Eukaryotic Cells
advertisement

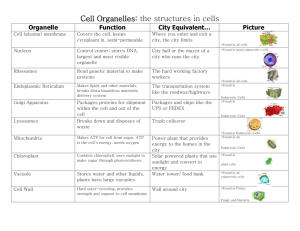
Mr. Altorfer Life Science Eukaryotic Cells of Plants and Animals Plants! Sixth Graders! Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells: Cells that have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Examples: Plant and animal cells. Plant and animal cells have some similar and some different parts. Let’s take a closer look! Eukaryotic Cells PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL Eukaryotic Cells Cell Membrane- A protective covering that holds the parts of the cell together. It separates the cell’s organelles from the cell’s environment. Nutrients and waste material move in and out of the cell through the cell membrane. FOUND IN BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS! Eukaryotic Cells BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS CONTAIN A CELL MEMBRANE Eukaryotic Cells Cell Wall- A rigid (hard and flexible) structure found surrounding all plant cells. Cell walls are not found in animal cells. Some bacteria and fungi do have cell walls. Eukaryotic Cells CELL WALLS HELP KEEP PLANTS UPRIGHT AND STANDING TALL! Why don’t animal cells need cell walls? Eukaryotic Cells Cytoplasm- The gel-like material that supports the organelles of the cell. Cytoplasm is found in ALL cells. Cytoplasm is a clear gel-like material. Eukaryotic Cells Cytoskeleton- A web of proteins that supports the cell. It keeps the cell’s membranes from collapsing. The cytoskeleton is found in both plant and animal cells. Eukaryotic Cells The cytoskeleton supports the cell. We will not be able to see this structure. Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus- A large organelle that controls the daily activities of the cell. The cell’s DNA (genetic material) is contained in the nucleus. Nucleolus- Contained within the nucleus. This is where ribosomes are made. Eukaryotic Cells The nucleus is the control center of the cell. Eukaryotic Cells Ribosomes- Organelles that make proteins for the cell. Ribosomes are the smallest and most numerous of all organelles. Some float freely around the cell while others may be attached to membranes in the cell. Plant and animal cells both contain ribosomes. Eukaryotic Cells Ribosomes are very small. They make proteins for a cell. Eukaryotic Cells Endoplasmic Reticulum- (ER) A series of folded membranes that produce proteins, lipids or other materials for the cell. The ER acts as an internal delivery system for the cell. Substances move from place to place in the cell by way of the ER. Plants and animal cells both contain ER. Eukaryotic Cells There are two types of ER: Rough ER- Contains ribosomes. Smooth ER- Does not contain ribosomes. Eukaryotic Cells The Endoplasmic Reticulum is a series of tubes and passageways that help to transport cellular materials. Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria- The power source of a cell. Sugar is broken down to produce energy. Both plant and animal cells have mitochondria. Eukaryotic Cells Mitochondria are the power source of the cell. Eukaryotic Cells Chloroplasts- Organelles found in plant and algae cells that allows them to make their own food from the sun. Photosynthesis- occurs in the chloroplasts. Sunlight + CO2 + H2O = Sugar + O2 Chloroplasts are NOT found in animal cells! Eukaryotic Cells Chloroplast make food for plant cells through the process of photosynthesis. Eukaryotic Cells Golgi Complex- The organelle that packages and distributes proteins. The Golgi complex looks like smooth ER. Both plants and animal cells contain Golgi Complex. Eukaryotic Cells The Golgi Complex help to process proteins. Proteins need to be packed for shipment to other cells. Eukaryotic Cells Vesicle- A small sac that surrounds material to be moved into or out of the cell. Both plant and animal cells contain vesicles. Eukaryotic Cells Lysosomes- Organelles that contain digestive enzymes. Old cell parts or waste materials are digested inside lysosomes. Found mainly in animal cells, rarely found in plant cells. Eukaryotic Cells Lysosomes help to digest old worn out cell parts. Eukaryotic Cells Vacuoles- Vesicles that store food, water and waste materials. Central Vacuoles- Found in plant cells. Filled with water, these vacuoles help to keep the plants stiff and rigid. Plant cells have very large central vacuoles. Animal cells have small vacuoles. Eukaryotic Cells Plant cells have very large central vacuoles. The vacuoles are filled with water and help to support the plant.