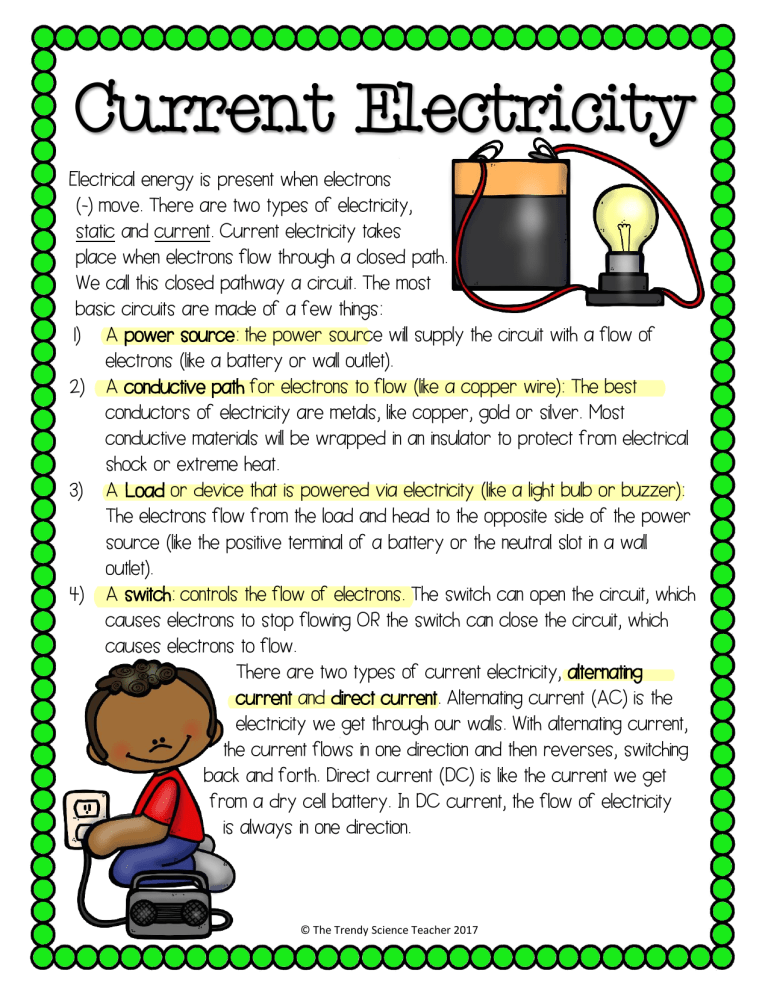
Current Electricity Electrical energy is present when electrons (-) move. There are two types of electricity, static and current. Current electricity takes place when electrons flow through a closed path. We call this closed pathway a circuit. The most basic circuits are made of a few things: 1) A power source: the power source wil supply the circuit with a flow of electrons (like a battery or wall outlet). 2) A conductive path for electrons to flow (like a copper wire): The best conductors of electricity are metals, like copper, gold or silver. Most conductive materials wil be wrapped in an insulator to protect from electrical shock or extreme heat. 3) A Load or device that is powered via electricity (like a light bulb or buzzer): The electrons flow from the load and head to the opposite side of the power source (like the positive terminal of a battery or the neutral slot in a wall outlet). 4) A switch: controls the flow of electrons. The switch can open the circuit, which causes electrons to stop flowing OR the switch can close the circuit, which causes electrons to flow. There are two types of current electricity, alternating current and direct current. Alternating current (AC) is the electricity we get through our walls. With alternating current, the current flows in one direction and then reverses, switching back and forth. Direct current (DC) is like the current we get from a dry cell battery. In DC current, the flow of electricity is always in one direction. © The Trendy Science Teacher 2017 Current Electricity Directions: 1. Read the passage. 2. Use a highlighter to highlight key terms in the passage. 3. Complete the sections below: Vocabulary Review: Write a definition for each term below: Current Electricity: electricity that flows through a closed circut Power Source: supplys flow of electron Conductor: elctrons flow through it Insulator:keeps electrons Load: what is being powerd Switch: breaks or connects a closed circut Alternating Current:a serirs of circuts Direct Current: one circut Reading Comprehension: Answer each question below: a. b. c. d. What components make a power souce load and conductor circuit?_________________________________ What is the difference between a conductor and a conductor moves electron a insulator stops them insulator? _______________________________ How are direct and alternating currents one alternates asnd one is on the same circut different?_______________________________ Predict what might happen to a closed electrical circuit if electricity will cut a switch OPENS the circuit.___________________ © The Trendy Science Teacher 2017