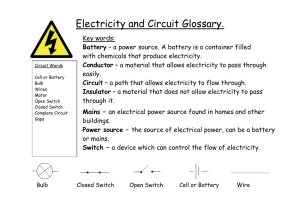
A closed path thru which electrons (electricity) flow A material that
advertisement

A Quick Introduction to Electricity Circuit Conductor Current Dry cell Electrical Field Electrical Power Electrolyte Chapter 21 A closed path thru which electrons (electricity) flow A material that allows electrons to flow easily The flow of electrons thru a wire measured in amperes (amps) A battery (power source) with an electrolyte made of a thick paste. The area surrounding an electron that a force on anything nearby with an electric charge. A solution that conducts electricity Electroscope A device used to detect electric charges Insulator A material that does NOT allow electrons to flow easily The unit used to measure electrical energy Potential difference = current X resistance An electric circuit where current can flow thru more than one path Kilowatt-hour Ohm’s Law Parallel circuit Potential difference Voltage; the difference in potential energy between 2 points Resistance Slowing or stopping the flow of electrons An electrical circuit where current can flow thru only one path Series Circuit A Quick Introduction to Electricity Chapter 21 Static electricity The net build-up of charges on an object; electricity that does NOT flow A battery (power source) whose electrolyte is a liquid Wet cell Circuit Symbols: Switch Ammeter Resistance Voltmeter Load Power Source (battery or outlet)