Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
advertisement

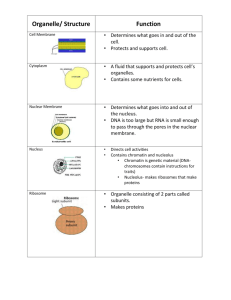
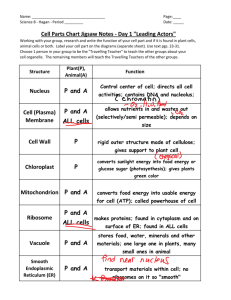
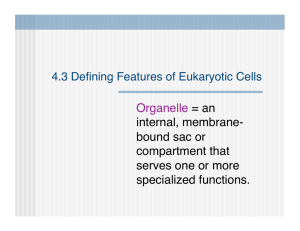
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall 1. Found in plants, fungi, algae, nearly all prokaryotes 2. Animals do not have cell walls 3. Allows water, O2, and CO2 to pass through 4. **Provides support and protection for the cell 5. Made of cellulose—a tough carbohydrate fiber 6. (Principle component of wood and paper) B. Cell Membrane 1. Thin, flexible layer that surrounds the cytoplasm 2. Composed mainly of phospholipids 3. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell in order to maintain homeostasis Magnification of Cell Membrane Nucleus C. Nucleus 1. Controls most cell processes and contains the hereditary information (DNA) 2. Found in almost all Eukaryotic cells 3. Contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA • Chromatin—Unwound form of DNA • Chromosomes—Condensed form of DNA D. Chromatin and Chromosomes 1. DNA bound to protein 2. Chromatin is the Stringy material seen in Nucleus 3. The chromatin Condense to form Chromosomes when cell divides Chromatin and Chromosomes E. Nucleolus 1. Dense region in nucleus where ribosomes are made Nucleolus F. Nuclear Envelope 1. Double membrane that surrounds nucleus 2. Contains thousands of Nuclear Pores— allow material to move in and out Nuclear Envelope 1. The Nuclear Envelope is a double membrane that contains pores so that substances can move in and out of the nucleus. G. Cytoskeleton 1. Network of protein filaments that help the cell maintain its shape 2. Aid in movement of organelles Cytoskeleton G. Cytoskeleton 3. Two types of fibers: a. Microtubules—hollow tubes of proteins • Help maintain shape • Act as track for movement of organelle • Form Centrioles –important when cell divides (separate chromosomes) • Bundles of Microtubules form cilia and flagella (movement) b. Microfilaments—movement and support of cell (long thin fibers) Organelles in Cytoplasm H. Ribosomes 1. Make proteins in the cell 2. Made of RNA and Protein 3. Make proteins specific to the instructions given by DNA 4. Some Ribosomes are attached to the Endoplasmic reticulum and some are free floating in the Cytoplasm. I. Endoplasmic Reticulm 1. Internal membrane system 2. Smooth ER is where components (parts) of cell membrane are assembled 3. Rough ER is where proteins are modified Rough ER J. Rough ER 1. Modifies Proteins—has Ribosomes attached • proteins made and then shipped into ER for modification Rough ER K. Smooth ER 1. Synthesize Lipids • Makes parts of cell membrane Golgi Apparatus L. Golgi Apparatus 1. Proteins move from ER to Golgi 2. Enzymes attach Carbohydrates and Lipids to the protein in the Golgi 3. Proteins are packaged and sent to their destination M. Lysosomes 1. Small packages filled with enzymes 2. Break down lipids, carbohydrates, proteins (food) to be used by cell 3.Break down old organelles 4. Remove debris N. Vacuoles 1. Saclike structure that stores water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates 2. Plant cells—single, large, central, fluid— turgor pressure a. Small Vacuoles are called Vesicles • used for transporting substances in the cell Vacuole Chloroplast O. Chloroplasts 1. Found in plants and other organisms— not in animal or fungal cells 2. Has double membrane 3. **Where photosynthesis occurs 4. Contain green pigment called chlorophyll 5. Have stacks of photosynthetic membranes Chloroplast Mitochondria P. Mitochondria 1. Release energy from stored food molecules 2. Use food to form ATP (Molecule that is used as energy in cell) 3. Enclosed by two membranes (inner folds and outer) Chemical reactions 4. Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells Mitochondria Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell Make a Venn Diagram to compare and contrast plant and animal cells: Plant cell Animal cell Both Number your paper from 1-11. Structure 1. 2. 3. 4. . . . . Function 1. 2. 3. 4. . . . . 7. 8. 9. 10. 6 . 11. 5. 1. 2. 4. 3. The Cell is Like a Protein Factory Write a paragraph that describes how proteins are made in the cell. Use the following words in your paragraph: Nucleus Ribosome Rough ER Golgi Apparatus Vesicles