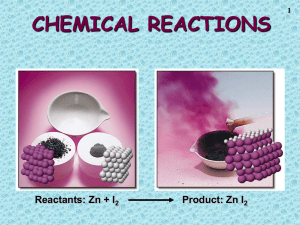
Net Ionic Equations

Equations
Double Replacement
Redox
Single Replacement (another redox)
Composition
Decomposition
Complex Ions
Combustion
Net Ionic Equations
In Chem 1 we wrote molecular equations
In AP Chem we write net ionic equations – equations that omit any spectator ions
To write net ionic equations, we must
KNOW our solubility rules and strong acids/strong bases (MAKE
FLASHCARDS)
Identification of Double
Replacement Reaction
Acid / Base
OH + H + H
NH
3
+ HF NH
2
O
4
+ + F -
Precipitation
Ba 2+ + SO
4
2-
Both
2 H + + SO
4
2-
BaSO
4
+ Ca(OH)
2
CaSO
4
+ 2 HOH
Redox
oxidation and reduction reaction
(oxidation is loss of electrons, reduction is gain of electrons – OIL RIG)
Use of key terms
MnO
4
H
2
O
2
Cr
2
O
7
2HNO
3
Metals with multiple oxidation states
Sn 2+ Sn 4+ Cr 2+ Cr 3+ Cr 6+
Acidic and Basic conditions
4 MnO
4
+ 12 H + + 20 H
2
O
2
4 Mn 2+ + 15 O
2
+ 26 H
(We will deal with this type MUCH later)
2
O
Redox / Single Replacement
Single Replacement
Like will replace like
2 Na + 2 H
2
O 2 Na + + 2 OH + H
2
Cl
2
+ 2 KI 2 K + + 2 Cl + I
2
Combustion
Reaction of a hydrocarbon/alcohol or other organic molecule with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water
C
3
H
8
+ 5 O
2
→ 3 CO
2
+ 4 H
2
O
CH
3
CH
2
OH + 3 O
2
→ 2 CO
2
+ 3 H
2
O
Decomposition/Composition
Decomposition has only one reactant and it breaks up into elements and /or compounds
MgCO
3
Ba(OH)
2
2 Al
2
O
3
MgO + CO
2
BaO + H
2
O
4 Al + 3 O
2
Decomposition / Composition
Composition has two reactants that combine into one product
S
8
+ 8 O
2
8 SO
2 nonmetal oxides plus water makes acids
SO
3
+ H
2
O 2 H + + SO
4
2metal oxides plus water makes bases
CaO + H
2
O Ca(OH)
2
Complex Ions
Particles that generally combine with ammonia and hydroxides to form complex ions with a charge
AgCl + 2 NH
Cu 2+ + 4 NH
3
3
Ag(NH
3
Cu(NH
3
Al 3+ + 4 OH Al(OH)
4
-
)
)
2
+
4
2+
+ Cl having the correct ligand number is not required but being consistent with number and charge is important
In Review
Identify type of reaction from list of 5 types
Equations need to be balanced
Check for appropriate charges
Remember not to include spectator ions
Remember practice questions about each of the 3 balanced net ionic equations