Chapter 5 SUPPLY fill in blank
advertisement

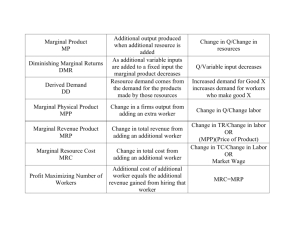
SUPPLY What is Supply? • _________________________ the quantities that would be offered for sale and all possible prices that could prevail in the market. • • • • The Law of Supply _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ If prices are high, suppliers will offer greater quantities for sale. If prices are low, suppliers will offer smaller quantities for sale. A change in ______________ will cause the Demand curve to shift. A change in quantity demanded will move____________________. Supply Curve • Individual Curve – Illustrates how the _______________ that a producer makes varies depending on the________ that will prevail in the market • Market Curve – Illustrates the ________________________ that all producers will offer in the market for any given ______________________ • Economist analyze supply – by listing quantities and prices in a _______________________ – Forms supply curve with and ____________________________ Change in Quantity Supplied • Quantity supplied: – The amount that producers _________ market at any given price • Change in Quantity Supplied; – The change in the amount offered for sale in response to a change in price • Illustrates a change in quantity supplied – Shows as a movement _________________________________ – Can increase or decrease amount of the product (movement from a to b) Change in Supply • Situation where suppliers offer different amounts of products for sale at all possible prices • Cost of inputs • ___________________________ • Technology • Number of sellers • ___________________________ • Expectations • Government Regulations • • • • Elasticity of Supply ______________________________: a measure of the way in which a quantity supplied responds to a change in price Elastic – Small increase in price leads to a larger increase in output— supply Inelastic – ________________________________________________ __________________ – A change in price causes a proportional change in supply Determinants of Supply Elasticity • How quickly a producer can act when a change in price occurs: – Adjust quickly =_________________ – Complex/advance planning = ______________________ • Factor of Substitution: – Easy =____________________ – Difficult = _________________ Chapter 5 section 1 Vocabulary A. Supply B. Quantity supplied C. Supply curve D. Supply elasticity E. Subsidy 1. Amount that producers bring to the market at any given price 2. Measure of the way in which quantity supplied responds to a change in price 3. A graph showing the various quantities supplied at each and every price that might prevail in the market 4. The amount of a product that would be offered for sale at all possible prices that could prevail in the market 5. A government payment to an individual, business, or other group to encourage or protect a certain type of economic activity The Theory of Production The Law of Variable Proportions • Short Run: – ________________________ will change as one variable input is altered, but other inputs are kept constant – i.e.: salting a meal (amount of input –salt- varies; so does the output – quality of the meal) • _____________________________ is affected – How is the output of the final product ___________________ as more units of one variable input or resources are added to a fixed amount of other resources? – i.e.: farmer may have all the land, machines, workers, and other items needed to produce a crop, but may have questions about the use of fertilizers , The Production Function • Concept that describes the relationship between changes in output to different amounts of a single input while others are constant • • • The Law of Variable Proportions Possible to vary all the inputs at the _______________________________ – Economist prefer only__________________ variable be changed at a time – b/c more than one = harder to gauge the impact of a single variable The Production Function Total product is the total _______________________the company produces – Total Product Rises • As more workers are added, total product rises until a point that adding more workers causes a _____________________________________ – Total product Slows • As more workers are added output continues to rise = it does so at a slower rate until it ________________________________________ – More workers “get in the way” The Production Function _______________________________ is the extra output or change in total product caused by adding one more unit of variable output – i.e.: worker 1’s output is 7; worker 2’s output is 13 together their output is 20 (figure 5.5) Three Stages of Production • Stage I: __________________________________ – Marginal output increases with each new worker – Companies are tempted to hire more workers (moves them to stage II) • Stage II: __________________________________ – Total production keeps growing but the rate of increase is smaller – Each worker is still making a positive contribution to total output (but diminishing) • Stage III: _________________________________ – Marginal product becomes negative – Decreasing total plant output A. B. C. D. E. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chapter 5 section 2 Vocabulary Law of variable Proportions Production function Raw materials Marginal product Total product Concept that describes the relationship between changes in output to different amounts of a single input while other inputs are held constant Total output produced by a firm The extra output or change in total product caused by the addition of one more unit of variable output Unprocessed natural products used in production States that in the short run, output will change as one input is varied while the others are held constant Cost, Revenue and Profit Maximization What kinds of cost do you have to consider? • _____________________________ – the cost that a business incurs even if the plant idle and output is zero. – Salaries – Rent – Property Taxes – _____________________________ – cost that does change when the business rate of operation or output changes – Electric power – Shipping charges • _______________________________ – Sum of the fixed and variable costs • __________________________ – Extra cost incurred when a business produces one additional unity of a product. • • • • Applying Cost Principles ______________________________ – Gas station is an example of high fixed cost with low variable cost – Ration of variable to fixed cost is low _____________________________ – An industry with low fixed cost Measure of Revenue Total revenue = – ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________ = – The extra revenue connected with producing and selling an additional unit Marginal Analysis • _____________________________________comparing the extra benefits to the extra cost of a particular decision • Break-even point is the _________________________ or total product the business needs to sell in order to cover its __________________________ • Businesses want – # of workers and level of output that generates max. profits – _________________________________: quantity of output is reached when marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal Chapter 5 Section 3 Vocabulary A. B. C. D. E. Fixed cost Variable cost Marginal cost Total revenue E-commerce 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cost that a business incurs even if the plant is idle and output is zero Extra cost incurred when a business produces one additional unit of product Cost that changes when the business rate of operation or output changes Electronic business or exchange conducted over the internet The number of units sold multiplies by the average price per unit