Planetary Winds Lab Worksheet: Earth Science
advertisement

,
Date
,i-'{lt,,
t"
4P
Lab: Planetarv
Winds
-o draw the Earth's Planetary Wind Belts
:irections
lfl,llr'-
-
\
'E
,
-
by carefutly following a set of
I
Ruter
Colored Pencil
Earth Science Reference Tables
of the
:ii'cie below, connect the tick-marks on both thb tefi and right sid'es
wi'th a pencil and a ruler.
North Pole
Snrrlh Pnle
13
Datg
Narne
-
r
numbers:
lines with th! foilowingrratitude
raberthe
paper
your
of
margin
2) In the right
90
0,30 N, 30 5,60 N,60 s, 90 N'
s
'
3)Writetheword.Lou..Fdiect|yonthe|inerepJesentingtheequator.I
Thisidentifiestneequatorasanareaofwarm|owpressure.
of the latitude lines
"Low", continue identifying the rest
and
"H!gl"
then
words
4) using the
o"girinirig the Equatoriar Low,
woros,
Arternate'*re
.iicre,
"i
you drew on vlu,
so,rth, towards each pole.
ff;N;;;:'ir,en
rlJ,
your
working
frorn
globe' Ivlake the arrows point
your
on
sections
6
the
of
5) Draw 3 arrows in each
areas to low {W?rm} areas'
fines repre"""t]ng ilLn tcoio]
6)Now,usingaco|oredpelg!|,deflecteachofthearrowstoshowhowEarth's
-i;i;iil*o-ulo
affectwind
directidn'
'
'
and to
to the right in the Northem Hemisphere
are
winds
Jeflgcted
Remember:
southern HemisPhere'
fr; l;nil
'
G
(Hint Look DOWNthe anow
it in the
TOWARD'9 the point and thendeflect
#H;;i; direaion)
'
, rrr
rhe 6 secrions containing
7)Usingthenarnesthat4nealbe|or|abe|eachofthe6seetions
u"t*"' write the label
deflested
to identify that
ail;;ilffi;tuino
"no*o
oifierent section on the circle'
ifrninEa"n
.
Rememben
-
wnds
FR,M wHr?H they come'
are named according to the direction
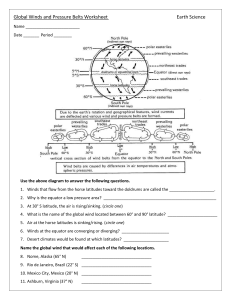
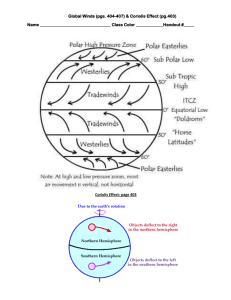
Po|areasbr|ie(NorthemandSqrlthemHemispheres)
ilodfieasttade
rt?e
SoufDeastfr&vin6
Pnvalting (Soutt) Weswties
Prcvailini Nordt) Westerlies
;
where the "mean position
8) Use a cOlored pencilto indicate
Hemispheres' i
for both #-niJttnem ano Southem
9)
t, t'
of Polar Jet stream" is
of
current shoring the pattem
conyection
draw
g|obe,
your
of
9
on the right side
gO N and 60 N latitudes'
t-ft"
u"t*!tn
air flow
ll
I
Date
Name
ouEsilotts '
,
,l
sheet''
Place your Answer to the foltowing questions on the ?nswer
I
1)
The deflection of wind, ocean water and objects flying through the air is known as
the:
'
2) This deflection is caused bY:
3) Tellwhat causes lrinds"?
'
,
4) On a molecular level, explain why cold air is heavier, (more dense) and therefore,
exerts more pressure than warm air.
5) Why then do winds blow from areas of cold, nign pressure to areas of low, warm
pressure?
6)
.
each'of the
Describe the air mass characteristics (temperature and humidrty), for
following:
a) The equatoriat ,low (00):
b) The 30 N & 3OoS subtroPical highs:
c) The 60oN &60 S sub Polar lows:
,
7l
is wetter at
is air drier at the 300N & 3o0s and 900N & 900s latitudes, while it
whv-OOott
the
& 600S and 0 latitudes?
ga) This drawing represents the location of wind belts at the time of the Equinoxes'
and
What will happJn io the positions of the Earth's wind belts during the Summer
winter seasons?
Sb) Give a good reason why this wilf happen.
15