Allusion - Mulvane School District USD 263
advertisement

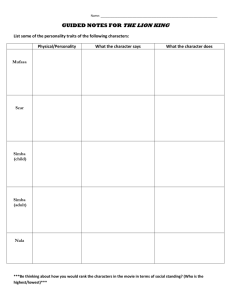
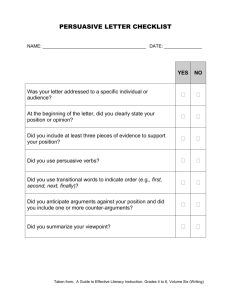
Allusion A reference to another work Example: When Anne Bradstreet refers to the Bible, it is an allusion. Analogy A comparison between two unlike things Example: They fight like cats and dogs. Appeals to emotion Persuasive arguments that rely on emotional responses Example: I was ripped away from my crying sister. Appeals to reason Persuasive arguments that rely on intellect and reason Example: There is no way to avoid this war. Bandwagon approach Persuasive technique that indicates most or all agree Example: Everyone joins the Rowdie Crowd. Bias Persuasive technique that uses people’s pre-conceived notions. Example: Showing a picture of a football player to sell a weightlifting machine because everyone thinks football players are strong. Citing Authority Persuasive technique that references expert testimony. Example: “Nine out of ten dentists recommend chewing Trident.” Flashback Interruption of the current action to tell what happened earlier. Example: Forrest Gump thinking and talking about his life growing up. Foreshadowing Clues about what will happen. Example: Mufasa tells Simba that he will one day be king. Glittering Generalities Persuasive technique that uses a general circumstance to encompass all possibilities. Example: “Graduating from high school is a million dollar decision.” Hyperbole Extreme exaggeration. Example: When kids say they will “NEVER” speak to each other EVER again. Idiom When words do not mean what they literally say. Example: Eating a “hot dog” does not mean consuming a canine that is overheated. Imagery Use of sensory words to appeal to the senses. Example: The flowers emanated the colors of the rainbow and the scent of heaven. Fact Something that can be proven to be true or false. Example: It is 75 degrees Fahrenheit outside. Opinion Something that cannot be proven and relies on impression. Example: Summer gets too hot. Propaganda Systematic promotion of ideas or doctrine. Example: When it is time to vote, people send out propaganda to support their issue or candidate. Irony When something happens or is said that is opposite of what is expected or meant. Example: Dying by choking on a “Lifesaver.” Metaphor A comparison not using “like” or “as.” Example: “Your eyes are shooting stars.” = Mood The emotional atmosphere of a literary work. Example: If a story has lightning flash and a storm rage outside, a gloomy or ominous mood is created. Onomatopoeia Words that sound like the verb they name. Example: BUZZ!!! Overstatement An exaggeration for effect. Example: I have told you a million times! Paradox A statement that seems selfcontradictory but is still true. Example: To live is to die. Personification Giving non-human objects human characteristics. Example: The dog’s eyes danced with excitement. Point-of-view Narrator’s involvement in the story. Example: The Lion King is told primarily from the point of view of Simba. Satire Writing that ridicules a person or institution to bring about change. Example: Romeo and Juliet satirizes young love and parents’ attempts to stop it. Simile A comparison using “like” or “as.” Example: “You are as pretty as a picture.” Statistics Persuasive technique that uses data to support the argument. Example: Score have risen 20% over the last year. Symbolism Use of a concrete object to represent an abstract idea. Example: The elephant skull in The Lion King is a symbol of danger and death. Testimonials Persuasive technique that uses recommendation from people who have experience with the issue. Example: “Proactive worked for me!” Tone Author’s attitude towards the subject. Example: The tone of Finding Nem0 suggests that we should not find “disabilities” “disabling.” Round Character A multi-faceted character with many traits who seems “real.” Example: In Finding Nemo, Marlin seems like a real father. Flat Character A character with only one or two traits who represents stereotype Example: In Finding Nemo, Darla is a fishkiller. Static Character A character who does not change despite the action in the plot Example: In Finding Nemo, Bruce the shark does not change. Dynamic Character A character who undergoes change as a result of the plot Example: Marlin learns that just because Nemo has a little fin, doesn’t mean he can’t be like all the other fish. Protagonist The main character in the story Example: All of the action revolves around Simba in The Lion King. Conflict The problem between the protagonist and the antagonist Example: Since Scar wants to kill Simba, there is a conflict between them. Climax The emotional highpoint (tensest moment) in the story Example: When we don’t know if Nemo has died in the net with the salmon, it is the climax. Rising Action The worsening of the conflict to the climax Example: When Scar meets with the hyena to create a conspiracy to kill Simba and take over Pride Rock, it is rising action. Falling action Events that occur to bring the climax to a resolution Example: When Nemo is found alive at the bottom of the net, but we don’t know how Marlin will react it is falling action. Subplots Miniature plots within the main action Example: Simba and Nala’s romance is a subplot in The Lion King. Parallel Episodes Events that happen simultaneously in the plot Example: While Marlin is looking for Nemo, Nemo is trying to escape from the aquarium. Antagonist The character or force working against the protagonist Example: Scar, the antagonist, is trying to create a conspiracy against Simba, the protagonist. Resolution The outcome of the conflict Example: Nemo is safe, and Marlin allows him to be a normal little fish, despite his little fin.