Forecasting Weather
advertisement

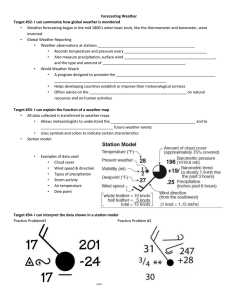
• Weather forecasting began in the mid 1800’s when basic tools, like the thermometer and barometer, were invented • Global Weather Reporting • Weather observations at stations around the world • Records temperature and pressure every few hours • Also measure precipitation, surface wind direction and speed, and the type and amount of cloud cover. • World Weather Watch • A program designed to promote the rapid exchange of weather information • Helps developing countries establish or improve their meteorological services • Offers advice on the effect of weather on natural resources and on human activities • All data collected is transferred to weather maps • Allows meteorologists to understand the current weather and to predict future weather events • Uses symbols and colors to indicate certain characteristics • Station model: a pattern of meteorological symbols that represents the weather at a particular observing station and that is recorded on a weather map • Examples of data used • • • • • • Cloud cover Wind speed & direction Types of precipitation Storm activity Air temperature Dew point • Scientists use lines on weather maps to connect points of equal measurement. • Lines that connect points of equal temperature are called isotherms • Lines that connect points of equal atmospheric pressure are called isobars • The spacing and shape of the isobars help meteorologists interpret their observations about the speed and direction of wind • Closely spaced bars indicate a rapid change in pressure and high wind speeds • Widely spaced isobars generally indicate a gradual change in pressure and low wind speeds • Isobars that form circles indicate centers of high or low air pressure • Marked with an H (high) or an L (low) • Weather maps are used to illustrate many different features • Isobars • Highs and lows in pressure • Fronts • Warm, cold, occluded, stationary • Conditions • Precipitation • Direction of air flow