Plants
advertisement
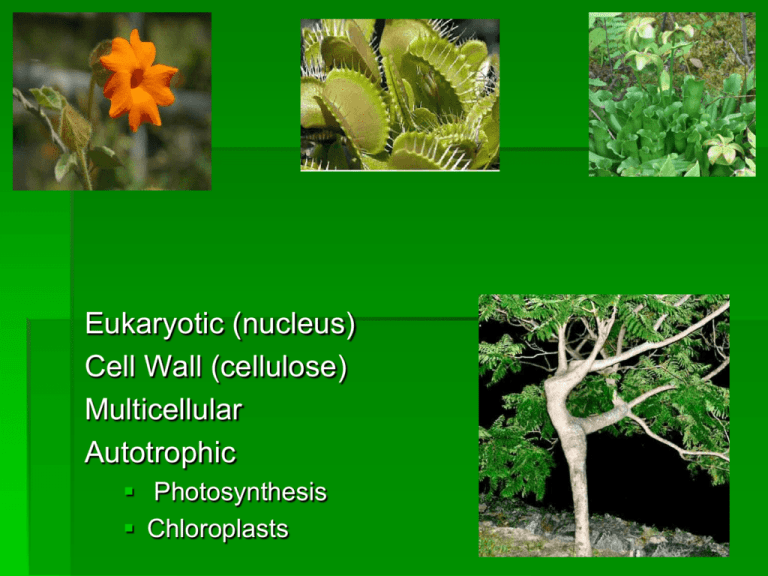
Eukaryotic (nucleus) Cell Wall (cellulose) Multicellular Autotrophic Photosynthesis Chloroplasts Plants Nonvascular Vascular Angiosperms Monocots Dicots Gymnosperms NONVASCULAR PLANTS Early Plants have no vessels, no roots, no stems or leaves. Examples: Mosses & Liverworts VASCULAR PLANTS Modern Plants have vessels to transport food and water. They have roots, stems and leaves. Most reproduce by seeds. Example: Grass, corn, trees, flowers, bushes GYMNOSPERMS "naked seeds" cone bearing (seeds grow on cones) needle like leaves usually stay green year round wind pollinated Examples: pine trees & evergreens ANGIOSPERMS flowering plants Seeds enclosed in a fruit most pollinated by birds & bees have finite growing seasons Examples: grasses, tulips, oaks, dandelions Divided into two main groups: Monocots & Dicots Ex. Lilies, onions, & corn Ex. Trees & ornamental flowers Parts of the Plant Foldable Instructions Fold a WHITE piece of paper in half On the cover draw a flower (include flower, stem, leaves, and roots) After drawing the flower, cut the drawing in 3 sections (flaps) one for the flower one for the stem and leaves and one for the roots Then under each flap you will be writing the corresponding information for each part. Flower Reproductive organ of the plant Flowers are usually both male and female PETAL: Leaf like flower organs, usually brightly colored. STAMEN: Male reproductive organ of a flower consisting of an anther and a filament. ANTHER: Pollen producing structure located at the tip of a flower’s stamen. PISTIL: Female reproductive organ of a flower DRAW IN INB, LEFT SIDE. Stems – complete on foldable Organ that provides support and growth; transport water through xylem and nutrients through phloem; organ from which leaves grow, can serve as storage. Two types of stems: herbacious and woody Xylem: vascular plant tissue made up of tubular cells that transport water and dissolve minerals from roots to the rest of the plant Phloem: Vascular plant tissue made up of tubular cells joined end to end; transport sugars to all parts of the plant. Leaves – complete on foldable Photosynthetic organ of the plant, used to convert sunlight into food Photosynthesis Equation: Parts Stomata: pores that let CO2 in and O2 out. Cuticle: waxy layer on upper surface that protects against water loss. Veins: transports water, nutrients and food. Made of xylem and phloem. Cuticle Veins Stomata Functions of Roots 1. 2. 3. 4. Anchor & support in the ground Absorb water & minerals Hold soil in place Two types: taproots fibrous roots Taproot Fibrous Roots Flower Structure Quiz Pistil Stamen Sepals Petal Anther 9. 10. Ovary Stigma Style Filament Stem 2 and 3 is known as the _______ 7 and 8 is known as the _____







