Arthropods
advertisement

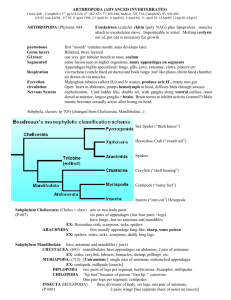
Arthropods Week 6 Phylum: Arthropoda • Common name = arthropods • Ex. Insects, spiders, crabs, shrimp, centipedes, lobsters, ticks Monday Arthropods • Arthropods have: – Segmented body • Head ⇛ Cephalothorax • Thorax • Abdomen – Tough exoskeleton made of chitin – Jointed appendages Evolution of Arthropods • Led to – Fewer appendages – Few segments – Highly specialized appendages • • • • • Antennae Pincers Walking legs Flippers Claws Feeding • Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores • Bloodsuckers, filter feeders, detritivores, parasites • Mouthparts range from pinchers to fangs to sickle-shaped jaws depending on diet Respiration • Terrestrial – Breathe thru a network of branching tracheal tubes – Air enters through spiracles = little openings along body – Spiders uses book lungs • Aquatic – Featherlike gills – Horseshoe crabs have book gills Circulation • Open circulatory system • Well-developed heart Excretion • Terrestrial – Malpighian tubules = saclike organs that extract wastes from the blood and add them to feces (digestive wastes) • Aquatic – Diffusion Response • Well-developed nervous system • All have a BRAIN Movement • Muscles are attached to exoskeleton • Pull of muscles against exoskeleton allows arthropods to move • All have jointed appendages Reproduction • Terrestrial – Internal fertilization • Aquatic – Internal or external fertilization Growth and Development • Exoskeletons DO NOT GROW, arthropods must MOLT • Molting = arthropod sheds entire exoskeleton and makes a new larger one • Molting arthropods are vulnerable and hide until they are done Crustaceans • • • • • Primarily aquatic Crabs, shrimps, lobsters, crawfish, barnacles 2 pairs of branched antennae 2 or 3 body segments Chewing mouthparts = mandibles Tuesday Associated Vocabulary • Cephalothorax = fused body segment consisting of head and thorax • Abdomen • Carapace = part of exoskeleton that covers the cephalothorax • Mandible = biting, grinding mouthpart • Chelipeds = claws • Swimmerets = flipper-like appendages for swimming Chelicerates • 2 body segments • Most have 4 pairs of walking legs • Horseshoe crabs, spiders, ticks, scorpions From Prentice Hall Biology, 2006 Eyelash mites Demodex folliculorum Brown Recluse Black Widow Associated Vocabulary • Chelicerae = mouthparts with fangs for stabbing and paralyzing prey • Pedipalps =mouthparts for grabbing prey • Book lungs • Book gills • Spinnerets = organs in spiders that contain silk glands for spinning webs Uniramians • Contains more species than all other animal groups combined! • • • • Jaws 1 pair of antennae Unbranched appendages Insects, centipedes, millipedes Centipedes and Millipedes • Millipedes – Highly segmented body – 2 pairs of legs per segment – Live under rocks and decaying logs – Roll up or secrete toxins for defense • Centipedes – 1 pair of legs per segment – Carnivorous and venomous – Live under rocks or in soil in humid areas Insects • • • • • 3 body segments = head, thorax, abdomen 3 pairs of legs 1 pair of antennae 1 pair of compound eyes 2 pairs of wings Wednesday Insects are the largest class of animals! Response to Stimuli • Compound eyes with many lenses detect tiny movements and color changes • Chemical receptors on mouthparts, legs and antennae (taste/smell) • Well-developed ears (grasshoppers have ears on their legs!) Adaptations for Feeding • 3 pairs of appendages used as mouthparts – Mandibles to saw/grind (ex. ant) – Tube-like mouthpart to suck nectar (ex. moth) – Sponge-like mouthpart to lap up food (e. fly) • Digestive enzymes in saliva – Bee saliva changes nectar from flowers into honey Movement and Flight • 3 pairs of legs – Walking, jumping, capturing/holding prey – Many species have spines or hooks on legs • 2 pairs of wings made of chitin • Evolution of flight allowed insects to disperse long distances and colonize many habitats Metamorphosis • Process of changing shape and form – Complete metamorphosis • Egg-larva-pupa-adult • Larva looks nothing like adult – Incomplete metamorphosis • Egg-nymph-adult • Nymphs look like adults Advantage = larva and adults don’t compete for resources Insects and Humans • Beneficial – Honey – Wax – Pollination – Silk – Food • Harmful – Damage wood – Damage clothes – Stings – Crop damage – Disease Insect Communication • Audio – Crickets • Visual – Fireflies • Chemical – Bees – Pheromones Insect Societies • Society = a group of closely related animals of the same species that work together for the benefit of the whole group – Bees – Ants – Termites • Castes = groups of individuals that perform specific functions