Chapter 14 and 15.doc
advertisement

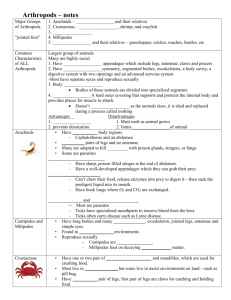
Chapter 14 and 15 Phylum Arthropoda Jointed appendages (more strength and coordination) Exoskeleton (like roundworms, when they outgrow their exoskeleton, molt and secrete a new one) Very diverse (more species of arthropods than any other phylum) Open circulatory system (blood vessels empty into the body cavity) hemocoel (blood vessels and coelom together) Metamorphosis (body plan changes during development) Groups of arthropods Trilobites (extinct Subphylum) Chelicerata (have chelicerae) Arachnids (spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites) Horseshoe crabs (aquatic) Sea spiders Crustaceans: biramious, susceptible to water loss (usually aquatic) 1) Malacostracans (Decapods: (crabs, lobsters, crayfish), shrimp, mysids, krill, isopods, amphipods) (big group) 2) Branchiopodans (fairy shrimp and brine shrimp) 3) Maxillopodans (copepods and barnacles) Chapter 15 Hexapods and Myriapods These two subphyla have waxy exoskeletons (unlike crustaceans), mostly terrestrial, uniramous appendages Myriapoda Millipedes (2 pairs of legs per segment) typically cylindrical, detritivores Centipede (1 pair of legs per segment), predators, venomous, longer legs than millipede, flatter body Pauropoda and Symphyla Hexapoda (insects and former insects) Insects (three segments, head, thorax, abdomen; three pairs of legs (thorax), 2 pairs of wings, 1 pair of antennae; specialized mouthparts) First flying animals 75% of known species are insects Tracheal gas exchange (decentralized gas exchange) system of tubes for gas exchange and gas distribution Limited thermoregulation Eusocial (hive) Orders 1) Beetles (25% of all species) Forewings are hardened and function for protection 2) lepidopterans (butterflies and moths) Coiled proboscis 3) true flies (dipterans) house flies, mosquitos, fruit flies, horse flies; one pair of wings, one pair of halteres 4) hymenopterans (ants, bees, wasps (not termites)) Frequently eusocial Related phyla Tardigrade (water bears) Ohychophora (velvet worms)