Ch1-3MF
advertisement

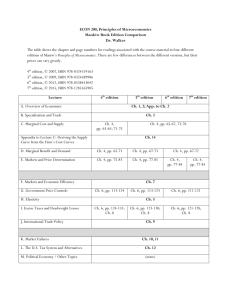
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE Professor Ivar Bredesen Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA What is special about international finance? • • • • Foreign exchange rate risk Political risk Market imperfections Expanded opportunity set Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA Course contents • The course is divided into three parts: – The International Financial Environment – Exchange Rate Behaviour – Exchange Rate Risk Management • Workload – 7.5 ECTS – Examination (80 %) and assignments (20 %) Cost and Management International Accounting: FinancialAn Management, Introduction, 2nd7th edition edition Jeff Colin Madura Drury and Roland Fox ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 ISBN 978-1-4080-3229-9 © 2011©Cengage 2011 Cengage Learning Learning EMEAEMEA Required reading Madura and Fox, 2nd ed. • Good, intermediate level text in international finance Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA We will cover the following chapters: – 1: Multinational Financial Management – 2: International Flow of Funds – 3: International Financial Markets – 4: Exchange rate determination – 5: Currency Derivatives – 7: International arbitrage and interest rate parity Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA We will cover the following chapters: – 8: Inflation, interest rates and exchange rates – 9: Forecasting exchange rates – 10: Measuring exposure to exchange rate fluctuations – 11: Managing transaction exposure – 12: Managing economic exposure and translation exposure • Note that we will cover some chapters in more depth than the textbook. It is therefore important to read the lecture notes also. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Financial Risk Management • The field of financial risk management normally contain the following: – Interest rate risk – Commodity price risk – Equity risk – Currency risk • This course will deal with currency risk • We need to know some finance to assess the instruments used to hedge currency risk and some economics to understand exchange rate behaviour Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Risk – This is risk that foreign currency profits may evaporate in dollar terms due to unanticipated unfavorable exchange rate movements. – Suppose $1 = ¥100 and you buy 10 shares of Toyota at ¥10,000 per share. One year later the investment is worth ten percent more in yen: ¥110,000. – But, if the yen has depreciated to $1 = ¥120, your investment has actually lost money in dollar terms. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA 1-8 Europe’s Sovereign-Debt Crisis of 2010 • In December of 2009 the new Greek government revealed that its budget deficit for the year would be 12.7% of GDP, not the 3.7% forecast. • Investors sold off Greek government bonds and the ratings agencies downgraded them to “junk.” • While Greece represents only 2.5% of euro-zone GDP, the crisis became a Europe-wide debt crisis. • The challenge remains that fiscal indiscipline of one eurozone country can escalate to a Europe-wide crisis. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA 1-9 The Greek Drama • Greece paid no premium above the German rate until late fall 2009. • The Greek interest rate rose until the bailout package on May 9. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA 1-10 Foreign Exchange Markets • The FOREX market provides the physical and institutional structure through which – The money of one country is exchanged for that of another country – The rate of exchange between currencies is determined – Foreign exchange transactions are physically completed • The FOREX market is extremely competitive and highly efficient Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Transactions in the Interbank Market • Transactions within this market can be executed on a spot, forward, or swap basis – A spot transaction requires almost immediate delivery of foreign exchange – A forward transaction requires delivery of foreign exchange at some future date – A swap transaction is the simultaneous exchange of one foreign currency for another Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Outright Forward Transactions • This transaction requires delivery at a future value date of a specified amount of one currency for another • The exchange rate is agreed upon at the time of the transaction, but payment and delivery are delayed • Forward rates are contracts quoted for value dates of one, two, three, six, nine and twelve months – Terminology typically used is buying or selling forward – A contract to deliver dollars for euros in six months is both buying euros forward for dollars and selling dollars forward for euros Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Swap Transactions • A swap transaction in the interbank market is the simultaneous purchase and sale of a given amount of foreign exchange for two different value dates • Both purchase and sale are conducted with the same counterpart • A common type of swap is a spot against forward – The dealer buys a currency in the spot market and simultaneously sells the same amount back to the same bank in the forward market – Since this transaction occurs at the same time and with the same counterpart, the dealer incurs no exchange rate exposure Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Size of the FOREX Market http://www.bis.org/publ/rpfxf10t.pdf • The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) estimates that daily global net turnover in traditional FOREX market activity to be US$4.0 trillion in April 2010, up from 3.2 trillion in 2007 – Spot transactions at $1,490 billion/day, up 48 % – Outright forward transactions at $475 billion/day – Swap transactions at $1,765 billion/day Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Global Foreign Exchange Market Turnover, April 2010 (daily averages, billions of U.S. dollars) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Turnover by instrument Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Turnover by currency Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Top trading centers Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Norway April 2010 (million USD) total, USD, Euro, Yen, GBP, Swiss Francs Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Direct and Indirect Quotes – A direct quote is a home currency price of a unit of a foreign currency • NOK 5/$ is a direct quote in Norway – An indirect quote measures how much foreign currency you can buy for one unit of your own • NOK 0.2/$ is an indirect quote in the Norway, • NOK 0.2/$ is a direct quote in the US and an indirect quote in Norway Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Interbank quotes are given as a bid and ask – The bid is the price at which a dealer will buy another currency and the ask or offer is the price at which a dealer will sell another currency – This is the bid/ask spread. bid/ask % spread = ask rate – bid rate ask rate – Example: ¥118.27 - ¥118.37/$ is the bid/ask for Japanese yen – Bid/Ask spread = (118.37 – 118.27)/118.37 = 0.0845 % Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Forward Quotations can be expressed in several ways – We will generally use the actual forward exchange rate – called an outright quote – Forward quotes are also quoted in terms of points i.e. how much they differ from the spot rate. A point is the last digit of a quotation, with convention dictating the number of digits to the right of the decimal – The difference between spot rates and forward rates can also be expressed as a % per-annum deviation from the spot rate (premium or discount) Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Expressing Forward Quotations on a Points Basis – The yen is quoted only to two decimal points – A forward quotation is not a foreign exchange rate, rather the difference between the spot and forward rates Bid Ask – Example: Outright spot: ¥118.27 Plus points (3 months) Outright forward: ¥116.84 ¥118.37 -1.43 -1.40 ¥116.97 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Forward Quotations in Percentage Terms – For direct quotes (i.e. quote expressed in home currency terms), the formula is Forward - Spot 360 f x x 100 Spot days H If > 0, the foreign currency is said to be trading with a premium, if < 0 the foreign currency is trading with a discount Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Euro spot and forward Jan 14 – 2013 http://markets.ft.com/RESEARCH/markets/DataArchiveFetchReport?Category=CU&Type=ESP&Date=01/14/2013 Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Cross Rates – Many currencies pairs are inactively traded, so their exchange rate is determined through their relationship to a widely traded third currency – Example: A Mexican importer needs Japanese yen to pay for purchases in Tokyo. Both the Mexican peso (MXP) and Japanese yen (¥) are quoted in US dollars • Assume the following quotes: Japanese yen ¥110.73/$ Mexican peso MXP 11.4456/$ Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Foreign Exchange Rates & Quotations • Cross Rates – The Mexican importer can buy one US dollar for 11.4456 Mexican pesos and with that dollar buy ¥110.73; the cross rate would be – 110.73/11.4456 = ¥9.6745/MXP Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA Currency Futures and Options Market • A currency futures contract specifies a standard volume of a particular currency to be exchanged on a specific settlement date. Unlike forward contracts however, futures contracts are sold on exchanges. • Currency options contracts give the right to buy or sell a specific currency at a specific price within a specific period of time. They are sold on exchanges too. Cost and Management Accounting: An Introduction, 7th edition Colin Drury ISBN 978-1-40803-213-9 © 2011 Cengage Learning EMEA