HEP Program Results 2008-2009
advertisement

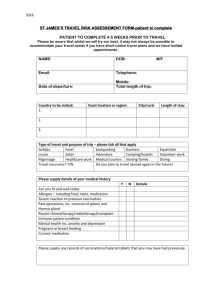
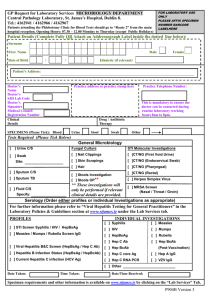
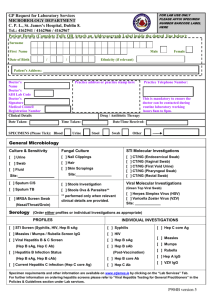
High School Equivalent Program (HEP) Results for 2008-2009 US Department of Education Office of Migrant Education OME Conference Philadelphia, PA November 15-19, 2010 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 1 Outline of Presentation Introduction Solutions to Previous Years’ Challenges Assumptions and Limitations Research Assumptions Research Limitations Presentation of HEP Data “Top 10 Programs” for GPRA 1 & 2 Results Summary and Conclusions Next Steps July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 2 Introduction: “Why are we here?” Share HEP 2009 APR program results 2009 “snapshot” data, using national HEP data 2009 comparison data, using data from groups of HEP projects 2006-2009 longitudinal data, using national HEP data Recognize high performing projects After our session, share ideas for program improvement July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 3 Top Reporting Issues from 2006-2008 Course Completers: The APR requires accurate information regarding students that complete the coursework but do not pass the GED and do not reenroll. Data Quality Checks: The APR requires use of data quality checks, in order to ensure a level of accuracy within the report. Over-Served: When HEP projects served more students than they were funded, the GPRA 1 for projects could exceed 100%. Persisters: When HEP projects reported large numbers of persisters, the GPRA 1 for projects could exceed 100%, or go below 0% . July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 4 Solutions to Known Reporting Issues Grantees carefully reviewed definitions and entered data within EMAPS for electronic Annual Performance Report (APR) with builtin “hints” for data quality checks. Office of Migrant Education adjusted GPRA 1 formula… July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 5 Adjusted GPRA Measure 1 Formula Option A: For grantees who actually serve LESS than the number funded to be served or serve exactly the total number funded to be served: GPRA Measure 1= total no. of HEP GED attainers [total no. funded to be served minus total no. of persisters] July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 6 Adjusted GPRA Measure 1 Formula Option B: For grantees who actually serve MORE than the number funded to be served: GPRA Measure 1= total no. of HEP GED attainers [total no. actually served minus total no. of persisters] July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 7 Research Assumptions and Limitations Assumptions: Accurate data is entered by grantees on APR. 100% fidelity to implementation of program objectives and corresponding services. Limitations: The total number of HEP programs in this analysis is statistically small (42), and a more effective analysis will necessarily involve student-level data. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 8 Presentation of National HEP Data July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 9 Performance: Effective and Efficient Overall performance on National GPRA Overall performance on efficiency measures Additional HEP research questions and results July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 10 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Target Not Met The percentage of HEP program exiters receiving a General Educational Development (GED) diploma. National Goal = 69% of students attain a GED 2008-2009 National Performance = 61% Performance results reflect, for the first time, accurate data and a “baseline” for the future. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 11 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met GPRA 1 Measure Y N 19 Grantees 23 Grantees 45% of all grantees 55% of all grantees Let’s review the following slides, in order to explain these data... July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 12 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met GPRA 1 Formula, Option A. For grantees who actually serve LESS than the number funded to be served or serve exactly the total number funded to be served: Total no. of HEP GED attainers 1,900 [Total no. funded to be served minus Total no. of persisters] (3,111-202) 1,900 2,909 July 20-22 2010 = 65% HEP 2009 Results 13 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met GPRA 1 Formula, Option B. For grantees who actually serve MORE than the number funded to be served: Total no. of HEP GED attainers [Total no. actually served Total no. of persisters] 1,540 2,657 July 20-22 2010 1,540 (3,383-726) = 58% HEP 2009 Results 14 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met GPRA 1 Formula. No. of students funded in =/under-served HEP projects = 3,111 (48% of total students) No. of students served in over-served HEP projects = 3,383 (52% of total students) Total = 3,111 + 3,383 students, = 6,494 students July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 15 National GPRA Measure 1 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met National GPRA 1 Formula. 65% (Met GPRA 1 through Option A) * .48 (weighted value) = 31.20% 58% (Met GPRA 1 through Option B) * .52 (weighted value) = 30.16% 31.20% (Served/Under-Served) + 30.16% (Over-served) 61.36%, or 61%. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 16 National GPRA Measure 1 Data Stratified GPRA 1 Chart 10 9 9 8 No. of Grantees = 42 8 7 7 7 6 6 5 4 3 2 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 17 National GPRA Measure 2 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met The percentage of HEP GED recipients who enter postsecondary education programs, upgraded employment, or the military. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 18 National GPRA Measure 2 Data (Effectiveness): National Goal Not Met National Goal = 80%, Performance = 74% 2,532 GED students placed 3,440 GED student attainers GPRA Measure 2: Met/ Not Met Y N July 20-22 2010 17 25 40.5% 59.5% HEP 2009 Results 19 National GPRA Measure 2 Data Stratified GPRA2 Chart 20 18 Total Grantees=42 16 14 11 12 9 10 8 6 6 3 4 2 0 1 4 4 2 2 0 0-9% July 20-22 2010 10-19% 20-29% 30-39% 40-49% 50-59% HEP 2009 Results 60-69% 70-79% 80-89% 90-100% 20 HEP: How effective when compared to a comparable national program? About one-third of adult education program clients stay long enough to advance to the next level of instruction. Unit costs vary by type of service component. Average costs per client-hour in ESL were a relatively low $4.28, compared to $6.11 for all ABE clients and $5.12 for those in ASE. Few local programs maintain client-specific records. As a result, the accuracy of program data reported by States is of concern. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 21 Efficiency Measure: Cost per GED (Reported in PART) Project efficiency ratios are calculated as, per budget period, the total budget awarded for that budget period divided by the number of GED Attainers. Total HEP Budget = Total No. GED Attainers July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results Cost per GED 22 Efficiency Measure: Cost per GED (Reported in PART) No national targets yet. Total HEP funding awarded Total No. GED Attainers students $18,912,210 = 3,440 HEP efficiency measure (Cost per GED): $5,498 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 23 Efficiency Measure: Cost per GED (Reported in PART) Cost Per GED HEP Efficiency Measure $10,000 $9,000 $8,000 $7,000 $6,000 $5,000 $4,000 $3,000 $2,000 $1,000 $0 $4,961 $4,830 2005-2006 2006-2007 $5,359 $5,498 2007-2008 2008-2009 Year July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 24 Cost per GED Attainer Placed (Not Reported in PART) Cost per GED Attainer Placed is calculated as, per budget period, the total budget awarded for that budget period divided by the number of GED Attainers who enter postsecondary education programs, upgraded employment, or the military. Total HEP Budget = Total No. GED Attainers Placed July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results Cost per GED Attainer Placed 25 Cost per GED Attainer Placed (Not Reported in PART) No national targets yet Total HEP funding awarded Total No. GED Attainers Placed $18,912,210 = 2,532 students Average Cost per GED Attainer placed: $7,469 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 26 Cost per GED Attainer Placed (not reported in PART) Cost Per Student Served Cost per GED Attainer Placed $10,000 $9,000 $8,000 $7,000 $6,000 $5,000 $4,000 $3,000 $2,000 $1,000 $0 $6,076 2005-2006 $7,461 $7,469 2007-2008 2008-2009 $6,464 2006-2007 Year July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 27 Number Funded vs. Number Actually Served: Grantees Over-served by 16% Total number funded to be served, per applications: 5,465 Total number actually served: 6,354 116% students served, compared to funded (a reduction of 8% from 2007-2008) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 28 Number Funded vs. Number Actually Served: Grantees Over-served by 16% Total number funded to be served, per applications: 5,465 Total number actually served: 6,354 116% students served, compared to funded (a reduction of 8% from 2007-2008) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 29 Number Funded and Number Actually Served 8000 7016 7000 6354 6000 5665 5465 5000 2007-2008 4000 2008-2009 3000 2000 1000 0 No. Funded July 20-22 2010 No. Served HEP 2009 Results 30 Number Funded, Number Actually Served, and GED Attainers HEP Number Funded/Served and GED Attainers/Placed 8000 7406 Number of Students 7000 6000 7016 6389 6311 5665 5000 4000 6354 6350 3721 3469 3457 5465 3440 3000 2000 3038 Number Funded Number Served GED Attainers Number Placed 2846 2483 2532 2007-2008 2008-2009 1000 0 2005-2006 July 20-22 2010 2006-2007 HEP 2009 Results 31 Is there a relationship between GPRA 1 results and costs? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 32 Is there a relationship between GPRA 1 results and costs? HEP Correlations CostPerGED Cost Per GED Pearson Correlation GPRA1 1 Sig. (2-tailed) .000 N GPRA1 -.626** Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) 42 42 -.626** 1 .000 N 42 42 **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). Correlation is significantly (p<0.01) negative. As higher percentages of students attain a GED, the costs of funding the GED decline. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 33 Office of Migrant Education Research Questions What service models have the most positive outcomes for GPRA 1 and GPRA 2, and are the most efficient? Commuter vs. Residential Open vs. Structured Small vs. Large What do we know about… Students requiring remediation The relationship between instructional hours and GPRA results The relationship between the percentage of English Learners (ELs) and GPRA results The relationship between screening scores and GED attainment Other baseline data July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 34 Commuter v. Residential v. Combination 42 Total HEP Programs Commuter: 25 Programs Residential: 3 Programs Combination of Commuter/Residential: 14 Programs July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 35 Commuter/Residential/Combination (GPRA 1) •ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) compares the means of the three populations: • Commuter projects • Residential projects •Combination projects. •Do we see anything significant to the .05 level? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 36 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA 1) HEP ANOVA GPRA1: Commuter-Residential-Combination Between Groups Sum of Squares 2884.755 df Mean Square 2 1442.378 Within Groups 18979.721 39 Total 21864.476 41 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results F 2.964 Sig. .063 486.660 37 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA1) HEP Report HEP GPRA1 Commuter-Residential-Combination 1.00 - Commuter Mean 66.0800 N 25 Std. Deviation 25.01653 2.00 - Residential 33.6667 3 1.52753 12.00 - Combination 65.3571 14 17.44268 Total 63.5238 42 23.09285 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 38 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA1) When we review the means (averages) of the three groups •Group 1 = Commuter •Group 2= Residential •Group 3 = Combination What can we tell about the GED attainment rates for these groups of students? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 39 Commuter/Residential/Combination (GPRA 2) HEP ANOVA GPRA2: Commuter-Residential-Combination Between Groups Sum of Squares 1790.184 df Mean Square 2 895.092 Within Groups 20698.221 39 Total 22488.405 41 F 1.687 Sig. .198 530.724 •Do we see anything significant to the .05 level? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 40 Commuter/Residential/Combination (GPRA 2) HEP Report GPRA2 Commuter-ResidentialCombination 1.00 - Commuter Mean 64.0800 N 25 Std. Deviation 25.66437 2.00 - Residential 84.3333 3 1.52753 12.00 - Combination 74.8571 14 19.38619 Total 69.1190 42 23.42003 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 41 Commuter/Residential/Combination (GPRA 2) When we review the means (averages) of the three groups •Group 1 = Commuter •Group 2= Residential • Group 3 = Combination •What can we tell about the placement rates for these groups of students? •Last year: •Commuter: Low (67%) •Combination: High (71%) •Residential: Mid (NA – “N”of 1) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 42 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA 1) Efficiency GED Cost Efficiency $20,000 $18,261 $15,000 $10,000 $7,118 $5,000 $5,498 $4,497 $0 Commuters July 20-22 2010 Residential Combination HEP 2009 Results Average 43 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA 1) Efficiency Commuter-Residential-Combination Efficiency $20,000 $17,886 $18,261 $15,000 Commuters $10,000 Residential $7,229 $7,118 $4,527 $4,497 GED Cost 2008 GED Cost 2009 Combination $5,000 $0 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 44 Commuter /Residential/Combination (GPRA 1) Efficiency Commuters: From $4,527 to $4,497 (Efficiency increased. Costs decreased by $30.) Residential: From $17,886 to $18,621 (Efficiency decreased. Costs increased by $735.) Combination: From $7,229 to $7,118 (Efficiency increased. Costs decreased by $111.) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 45 Open v. Structured 44 Total HEP Programs Open Enrollment: 30 Programs Structured Enrollment: 12 Programs July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 46 Open v. Structured (GPRA 1) Open-Structured Enrollment and GPRA 1 Levene's Test for Equality of Variances F GPRA1 Equal variances assumed Sig. 1.566 Equal variances not assumed July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results .218 t-test for Equality of Means Sig. (2-tailed) 40 .997 t .004 df .005 26.612 .996 47 Open v. Structured (GPRA 1) Group Statistics GPRA1 Open-Structured Enrollment 1.00 2.00 30 Mean 63.5333 Std. Deviation 24.86062 Std. Error Mean 4.53891 12 63.5000 18.92809 5.46407 N Anything significant to the .05 level? Any conclusions we can make? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 48 Open v. Structured (GPRA 2) Independent Samples Test Open-Structured Enrollment GPRA2 Equal variances assumed Equal variances not assumed July 20-22 2010 Levene's Test for Equality of Variances t-test for Equality of Means F Sig. t 3.991 .053 -1.318 -1.565 df 40 30.510 HEP 2009 Results Sig. (2Mean Std. Error tailed) Difference Difference .195 -10.45000 7.92850 .128 -10.45000 6.67814 49 Open v. Structured (GPRA 2) Group Statistics GPRA2 Open-Structured Enrollment 1.00 2.00 N 30 12 Std. Std. Error Deviation Mean Mean 66.1333 25.23508 4.60727 76.5833 16.74655 4.83431 Anything significant to the .05 level? Any conclusions we can make? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 50 Large v. Small 42 Total HEP Programs Large Programs: 15 Programs (enrollment >=125 students funded) Small Programs: 27 Programs (enrollment <125 students funded) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 51 Large v. Small (GPRA 1) Independent Samples Test Large – Small Grantee Levene's Test for Equality of Variances F GPRA1 Equal variances assumed .013 Sig. .909 Equal variances not assumed July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results t-test for Equality of Means t .472 Sig. (2-tailed) df 40 .640 .465 27.901 .645 52 Large v. Small (GPRA 1) Group Statistics GPRA1 Large – Small Grantee 1.00 2.00 N 15 27 Mean Std. Deviation 65.8000 24.02439 62.2593 22.92394 Std. Error Mean 6.20307 4.41171 Anything significant to the .05 level? Any conclusions we can make? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 53 Large v. Small (GPRA 2) Independent Samples Test Large-Small Levene's Test for Equality of Variances F GPRA2 Equal variances assumed .539 Equal variances not assumed July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results Sig. .467 t-test for Equality of Means t -.487 df 40 Sig. (2tailed) .629 -.463 25.000 .647 54 Large v. Small (GPRA 2) Group Statistics GPRA2 Large-Small 1.00 2.00 N 15 27 Mean Std. Deviation 66.7333 26.32887 70.4444 22.05820 Std. Error Mean 6.79809 4.24510 Anything significant to the .05 level? Any conclusions we can make? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 55 Instructional Hours: Do they make a difference in a student obtaining a GED, and being placed? Overall program - Correlation The coefficient of determination (R-squared) informs us as to how much of GED attainment and placement is explained by the independent variables (“1” explains a positive relationship, “0” is no relationship, “-1” explains a negative relationship). July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 56 Instructional Hours: Are they related to student GED attainment (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 57 Instructional Hours: Are they related to student GED attainment (GPRA 1)? Correlations GPRA1 GPRA1 Pearson Correlation 1 Avg. Instructional Hours .226 Sig. (2-tailed) .150 N Avg. Instructional Hours Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) 42 42 .226 1 .150 N 42 42 Overall, a slightly positive relationship between GED attainment and more hours of instruction. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 58 Instructional Hours: Are they related to the placement of GED attainers (GPRA 2)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 59 Instructional Hours: Are they related to the placement of GED attainers (GPRA 2)? Correlations Avg. Instructional Hours GPRA2 Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N Avg. Instructional Hours 1 GPRA2 .154 .330 42 .154 .330 42 1 42 42 Slightly positive relationship does exist between total student hours of instruction and GED placement. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 60 English Learners (ELs) What is the status of English Learners? HEP Projects English Language Needs 17 HEP Projects: English Language Needs 25 HEP Projects: No Reported Language Needs July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 61 English Learners (ELs) What is the status of English Learners? HEP Projects: English Learners 1,363 21% 4,991 79% July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results Reported English Proficient/No Data Reported English Learners 62 English Learners (ELs) What is the status of English Learners? Number of HEP Projects with Reported ELs 6 8 ELL 0-24%: GPRA 1 69% ELL 25-49%: GPRA 1 58% ELL 50-74%: GPRA 1 82% ELL 75-100%: GPRA 1 60% 1 2 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 63 English Learners (ELs) What is the status of English Learners? Seventeen out of a total of 42 HEP projects report that some HEP students have English language needs. A total of 1,363 HEP students have been identified as having English language needs. This number represents 21% of the total HEP population. A breakdown of CAMP projects by EL percentage follows: 0-24% ELs: 6 projects, 69% average GPRA 1 25-49% ELs: 1 project, 58% average GPRA 1 50-74% ELs: 2 projects, 82% average GPRA 1 75%-100% ELs: 8 projects, 60% average GPRA 1 What does this information tell us? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 64 Is there a correlation between the percentage of English Learners (ELs) and program effectiveness (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 65 Is there a correlation between the percentage of English Learners (ELs) and program effectiveness (GPRA 1)? Correlations ELLGPRA1 ELLGPRA1 ELLPct ELLPct -.145 .579 Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) 1 N Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) 17 -.145 .579 17 1 17 17 N A slightly negative relationship does exist between the percentage of English Learners and GED attainment. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 66 Is there a correlation between the percentage of English Learners (ELs) and placement of GED attainers (GPRA 2)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 67 Is there a correlation between the percentage of English Learners (ELs) and placement of GED attainers (GPRA 2)? Correlations ELLPct ELLPct Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N ELLGPRA2 Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). ELLGPRA2 1 -.509* .037 17 17 * -.509 1 .037 17 17 Moderately negative relationship does exist between percent ELs and GED placement. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 68 Math Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 69 Math Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 70 Math Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? Correlations GPRA1 MathScreening English Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N MathScreening English GPRA1 1 .215 .262 42 29 .215 1 .262 29 29 Slightly positive relationship does exist between higher Math screening levels and GED attainment. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 71 Math Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? Correlations GPRA1 GPRA1 Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N Pearson Correlation MathScreening Spanish Sig. (2-tailed) N **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). 1 42 .514** .007 26 MathScreening Spanish .514** .007 26 1 26 Moderately positive relationship does exist between higher Math screening levels and GED attainment. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 72 Reading Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 73 Reading Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 74 Reading Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? Correlations GPRA1 ReadingScreening English Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-tailed) N ReadingScreening English GPRA1 1 .272 .146 42 30 .272 1 .146 30 30 Slightly positive relationship does exist between higher reading screening scores and GED attainment. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 75 Reading Screening: Does a higher average screening score correlate with GED attainment (GPRA 1)? Correlations GPRA1 GPRA1 Pearson Correlation ReadingScreening Spanish 1 .364 Sig. (2-tailed) .062 N ReadingScreening Spanish 42 27 Pearson Correlation .364 1 Sig. (2-tailed) .062 N 27 27 Moderately positive relationship does exist between higher reading screening scores and GED attainment. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 76 What are other characteristics of HEP Projects? HEP Students (N=6,354) 3,316 >25 Yrs. 3,038 <=25 Yrs. 3,676 Female 2,678 Male 0 July 20-22 2010 1,000 2,000 3,000 HEP 2009 Results 4,000 77 What are other characteristics of HEP Projects? HEP Students (N=6,354) 52 Educational Impairments 831 Commute 20+miles 706 Moved 1+ times 0 July 20-22 2010 200 400 HEP 2009 Results 600 800 1,000 78 What are other characteristics of HEP Projects? Time to Completion for GED Attainers (N=3,440) 75 No. of GED attainers in >2 yrs. 315 No. of GED attainers in 1+ yr. <2 yrs. 3,050 No. of GED attainers in 1 yr. 0 July 20-22 2010 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 3,000 3,500 HEP 2009 Results 79 INTRODUCING… Top 10 Programs for GPRA 1 & GPRA 2 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 80 Top 10 Programs for GPRA 1 & GPRA 2 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 81 Top 10 Projects for GPRA 1 Highest performing HEP grantees for GED attainers. Four grantees are new to this list for 2008-2009, and are denoted by an asterisk (*). Five grantees have placed on both lists, and they are underlined in dark blue. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 82 Top 10 Performing Programs for GPRA 1 El Paso Community College (99%)* Treasure Valley Community College (95%)* Heritage University (94%) Somerset Community College (94%) Crowder College (93%)* University of South Florida (92%) Wake Technical Community College (91%) Chemeketa Community College (90%) Kansas State University (88%)* Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College (76%) tie University of Colorado at Boulder (76%) July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 83 Top 10 Projects for GPRA 2 Highest performing HEP Grantees for GED attainers that are placed. MUST have met the GPRA 1 national target of 69%. Seven grantees are new to this list for 2008-2009, and are denoted by an asterisk (*). Five grantees have placed on both lists, and they are underlined in dark blue. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 84 Top 10 Performing Programs for GPRA 2 Chemeketa Community College (100%) Northern New Mexico Community College (100%)* University of Colorado at Boulder (97%) Fort Scott Community College (89%)* Wake Technical Community College (88%) Central Washington University (81%)* Kansas State University (81%)* Heritage University (79)* Texas State Technical College at Harlingen (79%)* University of Oregon (74%)* July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 85 Efficient and Effective Met both GPRA 1 and GPRA 2 targets, and efficiency measure (cost per GED) was below the average, $5,498. University of Colorado: $1,274 Wake Technical Community College: $3,523 Chemeketa Community College: $3,534 Central Washington University: $4,226* Northern New Mexico Community College: $5,143* July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 86 Summary: What are program costs? Year No. Funded HEP Funding Cost Per GED 2005-2006 6,389 $18,459,591 $4,961 2006-2007 6,311 $18,397,791 $5,303 2007-2008 5,665 $18,526,796 $5,359 2008-2009 5,465 $18,912,210 $5,498 July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 87 Summary: What are the results (GPRA 1)? HEP GPRA 1 Results: 2008-2009 841, 13% 1,097, 17% GED Attainers Persisters 3,440, 55% Withdrawals Course Completers 928, 15% July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 88 Summary: What are the results (GPRA 2)? HEP GPRA 2 Results: 2008-2009 44, 2% 907, 36% Post-Secondary or Training 1,581, 62% July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results Upgraded Employment Military 89 Summary: Conclusions What we know: GPRA 1 NOT met, 61% with a national target of 69%. GPRA 2 NOT met, 74% with a national target of 80%. Percentage of students served in HEP is 116%. Program costs are rising slightly, per student funded/served. Students in projects that over-serve, in general, are not as successful in GED attainment as those that serve less than or equal to the number funded. Pure residential projects significantly underperform combination and commuter projects. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 90 Summary: Conclusions What we know: GPRA 1 results of projects with open enrollment and structured enrollment do not differ. Structured projects tend to place more students. There are no differences between GPRA 1 results for large and small projects. There is a slightly positive relationship between the number of hours a project provides to students, as they seek a GED. Twenty-one percent of HEP students are reported as English Learners, and projects with a higher percentage of ELs tend to place less students. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 91 Summary: Conclusions What we know: There is slightly positive relationship between higher scores in Math and Reading screening assessments, and GED attainment and subsequent placement. The majority of HEP students are 25 years of age and older, female, and 15% of HEP students commute more than 20 miles, one-way, to classes. July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 92 Summary What we don’t know: The level to which grantees’ practices affect GPRA 1 and GPRA 2 results Next Steps: Pilot Student-Level Data July 20-22 2010 HEP 2009 Results 93 OME Mission The mission of the Office of Migrant Education is to provide Excellent leadership, Technical Assistance, and Financial Support …to improve the educational opportunities and academic success of migrant children, youth, and agricultural workers and fishers, and their families. July 20-22 2010 THANK YOU for your hard work and improving the lives of 6,354 HEP students! HEP 2009 Results 94