Forecasting the weather
advertisement

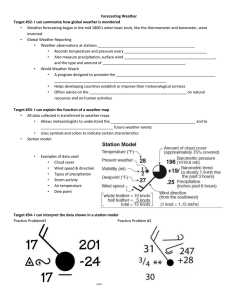
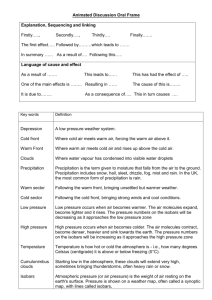
Explain how weather stations communicate weather data. Explain how a weather map is created. Explain how computer models help meteorologists forecast the weather List three types of weather that meteorologist have attempted to control. At any given point in time, meteorologists are sharing data from barometers, anemometers, and thermometers. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) sponsors a program called World Weather Watch to promote the rapid exchange of weather information. This organization helps developing countries establish or improve their meteorological services. The data that scientists collect is then placed into a weather map. A station model is a pattern of meteorological symbols that represents the weather at a particular observing station that is recorded on a weather map. Scientists use lines on weather maps to connect point of equal measurements. Lines that connect points of equal temperature are called isotherms. Lines that connect points of equal atmospheric pressure are called isobars. Closely spaces isobars indicate a rapid change in pressure and high wind speeds. Widely spaced isobars generally indicate a gradual change in pressure and low wind speeds. Isobars that form circles indicate centers of high or low air pressure. Centers that are marked with an H represent high pressure. Centers that are marked with an L represent low pressure. Fronts are identified by sharp changes in wind speed, direction, temperature, and humidity. Areas of precipitation are commonly marked with colors or symbols. Different forms of precipitation are marked with colors and symbols depending on how hard it is raining or snowing. Doppler Radar and satellite images supply most of the information. Temperature, wind direction, wind speed, cloudiness, and precipitation can usually be forecast accurately. But it is oftentimes difficult to predict precisely the time when precipitation will occur or the exact amount. This is why they compare models and data in order to predict what is happening. Meteorologists make four types of forecasts. Nowcasts mainly use radar and enable forecasters to focus on timing precipitation and tracking severe weather. Daily forecasts predict weather conditions for a 48-h period. Extended forecasts can be made for 0-5 days. However, accuracy decreases with each day. One main goal of meteorology is to reduce the amount of destruction caused by severe weather by predicting severe weather early. When meteorologist forecast severe weather, they issue warnings and watches. A watch is issued when the conditions are ideal for severe weather. A warning is given when severe weather has been spotted (thunderstorm or tornado) or is expected within 24-h (snowstorm or hurricane). Cloud seeding is when the clouds are made to rain. In this process, particles are added to the clouds that cause the clouds to precipitate. Hurricanes have also been seeded with freezing nuclei in an effort to reduce their intensity. Seeding a potential lightning storm with silver-iodide nuclei has seemed to modify the occurrence of lightning.