Supply PowerPoint
advertisement

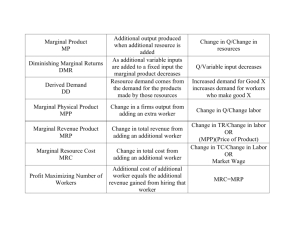
Need new tires $400 Need work done on car’s transmission $1,000 Speeding ticket less than 15 mph over limit $200 Speeding ticket more than 15 mph over limit $350 Ticket for running a red light $200 Car accident $500 Car accident $500 Car accident $500 Root canal needed $300 You need glasses $100 You find $10 You broke your leg $1,000 You have a sinus infection $150 You have pneumonia $350 Your irresponsible brother is broke and needs $400 to pay his bills Need new brakes $200 You need knee surgery $2,000 You are a bridesmaid in a wedding $600 ($250 airfare, $100 hotel, $200 dress, $50 wedding gift) Need new tires $400 Speeding ticket less than 15 mph over limit $200 Speeding ticket less than 15 mph over limit $200 Speeding ticket less than 15 mph over limit $200 DEFINITION: The willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale. Law of Supply: Suppliers will normally offer more for sale at high prices and less for sale at lower prices. As price decreases, quantity supplied decreases: P Qs As prices increase, quantity supplied increases: PQs Price and quantity supplied have a direct relationship Why will suppliers normally offer more for sale at high prices and less for sale at lower prices? Correct Answer: They can increase their profits if they supply more when the price is higher Shows how much of a good or service an individual producer is willing and able to offer for sale at each price in a market. The Smiths’ Tomato Supply Schedule Price per Pound ($) Quantity Supplied (in pounds) 2.00 50 1.75 40 1.50 34 1.25 30 1.00 24 .75 20 .50 10 Shows how much of a good or service an individual is willing and able to offer for sale at each price Shows how much of a good or service all producers in a market are willing and able to offer for sale at each price. Price per Pound ($) Quantity Supplied (in pounds) 2.00 350 1.75 300 1.50 250 1.25 200 1.00 150 .75 100 .50 50 Shows the data from the market supply schedule An ________ supply schedule and graph shows how much Ms. Smith would be willing to sell her tomatoes at each and every price A _________ supply schedule and graph shows how much all tomato producers would be willing to sell their tomatoes at each and every price Janine owns a small factory that produces custom blue jeans Three sewing machines Three workers- 12 pairs/day How will hiring one more worker affect production? ◦ Change in total product that results from hiring one more worker is called the marginal product # of workers Pairs of Jeans made New Employee’s Marginal Product 3 worker 12 pairs/day 4 workers 19 pairs/day 7 pairs of jeans 5 workers 29 pairs/day 10 pairs of jeans How did marginal product increase? ◦ Work on sewing machines PLUS cut cloth, package jeans, clean shop ◦ Fourth employee helped with other tasks and first three employees could spend more time sewing ◦ Fifth employee allowed labor to be divided even more efficiently ◦ Each worker focused on a particular facet of production (specialization) # of Workers Total Product Marginal Product 0 0 0 1 3 3 2 7 4 3 12 5 4 19 7 5 29 10 6 42 13 7 53 11 8 61 8 9 66 5 10 67 1 11 65 -2 With up to six employees, Janine’s operation experiences increasing returns (each new worker adds more to total input than the last) With between seven and ten employees, Janine’s operation experiences diminishing returns (each new worker causes total output to grow but at a decreasing rate. With eleven employees, total output actually decreases (employees become crowded and operations become disorganized) Fixed costs- expenses that the owners must pay for whether they produce nothing, a little, or a lot ◦ Examples: Janine’s mortgage on her factory, insurance, and utility bills Variable costs- business costs that vary as the level of production output changes. ◦ Examples: wages, fabric, thread, zippers, buttons, shipping costs Total cost- add fixed and variable costs together Marginal cost- the additional cost of producing one more unit of a product Linda owns a candle shop. Linda can make 10 candles a day with 2 workers. When she hires a 3rd worker, she can make 16 candles a day. Regardless of how many candles she makes, Linda always spends a monthly amount of $1000 on rent for her shop, $200 on insurance, and $100 on utilities. She also spends an average of $5 on wax, scents, and wage costs per candle. 1. What is the marginal product of hiring a 3rd worker? 6 Candles 2. What are her monthly fixed costs? $1300 ($1000 rent+$200 insurance+$100 utilities) 3. What are her variable costs if she makes 300 candles a month? $1500 ($5 for wax, scents, and wage x 300 candles) 4. What are her monthly total costs? $2700 ( $1300 fixed costs+ $1500 variable costs) 5. What is the marginal cost of producing a 301st candle? $5, additional cost of one extra candle A change in quantity Price supplied doesn’t shift the supply curve. The change refers to movement along the curve itself. Supply of Bracelets Occurs because of a change in… PRICE!!!!!! • As you move to the right along the curve, the quantity supplied increases. • As you move to the left along the curve, the quantity supplied decreases. Quantity Supplied 1. When the price is $0.75 you supply 20 bracelets. What is the Price new quantity supplied when the price is $1.75? 40 bracelets Supply of Bracelets 2. What caused this change in quantity supplied? Price Quantity Supplied Change in supply occurs when something prompts producers to offer different amounts of sale at every price. ◦ ◦ When production costs increase, supply decreases When production costs decrease, supply increases. 1. Input costs- the price of the resources needed to produce a good or service example: nutrition bars that contain peanuts, price of peanuts increases, cost to make nutrition bars increases 2. Labor productivity- the amount of G/S a person can produce in a given time example: better-trained and more-skilled workers can produce more goods in less time 3. Technology- the application of scientific methods and discoveries to the production process, resulting in new products or manufacturing techniques. example: personal computer enables workers to be more productive 4. Government action- taxes, subsides, or regulations can affect production example: excise tax- on alcohol and tobacco, things whose consumption the government is interested in discouraging 5. Producer expectations- expectations of price changes can affect the quantity producers are willing to supply example: a gas station expects the price of gas to be higher in the future, he or she may save some gas to sell later, thereby decreasing supply 6. Number of producers- More producers= reduction in supply. Less producers= increase in supply Example: Mike’s doughnut shop is the only doughnut shop in town. He supplies 1,000 doughnuts a day. If 2 other doughnut shops open, the increased competition might cause Mike to only supply 500 doughnuts a day. 1. A TV factory fires a bunch of 4. Ms. Frey has a business selling workers because they are cookies. She does so well, having financial problems Bilbrey, Gilchrist and Westerfeld start their own cookie making Labor Productivity (Supply business. Decrease) Number of Producers (Supply Decrease) 2. It is the week before Valentine’s Day. Candy producers anticipate 5. In order to discourage the sale that they will receive a higher of fireworks, the government price for their goods, which leads creates an excise tax on the them to change the amount of product candy they supply that week Government Action (Supply Producer Expectations Decrease) (Supply Increase) 3. The price of rubber increases, which affects the production at a local bike shop Input costs (Supply Decrease) 6. A marketing firm gets the latest and best computers for their employees Technology (Supply Increase) Which curve demonstrates the change in supply if you produce t-shirts and your company got new, more efficient sewing machines? A. B. c. D. Which curve demonstrates what would happen to supply if you produced t-shirts and Target decided to put your shirts on sale? (Target decreases the price of your product) A. B. c. D. Which curve demonstrates the change in supply if you produce t-shirts and the price of cotton increased? A. B. c. D. Demand Supply Do on your own