The Subjunctive Mood (with Examples)
advertisement

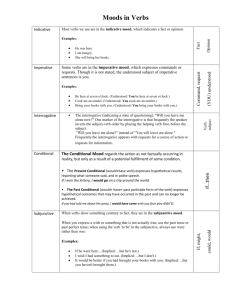
Verb Mood Study Guide What Is the Subjunctive Mood? (with Examples) The subjunctive mood is the verb form used to express a wish, a suggestion, a command, or a condition that is contrary to fact. The form of a verb in the subjunctive mood may differ from the form with the same subject which is not in the subjunctive mood. For example: I was in your position two years ago. (not in the subjunctive mood) If I were in your position, I would do the same. (subjunctive mood) Examples of the Subjunctive Mood Here are some examples of verbs in the subjunctive mood: I wish it were still in use. (it was becomes it were) The board recommended that the motion be passed immediately. (motion is passed becomes motion be passed) She suggests that Mark work full time from Saturday. (Mark works becomes Mark work) He said it was essential that Johan guard the box. (Johan guards becomes Johan guard) It is imperative that the game begin at once. (game begins becomes game begin) Through common usage, the non-subjunctive forms of verbs are gradually replacing the subjunctive forms. Many of the examples above sound incorrect. In summary, the changes are: Non-subjunctive Form Nonsubjunctive Example Subjunctive Form Subjunctive Example is He is allowed. be It is essential he be allowed. was I was ordered. were If I were ordered, I'd go. present verbs in the third person singular (i.e., ending s) He cooks. remove the s I wish that he cook. Verbs Which Attract the Subjunctive Mood The following verbs often attract the subjunctive mood: ask, command, demand, insist, order, recommend, suggest, and wish. Adjectives Which Attract the Subjunctive Mood The following adjectives often attract the subjunctive mood: crucial, essential, important, imperative, and necessary. What Is Mood? Mood is the form a verb takes to show how it is to be regarded (e.g., as a fact, a command, a wish, an uncertainty). There are three major moods in English: The Indicative Mood. This states facts or asks questions. For example: o They are playing the guitar. o Are they playing the guitar? The Imperative Mood. This expresses a command or a request. For example: o Play the guitar! o Please play the guitar. The Subjunctive Mood. This shows a wish or doubt. For example: o I suggest that Lee play the guitar. o I propose that Lee be asked to play the guitar. o If I were Lee, I would play the guitar. What Is Mood in Grammar? (with Examples) Mood is the form a verb takes to show how it is to be regarded (e.g., as a fact, a command, a wish, an uncertainty). There are three moods in English: The Indicative Mood The Imperative Mood The Subjunctive Mood The Indicative Mood (with Examples) The indicative mood states a fact or asks a question. For example: She is driving the car. Is she driving the car? The Imperative Mood (with Examples) The imperative mood expresses a command or a request. For example: Drive the car! Please drive the car. The Subjunctive Mood (with Examples) The subjunctive mood shows a wish or doubt. For example: I suggest that she drive the car. I propose that she be asked to drive the car. If I were there, I would drive the car. Mood and Sentence Type With the exception of an imperative sentence, the sentence type gives no indication to the mood. Look at these examples: Mood Sentence Type Indicative Mood Imperative Mood Subjunctive Mood It has arrived. (declarative sentence) It's arrived! (exclamatory sentence) Has it arrived? (interrogative sentence) Please leave. (imperative sentence) Get out! (imperative sentence and an exclamatory sentence) If I were there, I would. (declarative sentence) I demand he be removed! (exclamatory sentence) What if he were there? (interrogative sentence)