Basic Electrical Circuits
advertisement
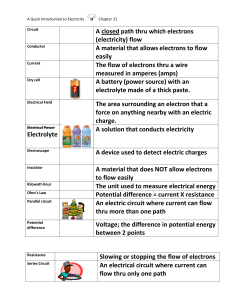
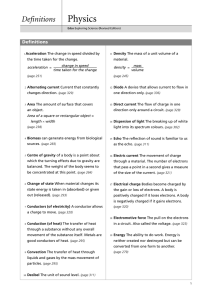
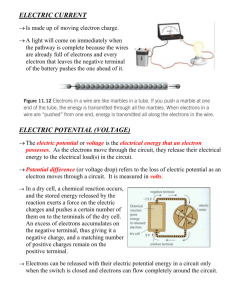
Basic Electrical Circuits Advanced Design Applications Mr. Brooks What is electricity? The movement of electrons through an electrical circuit. Electrons Atom has three parts Proton Neutron Electron Key terms Current: The flow of electrons through a circuit. The amp is the unit of electrical flow. Voltage: The electromotive force that pushes electrons through a circuit. The volt is the unit of electromotive force. Resistance: The opposition to the flow of electrons. The ohm is the unit for the resistance to electrical flow. Where does electricity come from? Three main sources: Occurs naturally Direct current (Batteries) Alternating Current (Generators) Electricity in nature Lightning Solar storms Electric eels Polar auroras Direct Current Direct current is a unidirectional flow of electric current. Electricity flows at a constant, steady rate. Examples of power sources that use AC are: Batteries Solar Cells Alternating Current Alternating Current is a flow of electricity that is not constant. In fact the direction of current flow periodically switches direction. Examples of AC are: Generators Home power outlets Generator A generator uses magnets Magnets to push electrons through a circuit, much like a pump pushes water through a pipe. Breadboard A breadboard is a prototyping device that allows the user to create/experiment with electrical circuits. Resistors We will now construct the “resistor” circuit in our electronics labs and answer the following questions in your notes. What does a resistor do? How does it work? What devices use resistors? Diodes We will do the “diode” circuit in our electronics labs. What is a diode? How does it work? What devices do you think Use diodes? LED We will do the “LED” lab in our electronics lab kits. What is an LED? How does it work? What devices use LEDs? Capacitor We will do the “capacitor” activity in our electronics lab kits. What is a capacitor? How does it work? What are some devices that use capacitors?