Global Winds Worksheet: Earth Science for Middle School
advertisement
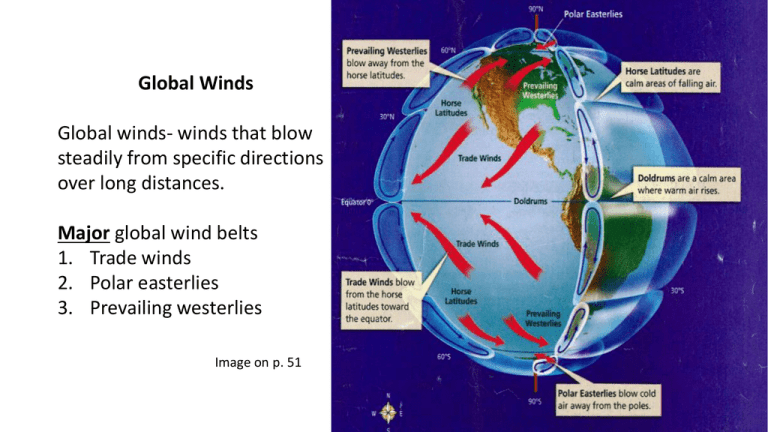
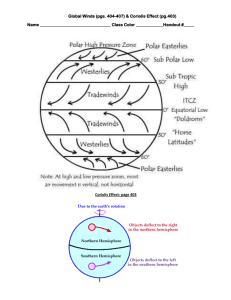
Global Winds Global winds- winds that blow steadily from specific directions over long distances. Major global wind belts 1. Trade winds 2. Polar easterlies 3. Prevailing westerlies Image on p. 51 Global Winds Doldrums • Direct sun rays hit equator and strongly heats Earth’s surface • Warm air will ______ (rise or sink) creating ______ (high or low) pressure. • Cool air moves in but is warmed rapidly • Little horizontal motion so winds near equator are weak Horse Latitudes • Latitude- distance from equator measured in degrees • ~30 N and S latitudes, the air stops moving toward poles and sinks creating a belt of air • How did this wind belt get its name “Horse Latitudes”? Write a sentence in your own words. Global Winds Trade Winds • Between 30 L and the equator in both hemispheres • Rotation of Earth causes trade wind to curve west • Named because sailors relied on them to sail from Europe to Americas Westerlies • Between 30 and 60 L in both hemispheres. • Rotation of Earth causes wind to curve east • Can carry moist air over the U.S. producing rain and snow Global Winds Polar Easterlies • Between poles and 60 L in both hemispheres • Rotation of Earth causes winds to curve west • Can carry cold Arctic air over most of U.S. producing snow and freezing weather.