Creating an innovative culture - Pennsylvania NewsMedia Association
advertisement

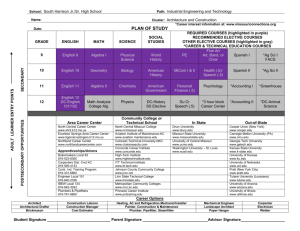
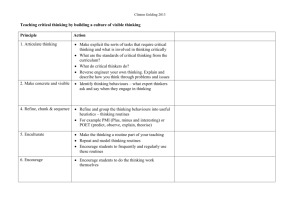
Creating an innovative culture Strategies for weaving engagement into your organizational fabric JONATHAN GROVES, PH.D. DRURY UNIVERSITY / SGF MEDIA CONSULTING NOV. 13, 2015 PENNSYLVANIA NEWSMEDIA ASSOCIATION @grovesprof @grovesprof @grovesprof Journalists Community 30,000 unique visitors 130,000 page views @grovesprof What is your mission statement? @grovesprof STRATEGY • Mission/goals • Competitive analysis • Allocation of resources E N V I R O N M E N O T R G A N I Z A T @grovesprof What are your strengths and weaknesses? What are the opportunities and threats? INNOVATION • Audience analysis • Circumstance-based strategy • Iterative processes STRATEGY • Mission/goals • Competitive analysis • Allocation of resources E N V I R O N M E N O T R G A N I Z A T @grovesprof Disruptive innovation (Christensen & Raynor, 2003) Performance Sustaining strategy Keep improving what we do well for our existing clients Client expectations Low-end disruption Addressing overshot customers New-market disruption Competes against nonconsumption Time Thinking disruptively • What are the jobs to be done? • What are “good enough” ways to do those jobs? • What innovative structures can you develop? • How can you reward and encourage creativity and risk? • What are the circumstances in which your product/service is being used? What is rewarded and acknowledged in your organization? Immediate INNOVATION • Consumer analysis • Circumstance-based strategy • Iterative processes STRATEGY • Mission/goals • Competitive analysis • Allocation of resources CULTURE • Shared assumptions • Sources of resistance • Success creation Long-term E N V I R O N M E N O T R G A N I Z A T What are your routines? LEVELS OF CULTURE I. ARTIFACTS • Tangible structures/processes • Rituals and routines • Observed behavior • Myths and stories II. ESPOUSED BELIEFS/VALUES • Goals, values, aspirations • Ideologies • Rationalizations III. BASIC UNDERLYING ASSUMPTIONS • Unconscious beliefs and values Shared assumptions arise only over the course of time and common experience. —Edgar Schein Anxiety comes when assumptions are challenged The role of leadership • What leaders pay attention to, monitor, and control • How leaders react to critical incidents and organizational crises • How leaders allocate resources • How leaders allocate rewards and status • How leaders model behavior • How leaders recruit, select, promote, and excommunicate Identify your critical moment @grovesprof Diffusion of innovations (Rogers, 2003) • Adoption affected by: – Advantages – Compatibility – Complexibility – Trialability – Observability @grovesprof One path to engagement SEO DESIGN CONTENT/ SOCIAL MEDIA ATTENTION (Message) USAGE (Ease of use) HABIT (Consistent content) SOCIAL MEDIA/ COMMENTS/ USERS CONNECTION (Interaction/emotionality) COMMUNITY (User-generated) @grovesprof Adapting to the new media • What new media fit within your culture? • How do you make it part of the routine? • How do you reward and acknowledge the new behavior? @grovesprof Engaging your audiences Measure your success Thank you! Dr. Jonathan Groves Associate Professor and Chair, Communication Drury University Principal, SGF Media Consulting Twitter: @grovesprof E-mail: jgroves@drury.edu Blog: leannewsroom.com