Notes 02 - Strategy and Performance
advertisement
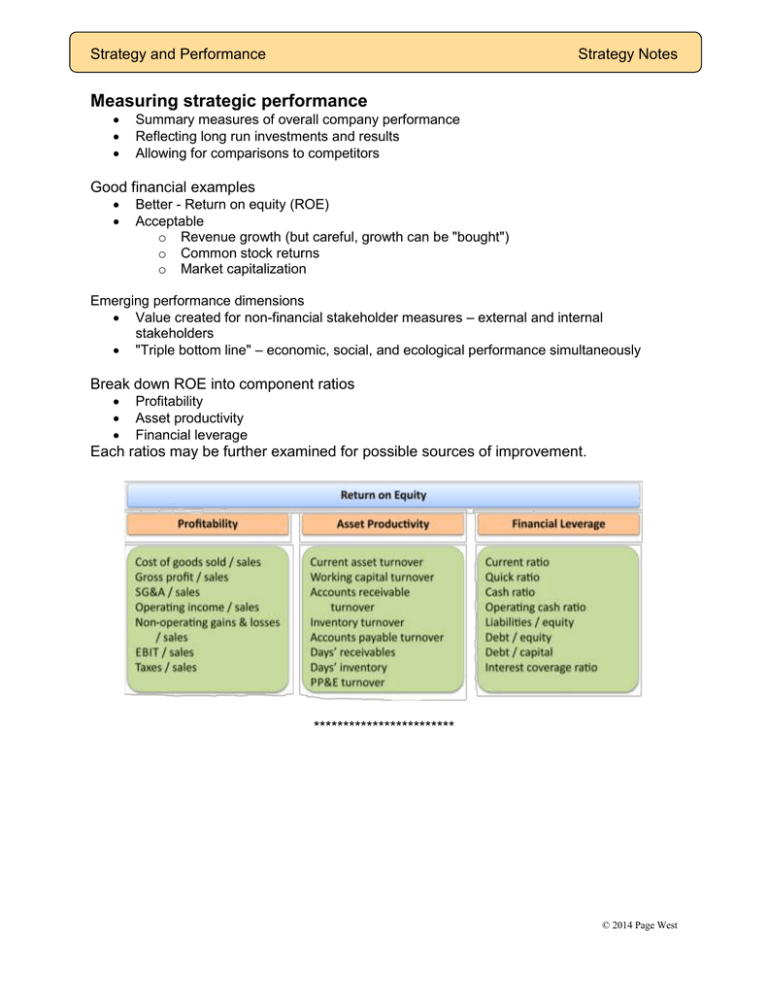
Strategy and Performance Strategy Notes Measuring strategic performance Summary measures of overall company performance Reflecting long run investments and results Allowing for comparisons to competitors Good financial examples Better - Return on equity (ROE) Acceptable o Revenue growth (but careful, growth can be "bought") o Common stock returns o Market capitalization Emerging performance dimensions Value created for non-financial stakeholder measures – external and internal stakeholders "Triple bottom line" – economic, social, and ecological performance simultaneously Break down ROE into component ratios Profitability Asset productivity Financial leverage Each ratios may be further examined for possible sources of improvement. ************************ © 2014 Page West Detailed financial statement analysis Reveals patterns of strategic investment Helps identify differences among competitors Methods Current financial statement comparisons Common-sized financial statement comparisons Operating ratio comparisons Trend analysis – one company over time Understand differences between types of margins and how competitors fare on each Gross margin Operating income Net income Consider economic logic & operating characteristics for companies & industries Kodak followed the "razor blade" model – sell cameras at breakeven, sell film at hefty gross margins. Once a camera is bought, the consumer must buy the film – lockin. Microsoft & Sony follow similar approach with their video game consoles. Saks Fifth Avenue – sells small quantities of expensive merchandise, with large markups on every item. Large retail "box" stores – "stack it high, move it out" – put money in the bank by selling vast quantities with smaller markups on each item. These companies earn ROE by combining profitability and asset productivity (moving vast quantities of inventory efficiently thru warehouses and stores).