a detailed log book? Hint: Pages 6-14 4. How can a widely accepted scientific 4. New evidence supports a new theory instead of the old one. theory be replaced by a new theory? magma __________________. Hint: Page 65 5. What is an independent variable? 5. Independent Variable: a factor changed by the experimenter Dependant variable? Control? Dependant Variable: factors being measured in an experiment Constant? Control: standard to which experimental results are compared Hint: Page 10, Unit 1 Notes Constant: Variables that do not change in an experiment. 6. Sponge Bob notices that his pal Gary is 6. Independent: Cures (seaweed and Dr. Kelp) suffering from slimotosis, which occurs when the Dependant: Slime and Odor shell develops a nasty slime and gives off a horrible odor. His friend Patrick tells him that rubbing seaweed on the shell is the perfect cure, while Sandy says that drinking Dr. Kelp will be a better cure. Sponge Bob decides to test this cure by rubbing Gary with seaweed for 1 week and having him drink Dr. Kelp. After a week of treatment, the slime is gone and Gary’s shell smells better. What is the independent variable in this experiment? What is the dependent variable? Hint: Review the scientific method- Page 8 in book, Unit One in portfolio) 7. What is science? What is a scientist? Hint: Unit 1 Portfolio 8. When completing science experiments, scientists should be accurate and precise. Define accurate and precise. How does accuracy affect an experiment? 7. Science: process of observing, studying, and thinking about things in your world to gain knowledge. Scientist: One whose activities make use of the scientific method to answer questions regarding the world around them. A scientist may be involved in original research, or make use of the results of the research of others 8. Accuracy: how close you come to the standard Precision – Degree of exactness with which an object is measured. • Depends on measuring instrument 9. What is the difference between a hypothesis and a Answers will vary regarding accuracy and experiments- possible answers: If not accurate, results of experiments are not valid. Data is not reliable. Inaccurate data will cause one to misinterpret results of experiment. 9. Theories have been confirmed through tests; hypothesis theory? have not Hint: 10. What is a scientific law? Describe Newton’s 1st, 2nd, and 3rd Law of motion. Bonus: Relate Disney World’s Space Mountain roller coaster ride ( by the way, maximum speed is only about 25mph and the ride only lasts 2 ½ minutes) and Newton’s Laws of Motion. Hint: Page 19 and Unit 1 Notes 11. What is the formula for density? Calculate the density of an object with 10. A scientific law is a rule that describes the behavior of something in nature. Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: an object will continue in motion or remain in rest until it is acted upon by an outside force. Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion: when a force acts on an object, the object will change speed, direction, or both. Newton’s Third Law of Motion: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Rollar coaster example and possible answers: 1st Law: brakes 2nd Law: the force one feels when going down is affected by the weight of the “cars” and gravity. 3rd Law: banked curves 11. D=m/v. D= .20 g/cubic centimeter. a mass of 20 grams and a volume of 100 cubic centimeters. Hint: Unit 2 13. What is matter? _______ and _________ are not considered matter because ________________________________. Hint: Page 34 12. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Heat and light as they have no mass and do not take up space. 13. The word atom comes from the Greek word " indivisible". How are atoms indivisible? Hint: Page 34 13. Atoms can not be divided without losing their 14. The Periodic Table contain more metals, non metals, or gasses? Hint: Periodic Table 15. What is the difference between a covalent and ionic bond? Hint: Page 41 14. metals 16. What is the chemical symbol for iron? Hint: Periodic Table 17. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in a stable Hint: Page 70 and notes 18. What is the atomic mass of silver? Hint: Page 66 19. What are the negatively charged particles orbiting chemical properties. Remind students: atoms are the building blocks of matter. 15. Covalent: share electrons. Ionic: Ionic bonds are formed by the attraction between two oppositely charged ions. Usually occurs between positive metals and negative nonmetals. 16. Fe 17. Protons: 9 Neutrons: 10 Electrons: 9 18. 108 19. Electrons an atom called? 20. Who is Alfred Wegner and what is Pangaea? Hint: 20. No. A diamond is harder than a streak plate and will scratch the plate.