Chapter 12
advertisement

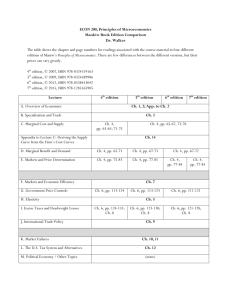
Chapter 12 Managing Economic Exposure and Translation exposure Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA Chapter Objectives • • To explain how an MNC’s economic exposure can be hedged. To explain how an MNC’s translation exposure can be hedged. Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA Economic Exposure • Economic exposure refers to the impact exchange rate fluctuations can have on a firm’s future cash flows. • Recall that corporate cash flows can be affected by exchange rate movements in ways not directly associated with foreign transactions. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Economic Exposure The economic impact of currency exchange rates on us is complex because such changes are often linked to variability in real growth, inflation, interest rates, governmental actions, and other factors. These changes, if material, can cause us to adjust our financing and operating strategies. PepsiCo Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Scandinavian Business Seating Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Scandinavian Business Seating Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Use of the Income Statement to Assess Economic Exposure • An MNC can determine its exposure by assessing the sensitivity of its cash inflows and outflows to various possible exchange rate scenarios. • The MNC can then reduce its exposure by restructuring its operations to balance its exchange-rate-sensitive cash flows. • Note that computer spreadsheets are often used to expedite the analysis. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA How Restructuring Can Reduce Economic Exposure • Restructuring to reduce economic exposure involves shifting the sources of costs or revenue to other locations in order to match cash inflows and outflows in foreign currencies. • The proposed structure is then evaluated by assessing the sensitivity of its cash inflows and outflows to various possible exchange rate scenarios. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Example from ch 10 – Mannerton plc • Mannerton plc sells to the UK and Europe – A strong € increases UK sales somewhat due to increased competitiveness – European sales are assumed to be constant at €40 and European costs are much higher (about € 200) • Mannerton therefore lose money if the € appreciates Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Impact of exchange rate movements Euro exc. rate UK sales (£) European sales (€ 40) Total sales Scenario 1 Scenario 2 Scenario 3 0,6 0,7 0,8 300,00 304,00 307,00 24,00 28,00 32,00 324,00 332,00 339,00 Cost of goods sold: UK costs European Costs Total costs 50,00 120,00 170,00 50,62 141,73 192,35 51,08 163,46 214,54 Gross profit 154,00 139,65 124,46 Operating expenses: UK fixed costs UK variable costs Total 30,00 30,72 60,72 30,00 31,10 61,10 30,00 31,38 61,38 EBIT 93,28 78,56 63,08 Interest expense: UK interest European interest (10 m €) Total 3,00 6,00 9,00 3,00 7,00 10,00 3,00 8,00 11,00 Earnings before taxes (EBT) 84,28 68,56 52,08 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Mannerton plc • Mannerton should change its operational structure by increasing European sales and decreasing the share of European costs – Increase € sales by 20 by spending £2 on advertising – £10 on materials from UK and £1 mill on other exp. – Reduce € costs by €100 and increasing £ costs by 50 – Increase £ borrowing by £3.5 and reduce £ borrowing by €5 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Different operational structure Euro exc. rate UK sales (£) European sales (€ 40) Total sales Scenario 1 Original Proposed 0,6 0,6 300,00 300,00 24,00 36,00 324,00 336,00 Scenario 2 Original Proposed 0,7 0,7 304,00 304,00 28,00 42,00 332,00 346,00 Scenario 3 Original Proposed 0,8 0,8 307,00 307,00 32,00 48,00 339,00 355,00 Cost of goods sold: UK costs European Costs Total costs 50,00 120,00 170,00 130,00 60,00 190,00 50,62 141,73 192,35 131,55 70,83 202,38 51,08 163,46 214,54 132,71 81,67 214,38 Gross profit 154,00 146,00 139,65 143,62 124,46 140,62 Operating expenses: UK fixed costs UK variable costs Total 30,00 30,72 60,72 32,00 31,72 63,72 30,00 31,10 61,10 32,00 32,10 64,10 30,00 31,38 61,38 32,00 32,38 64,38 EBIT 93,28 82,28 78,56 79,52 63,08 76,24 Interest expense: UK interest European interest (10 m €) Total 3,00 6,00 9,00 6,50 3,00 9,50 3,00 7,00 10,00 6,50 3,50 10,00 3,00 8,00 11,00 6,50 4,00 10,50 Earnings before taxes (EBT) 84,28 72,78 68,56 69,52 52,08 65,74 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Earnings before tax £ million Revenue is more stable 90 80 70 60 50 1 2 3 Scenarios From the Mannerton example in the text, the original steep slope is replaced through reducing exposure by the dotted lesser slope. It is less risky, fewer losses but fewer gains from exchange rate variation Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA A Case Study in Hedging Economic Exposure • Silverton Co., a U.K. firm, has three independent units that conduct some business in Europe. It is concerned about its exposure to the euro. • To determine whether it is exposed and the source of the exposure, Silverton applies a series of regression analysis to its cash flows and the euro’s movements. • PCFt = a0 + a1(%∆€)t + µ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Assessment of Silverton’s Cash Flows and the Euro’s Movements Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Regression output Unit A SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0,304404315 R Square 0,092661987 Adjusted R Square -0,036957729 Standard Error 3,394370714 Observations 9 ANOVA df Regression Residual Total Intercept X Variable 1 1 7 8 SS MS F Significance F 8,23662107 8,236621 0,714875713 0,425783 80,65226782 11,52175 88,88888889 Coefficients Standard Error -0,142548596 1,132067678 -0,282937365 0,334637828 t Stat P-value Lower 95% Upper 95%Lower 95,0% Upper 95,0% -0,12592 0,903336505 -2,81946 2,534366 -2,81946 2,534366 -0,8455 0,425783335 -1,07423 0,508355 -1,07423 0,508355 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Regression output Unit B SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0,425963344 R Square 0,18144477 Adjusted R Square 0,064508309 Standard Error 2,558992348 Observations 9 ANOVA df Regression Residual Total Intercept X Variable 1 SS MS F Significance F 1 10,16091 10,16091 1,551652649 0,252966588 7 45,83909 6,548442 8 56 CoefficientsStandard Error t Stat P-value -0,63174946 0,853458 -0,74022 0,483247208 0,31425486 0,252281 1,245654 0,252966588 Lower 95% Upper 95%Lower 95,0% Upper 95,0% -2,649856724 1,386358 -2,64986 1,386358 -0,282295192 0,910805 -0,2823 0,910805 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Regression output Unit C SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics 0,932567514 Multiple R 0,869682169 R Square 0,851065335 Adjusted R Square 0,671521457 Standard Error 9 Observations ANOVA df Regression Residual Total Intercept X Variable 1 1 7 8 Significance F F MS SS 0,000245334 21,06563475 21,06563 46,71483 3,156587473 0,450941 24,22222222 P-value t Stat Coefficients Standard Error 0,223961317 2,705072 0,030415 0,605831533 0,066202693 6,834825 0,000245 0,452483801 Upper 95,0% Lower 95% Upper 95%Lower 95,0% 0,076247171 1,135416 0,076247 1,135416 0,295939308 0,609028 0,295939 0,609028 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Translation Exposure • Translation exposure results when an MNC translates each subsidiary’s financial data to its home currency for consolidated financial reporting. • Translation exposure does not directly affect cash flows, but some firms are concerned about it because of its potential impact on reported consolidated earnings. Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA