Biomolecules Homework
advertisement

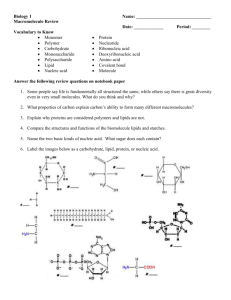
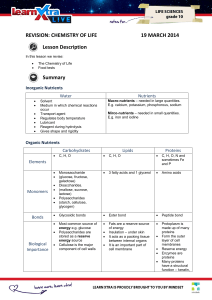
BIOMOLECULES Name ______________________________________ CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates include monosaccharides, ___________________________, and polysaccharides. An example of a monosaccharide is ______________________ which has the molecular formula ____________________. Polysaccharides are categorized as structural or ________________________________, polysaccharides. The structural polysaccharide _____________________ composes the cell walls of plant cells and is not digestible by humans. This tough polysaccharide is digestible by ________________________________, (animal) because of symbiotic microbes in the gut. Another structural polysaccharide, ___________________, forms the tough exoskeleton of insects. Storage polysaccharides in plants are ______________________________, which can be converted to energy when the plant requires it. In animals, the storage polysaccharide is _____________ found in muscle and liver. Polysaccharides are composed of many units of _________________ monomers. The carbohydrate known as “blood sugar” is _________________________ while the predominant carbohydrate found in a potato is _________________. PROTEINS The building blocks of proteins are ____________ ____________. They get their name from the ____________________ functional group. Most proteins have a ________________________, shape which enables the protein to function. Amino acids are first strung into a linear ________________________ which then folds to form the functional protein. Proteins exhibit up to 4 levels of complexity. The primary protein structure is the sequence of amino acids. This molecule’s secondary structure is composed of ________ ___________ and beta pleated _________________________. The _____________________________. structure consists of a 3 dimensional molecule that has a function. Some proteins, but not all, have a quaternary structure. These proteins have multiple ______________________________. An example of a protein with a quaternary structure is ______________________________. When proteins are __________________ed they lose function because they lose shape. . An example of a pigment protein is _______________ while an example of a transport protein is ________________. LIPIDS ___________________ fats have many hydrogen atoms attached to carbons chains, while ___________________ fats have less hydrogen atoms due to double bonds between carbons. Less hydrogens cause these lipids to be ______________________________. at room temperature. Animal fat is ____________________at room temperature. A lipid with 3 hydrocarbon chains is referred to as a ______________________________. Fats are needed to make ___________________________ hormones. The lipid used to make these hormones is ___________________________. Lipids are also used to build ________________________ which are an important component of cell membranes, and to cushion organs and insulate the body. 1 NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids include RNA and _________________. The architecture of the DNA molecule is described as a _____________ helix and contains the 4 nucleotide monomers G, ____, _____, ______. The sugar in DNA is ___________________________ which forms the “backbone” of the molecule with phosphate groups. The bases face internally with G bonding to _______ and T hydrogen bonding to _______. DNA is important to cells because it carries the code for cells to make __________________________. Identify the TYPE of biomolecule (carbohydrate, lipid, protein, or nucleic acid) _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ ________________________ __________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ 2