Group 2
advertisement

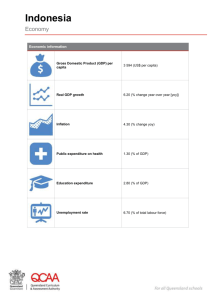
• • • • • • • • • • • • Population – 1.23 Billion / Capital – New Delhi / 29 states Continent - Asia / Region - South Asia / Indian subcontinent Currency – Indian Rupee (INR) GDP – $ 1.8 Trillion GDP (by PPP) - $ 4000 Trillion GDP Growth – 4.7 % GDP Per Capita - $ 1500 GDP By Sector – Agriculture ( 13.7%) / Industry – (21.5%) / Services - 64.8%) Inflation (CPI) – 7.4 % ( WPI being 5.4%) Unemployment – 8% Main Industries Agriculture, Petroleum products, Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals, Software, Textiles, Steel, Transportation Equipment, Machinery, Cement, Mining, Construction Ease of Doing Business – 134th • 1.2 billion people and the world’s fourth-largest economy • After 67 years of independence, the country has witnessed huge agricultural revolution that has transformed the nation from a grain importer into a global agricultural powerhouse that is now a net exporter of food. • Life expectancy has more than doubled, literacy rates have quadrupled. • Will soon have the largest and youngest workforce the world. • In the middle of a massive wave of urbanization as some 10 million people move to towns and cities each year in search of jobs and opportunity which is the largest rural-urban migration of this century. Till the 90’s India depended on West Asia for oil, South Africa for gold, US for technology, South east Asia for vegetable oil etc. To buy these items from the world market, we needed US dollars - the global currency of trade. Since 1960s, India depended on the Soviet Union for exports thereby missing the opportunity to develop good economic relationships with the US and Western Europe. However, when Soviet Union cracked and split into multiple nations, India had a problem as the exports went down significantly. Added to this woe, the 1991 war with Iraq led to destruction of India’s oil imports and the prices shot up substantially. This had a huge effect on Indian economy as India’s primary buyer was gone and on the other hand, our primary sellers were in war. Thus, 1991 was the year of perfect storm, with a domestic political crisis inside and an economic crisis outside. This took India to IMF, where the country pledged its gold reserves in return for an interim loan of $3.9 billion - 67 tons of gold was taken in two aircraft to London & Switzerland. In 1991, Under the New Prime Minister, India started its economic reforms of the 1990s abolishing the oppressive licensing controls on industry and foreign trade, allowed the market to determine the exchange rate, drastically reduced protective customs tariffs, opened up to foreign investment, modernised the stock markets, freed interest rates, strengthened the banking system and began privatisation of public enterprises. The new Govt accepts and understands the challenging situation due to Sub 5% growth + high inflation , continued slow-down in many emerging economies a threat to sustained global recovery. Recovery seen with the growth rate of world economy projected at 3.6 per cent in 2014 vis-à-vis in 2013. The first Union Budget for 2014-15 by the new Govt has various steps announced which are only the beginning of the journey towards a sustained growth of 7-8 per cent within the next 3-4 years along with macro-economic stabilization. Various economic initiatives as well as focused approach towards the Industry, Investment and Infrastructure has also been identified in the recent budget. India is the only large emerging market (EM) that doesn’t follow the route of Inflation Targeting. Other than China, which targets the exchange rate, all large EMs target inflation. Inflation targeting: is an economic policy in which a central bank estimates and makes public a projected, or "target", inflation rate and then attempts to steer actual inflation towards the target through the use of interest rate changes and other monetary tools. This is one of the main reasons why India saw a rise in inflation after the global financial crisis, while other EMs experienced a downward pressure on prices. After 1990, inflation targeting was adopted by 34 countries. The OECD countries were among the first to adopt it and, after 2000, a number of emerging economies such as Brazil, Chile, Colombia, South Africa, Thailand, South Korea, Mexico, Peru, the Philippines, Indonesia, Turkey and many east European countries followed suit. India had registered over 9 per cent growth for a few years before the global financial meltdown of 2008 pulled it down. The economic growth rate slipped to decade's low of 4.5 per cent in 2012-13. It inched up to 4.9 per cent in 2013-14. In the current fiscal the growth rate is expected to touch 5.5 per cent. Unemployment Rate in India decreased to 5.20 % in 2012 from 6.30 % in 2011. Unemployment Rate in India averaged 7.58 % from 1983 until 2012 and reached the all time high of 9.40 % in 2009. As of June’14, it is 8.8% INDIA’S INWARD INVESTMENT SCENARIO FDI INFLOWS 35.8 (US$ bn) 32 27 26.7 22 22.8 24.2 16.4 2.4 4 2.6 2.1 3.7 6 2000-01 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 2005-06 2006-07 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 Rich demographic dividend Huge domestic market • India has a very young population - Over 62% of India’s population is in the age-group of 15-59 years • India 2nd largest populated country India to be fifth largest consumer market by 2025 2005 5% population middle class 2025 41% population middle class Emerging knowledge hub India has third largest technical and scientific manpower pool in the world Prowess in Information technology is well acknowledged DEFENCE Composite cap in manufacturing increased to 49% from 26%, with full Indian management and control through the FIPB route; FDI beyond 49% allowed under approval route on case to case basis INSURANCE Composite cap in insurance sector increased to 49% from current level of 26%, with full Indian management and control through the FIPB route. eBiz CONSTRUCTION Requirement of the minimum built up area and capital conditions for FDI reduced; Projects which commit 30% the total project cost for low cost affordable housing exempted MANUFACTURING Manufacturing units with FDI under the automatic route allowed to sell their products through retail, including e-commerce platforms, without any additional approval. Vision is to transform the business environment by enabling fast and efficient access to G2B services through an online portal. All Central Government Departments and Ministries will integrate their services with eBiz by December 31, 2014 TAIWANESE INVESTMENTS IN INDIA As per fdiMarkets (Financial Times), Taiwanese outward investments third highest in India after China & Vietnam, in terms of number of projects and number of jobs created No of FDI projects 81 Total jobs created 27,129 Average project size (jobs) 334 FDI Projects from Taiwan into India Period – January 2003 – June 2014 Top Sectors Electronics - Communications - Business Machines & Equipment - Electronic Components - Semiconductors Industrial Machinery, Equipment & Tools Software & IT services Transportation Others - Metals - Chemicals - Food & Tobacco - Textiles - Rubber Success Stories - Many Taiwanese brands have become household names in India TAIWANESE INVESTMENTS IN INDIA Destination state Projects companies Total Average Maharashtra 16 12 2,426 151 Tamil Nadu 10 8 12,636 1,263 Karnataka 9 8 838 93 Delhi 8 8 707 88 Gujarat 5 3 2,732 546 Andhra Pradesh 3 3 1,392 464 Haryana 2 2 1,042 521 NCR GUJARAT MAHARASHT RA ANDHRA PRADESH KARNATA KA TAMIL NADU No of Jobs India never invaded any country in her last 100000 years of history. When many cultures were only nomadic forest dwellers over 5000 years ago, Indians established Harappan culture in Sindhu Valley (Indus Valley Civilization) The name 'India' is derived from the River Indus, the valleys around which were the home of the early settlers. Chess was invented in India. Algebra, Trigonometry and Calculus are studies, which originated in India. The 'Place Value System' and the 'Decimal System' were developed in India in 100 B.C. India is the largest democracy in the world, the 7th largest Country in the world, and one of the most ancient civilizations. India has the largest number of Post Offices in the world. The world's first university was established in Takshila in 700 BC. More than 10,500 students from all over the world studied more than 60 subjects. Ayurveda is the earliest school of medicine known to mankind. The Father of Medicine, Charaka, consolidated Ayurveda 2500 years ago. India was one of the richest countries till the time of British rule in the early 17th Century. Christopher Columbus, attracted by India's wealth, had come looking for a sea route to India when he discovered America by mistake. The value of "pi" was first calculated by the Indian Mathematician Budhayana, and he explained the concept of what is known as the Pythagorean Theorem. He discovered this in the 6th century. Until 1896, India was the only source of diamonds in the world India exports software to 90 countries. The Natural Resource Curse The Economic Growth 2010 2011 2012 2013 The Economic Growth of the World 5.1 3.9 3.2 3.5 ASEAN 5 (Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam) 7.0 4.5 5.7 5.5 The Economic Growth of the Indonesia 6.2 6.5 6.3 5.8 18 Factors Fuel subsidy Growing middle class Commodity boom Problems Current account deficit Fiscal deficit Middle income trap Creating value added industries by increasing the share of manufacturing in the GDP Increase the Investment (I) in Y=C+I+G+NX Indonesia is one of the 25 largest 90 exporting countries 80 (UNCTAD, Global Value Chains and 70 Development 2010) 60 developing 82 68 56 52 50 Indonesia’s level of participation in 40 the GVC is 44% lower compared to 30 the other South East Asian countries. As a results, Indonesia as an exporting countries for natural and raw resources has a lower value 44 Singapore Malaysia Philippines Thailand Indonesia 20 10 0 added relative to the other ASEAN-5 countries. Sumber: Global Value Chains and Development 2010 Insufficient Capacity to Innovate, 2% Tax Regulation, 5% Foreign Currency Regulations , 5% Corruption, 14% Crime and Thieft, 4% Poor Public Health , 2% Inadequate Educated Workforce, 4% Inefficient Government Bureaucracy, 15% Government Instability, 5% Tax Rates, 3% Inadequate supply of Infrastructure, 9% Inflation, 6% Restrictive Labor Regulations, 7% Poor Work Ethic in National Labor Force, 7% Access to Financing, 5% Policy Instability, 5% Source: Global Competitiveness Report 2013-2014 New mining law and labor law: wrong signal? Fiscal Decrease the cost of fuel subsidy, increase budget for infrastructure Monetary There is no pressure for Indonesia to raise the interest rate at 7.5%; the inflation are maintained at steady levels on 4.82% in May 2014 Investment expansion in Automotive Industries. By end of June, the country’s foreign exchange reserves have expanded marginally to USD 107.7 billion from USD 107 billion in May 2014. Demographic bonus Total Population based on 2010 census is 237.5 million people. The population in Indonesia is dominated by people in the age of 0 – 19 years old. This condition represents high level of birth - The India-Taipei Association (ITA) has been established in Taipei since 1995 to promote nongovernmental interactions between India and Taiwan. - In 2002, Taiwan and India signed the Bilateral Investment Promotion & Protection Agreement. - In 2003, the Ministry of Economy Affair set India as the 10 major target market. - India was Taiwan’s 16th largest trading partner as of 2013. It was Taiwan’s 14th largest export market and 16th largest supplier of imports. - More than 70 Taiwanese enterprises have invested or set up factories in India, mostly in computer industry and shoes industry. The accumulated amount of investment was more than USD 1.4 billion. - Major Taiwanese exports to India include IT products, machinery and other electronic products. - The top 5 items India exports to Taiwan are oil, iron and steel, organic chemical, cereal and cotton. - Indonesia was Taiwan’s 11th largest trading partner. It was Taiwan’s 13th largest export market and 11th largest supplier of imports. For Indonesia, Taiwan is its third largest trading partner behind Japan and China. - Indonesia enjoyed USD 2 billion trade surplus with Taiwan in 2013. The number is increasing significantly every year from 2003, when the surplus was only USD 1.1 billion. On average, Indonesian trade surplus with Taiwan grew by 37% annually in the last 10 years. - Taiwan's exports to Indonesia are mainly in form of gasoline, diesel, steel, textiles, IT products such as computers and mobile phones. - Indonesian exports to Taiwan are mainly in form of gas, coal, rubber, tin, wood products, electronic equipment and paper industry material. It is also one of Taiwan’s most important supply sources of oil, gas and coal.