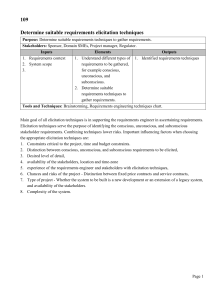
Expert Opinion Elicitation
advertisement

Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation Robert C. Patev North Atlantic Division – Regional Technical Specialist (978) 318-8394 “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Subjective Estimation • Elicitation Process – Background – Expert-Opinion Elicitation (EOE) Process • Probability – Axioms of Probability – Medians and Percentiles • Training Example “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Subjective Estimation • Uses of one or more experts to estimate a probability (qualitative or quantitative) for use in engineering risk analysis – Good for first estimate of probabilities – Quick, cost effective and efficient method – Problems: • • • • • Not a formal elicitation Usually not well documented Probabilities may not be repeatable or defendable Probabilities may be highly subjective and biased Probabilities have larger uncertainties compared to structured elicitation values “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Subjective Estimation • How good are we at quantifying subjective estimates? • Let us see….. “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Subjective Estimation • How good are we at quantifying subjective estimates? – Class Example: • How may ships passed through the Panama Canal last year? – Give best estimate “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Background – Process developed by RAND Corporation in late 1950’s - early 1960’s • Delphi Method • Scenario Analysis – Effects of thermonuclear war – Civil Defense strategic planning • Examine if U.S. population could survive a nuclear attack “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Background – Definition – A formal (protocol), heuristic (through discussion) process of obtaining information or answers to specific questions called issues • e.g., failure rates or probabilities, and failure consequences “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Background – EOE is used for preliminary risk evaluation (screening) is not really intended to replace more complex reliability models – EOE has been used by industry and government agencies to develop failure probabilities when there is a lack of failure information “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Drawbacks – Subjective process • Not consensus building • Inherently contains bias and dominance – Difficult to process result to determine reliability or hazard rates • Assumptions need to be made • Current Usage in USACE – Supplement to other models • Calculate reliability (not for critical components) • Event tree probabilities • Used in consultation with HQUSACE “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • EOE Process – Participants • Experts • Observers • Listeners • Technical Integrator and Facilitator • Peer Reviewers – ITR process and results “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • EOE Process – Identification and Selection of Experts • Strong relevant expertise • Familiarity and knowledge with issues • Willingness to act as impartial evaluators • Willingness to participate, prepare, and provide needed input • Strong communication skills, interpersonal skills, and ability to generalize “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • EOE Process – Inform experts of issues • “Read ahead” materials • Site visits – Train experts – Elicitation • First opinion • Discussion among experts • Second opinion “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Probability – General expressions • Percent (1% probability of failure) • Fraction (1/100) • Relative frequency (1 out of 1000) – Axioms of Probability • 0 < Pf < 1 • Sum of probabilities over all possible outcomes must equal 1. – This assume events are independent. “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Statistics – Median • e.g., Median income, median age • Rank value • For odd n, value with rank of (n+1)/2 • For even n, average of value with rank n/2 or (n/2) + 1 • Used to limit extreme values – Average • Sum of Xi divided by sample size “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Median Vs. Average • Sample 1 – – – – – 100 100 200 300 400 • Median = 200 • Average = 220 • Sample 2 – – – – – 100 100 200 300 2000 • Median = 200 • Average = 540 “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Percentiles – A p-percentile value (Xp) based on a sample is the value of the parameter such that p% of the data is less than or equal to Xp • e.g., The median is the 50th percentile “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Chickamauga Lock and Dam Chickamauga Lock and Dam Expert Elicitation Issue #4 - River Wall Blocks Event Name Full Description of Issue First Response Question #1a: Unconstrained flow of water through the river wall adversely effecting the ability to dewater the lock and/or filling/emptying operation Expert-opinion elicitation Given the failure mode identified for the river wall without any advanced maintenance (fix-asfails scenario), what is the probability of that failure by the year 2005? Expert #1 Expert #2 Expert #3 Expert #4 Expert #5 Expert #6 Minimum = Median = Maximum = Median = 0.10% 0.0% 0.0% 0.1% 0.1% 0.1% 1.0% 0.01% 0.10% 1.00% “ Building Strong “ Summary Table Second Response Median = 0.0% 0.0% 0.1% 0.1% 0.1% 1.0% 0.01% 0.10% 1.00% 0.1% Minimum = 0.01% 25 Percentile = 0.03% Median = 0.10% 75 Percentile = 0.10% 90 Percentile = 0.55% High = 1.00% Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Chickamauga Lock and Dam Chickamauga Lock and Dam Expert Elicitation Issue #4 - River Wall Filling/Emptying Cracking Event Name Full Description of Issue First Response Question #1d: Unconstrained flow of water through the river wall adversely effecting the ability to dewater the lock and/or filling/emptying operation Expert-opinion elicitation Given the failure mode identified for the River Wall Blocks without any advanced maintenance (fixas-fails scenario), what is the probability of that failure by the year 2050? Expert #1 Expert #2 Expert #3 Expert #4 Expert #5 Expert #6 Minimum = Median = Maximum = Median = 30.00% 30.0% 20.0% 40.0% 30.0% 50.0% 30.0% 20.00% 30.00% 50.00% “ Building Strong “ Summary Table Second Response Median = 30.0% 25.0% 40.0% 30.0% 40.0% 30.0% 25.00% 30.00% 40.00% 30.0% Minimum = 25.00% 25 Percentile = 30.00% Median = 30.00% 75 Percentile = 37.50% 90 Percentile = 40.00% High = 40.00% Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Chickamauga Lock and Dam Chickamauga Lock and Dam Expert Elicitation Issue #4 - River Wall Blocks Event Name Full Description of Issue Expert-opinion elicitation First Response Question #3a: Unconstrained flow of water through the river wall adversely effecting the ability to dewater the lock and/or filling/emptying operation Given the fix-as-fails probability of failure for the river wall filling/emptying system, what is the probability that the chamber closure time would be 30 days for less? Between 31 and 89 days? 90 days or greater? NOTE: All three branches must add up to a total of 1. Expert #1 Expert #2 Expert #3 Expert #4 Expert #5 Expert #6 Summary Table Second Response Minimum 25 Percentile Median 75 Percentile Maximum = = = = = < 30 days 31-89 days 90 day + < 30 days 31-89 days 90 day + 99.0% 80.0% 95.0% 95.0% 90.0% 85.0% 1.0% 15.0% 5.0% 5.0% 8.0% 10.0% 0.0% 5.0% 0.0% 0.0% 2.0% 5.0% 99.0% 80.0% 95.0% 95.0% 90.0% 85.0% 1.0% 15.0% 5.0% 5.0% 8.0% 10.0% 0.0% 5.0% 0.0% 0.0% 2.0% 5.0% 80.00% 86.25% 92.50% 95.00% 99.00% 1.00% 5.00% 6.50% 9.50% 15.00% 0.00% 0.00% 1.00% 4.25% 5.00% 80.00% 86.25% 92.50% 95.00% 99.00% 1.00% 5.00% 6.50% 9.50% 15.00% 0.00% 0.00% 1.00% 4.25% 5.00% “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Chickamauga Lock and Dam Cumulative Probabality of Failure (curve-fit) 1.000 Probabality 0.800 0.600 Cumulative 0.400 0.200 0.000 2000 2010 2020 2030 2040 2050 2060 2070 Year “ Building Strong “ Delivering Integrated, Sustainable, Water Resources Solutions Expert-Opinion Elicitation • Class Example – Six experts required – Unknown issue given to experts • Define assumptions of issue • Elicit first values • First results • Expert Discussion • Elicit second values • Show final elicitation results “ Building Strong “