Language Assessment
advertisement

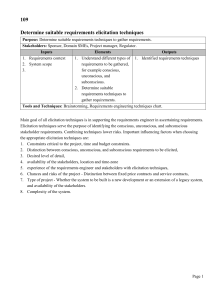
Language Assessment EUROPEAN SCALES OF LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY BASIC CONCEPTS IN ASSESSMENT ASSESSING ORAL PERFORMANCE Global Scale Basic User Independent User Proficient User A1, A2 B1, B2 C1, C2 (Common European framework of reference for languages. Learning, teaching, assessment.) Assessment Informal Formal Formative (over time) Summative (outcomes at the end of instruction) How to Test Speaking? What is a speaking task? …activities that involve speakers in using language for the purpose of achieving a particular goal or objective in a particular speaking situation. (Bachman and Palmer as cited in Sari Luoma Assesing speaking. p. 31) Types of classroom speaking performance: Imitative (like a tape recorder) Intensive (rhymes, learners ‘go over’ certain forms of the language) Responsive (short replies to teacher-or student-initiated questions or comments.) Transactional (dialog to convey or exchange specific information) Interpersonal Dialog to maintain social relationships Extensive (planned or impromptu monologues) (Based on H.D. Brown Teaching by Principles pp.271274) Steps in designing classroom assessment procedures: Specify the category of speaking performance. Consider the micro- and macroskills that you are going to assess. Think of the genre of spoken language. Some suggestions for consideration: Imitative speaking tasks Repeating the sentences Intensive Learning a rhyme S1-Whole class (What did you do on holiday?) Completing a dialogue Acting out a dialogue Reading aloud (for checking pronunciation) Picture-cued elicitation of a grammatical item Some suggestions: Responsive Question elicitation (ask me about my favourite film) Picture-cued elicitation of response (Q-A) Map-cued elicitation Question and answers Some suggestions: Interactive tasks Role plays Interviews Debates Extensive Retelling a text Describing a picture Describing one’s favourite film, ….. What to evaluate in a speaking task? Accuracy in phonology, vocabulary and grammar. Fluency and discourse (cohesion, sociolinguistic appropriateness). Accomplishing the objective of the task. Suggested reading: Brown, H. D. (2007). Teaching by principles: An interactive approach to language pedagogy. Longman: New York. Common European framework of reference for languages. Learning, teaching, assessment. (2001). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Harmer, J. (2007). The practice of English language teaching. Fourth edition. Harlow: Longman. Luoma, S.( 2004). Assessing speaking. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Weir, C. J. (1990). Communicative language testing. Prentice Hall International