Classification
advertisement

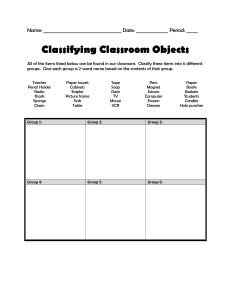
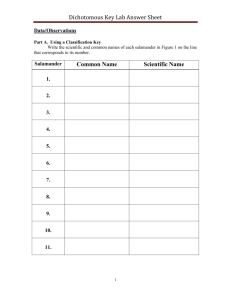
“Grouping together items into categories based on a set criteria” Group Activity -get yourselves into groups of 4 -Brainstorm and list 20 domesticated animals -your job is to group your list of animals into different categories -you MUST: -use more than three categories -be prepared to describe the criteria you used for your groupings “Systematic grouping of organisms into categories on the basis of defined criteria” Taxonomy “the science of classifying ALL organisms” -Very general - millions of species? - how to start classifying? • behaviour • where they live/habitat • appearance and characteristics (MORPHOLOGY) Mosquitoes –50 species Seed plants – 260 000 species Challenges to Classification? - Yesterday? • Variation: o over space and time o among individuals DNA Evolution The biggest classification problem has always been consistency (Coles notes) • Ancient Greece -First to introduce classification and binomial definition - classify ALL LIVING things (Historia Animalium) - blood/no blood, water/land -Hierarchical; each organism fixed position Great Chain of Being Aristotle (384 – 322 BC) • Humans • Animals • Plants Issues? -complex plants below simple animals -little genetic relationship -Evolution? -Virtually no innovation to Aristotle’s work till the 16th century -virtually 2000 years!!! -shamans/Aboriginal healers/Andrea Cesalpino • Irregularity amongst names -needed agreed upon set of naming guidelines -Scientific naming - the father of taxonomy - 2 key contributions to classification: 1. Consistent way of grouping species according to morphological similarities 2. Naming system - 2 parts 1. Genus species; capitalized, italicized 2. species specific species; italicized Gerbera hybrida -standard naming system for all organisms Systema Nature (1735) -simple -convenient -flawed Ursus americanus Share many characteristics Ursus maritimus Share few characteristics Phascolarctus cinereus General/fewer similarities kingdom Animalia phylum Chordata class Mammalia order Primates family Hominidae genus Homo species sapiens Ranks based on shared characteristics -each level = taxon Specific/more - refined into subcategories “structure in which a large set of items is broken down into smaller subset, ultimately leading to the smallest available classification unit.” - series of branching two-part statements used to identify organisms - large set broken down to smallest classification unit - larger number of species, the more specific questions become Difficulties? • number of species • distinguishing characteristics are internal • agreeing on criteria Dichotomous Key practice Page 18 Textbook Activity Get into groups of 4-6 Within your group you will be creating your own dichotomous key The subject of your key will be classifying each member of your group Remember dichotomous keys “are a series of branching two-part statements used to identify organisms.” Therefore your keys need to contain multiple steps and be specific When, finished, you must demonstrate the viability of your key to Mr. Faulhafer for assessment Complete questions 5 and 8 on page 20 of textbook





![[Type text] Taxonomy and Classification Notes Taxonomy: the study](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006833839_1-e22256a74f9158844d75d24ddb12e551-300x300.png)