ANTHROPOLOGY
advertisement

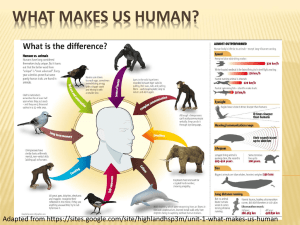
~ PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY ~ Examines the evolution of humankind over the last few million years and compares the genetic characteristics of humans with other biologically similar animals Paleoanthropology Primatology Human Variation PALEOANTHROPOLOGY: “BONES AND STONES” Study of human ancestors, known as hominins, based on evidence from the past Most evidence is the form of fossils (preserved remains of biological matter): * skeletal remains *ancient tools Famous Paleoanthropologists: *animal bones Donald Johanson Louis and Mary Leakey Raymond Dart 1974 “Lucy” discovered in Ethiopia Part of Australopithecs afarensis –member of human family that walked 3.2 million years ago Complete handout “Paleoanthropologists” using pp. 38-43 of the textbook PRIMATOLOGY Study the anatomy and behaviours of living primates (Primatologists are not always anthropologists – may be trained in biology or zoology but research is always relevant to anthropology) Study primates by observing them in both their natural habitats and in laboratories Famous primatologists: Jane Goodall (Chimpanzees in Tanzania) Dian Fossey (Gorillas in Rwanda) Birute Galdikas (Orangutans in Borneo) PRIMATES AND HUMANS Genetic make up of primates and human beings varies by only 1-2% Because humans and primates share physical and social characteristics, physical anthropologists look to primates for clues to the evolution of humans and their behaviour SIGNIFICANT SHARED FEATURES Opposable thumbs 3D/binocular vision (judgment of distance) Highly developed brain with large capacity to learn & think Children remain dependent for long periods of time and require a lot of care in order to learn and develop into independent adults Social, depends on group for survival Capacity for aggression and defense of territory DISTINCTIVE HUMAN FEATURES Bipedalism Complex system of morality and spirituality that influence and motivate behaviour Ability to communicate complex & abstract ideas through language Teach the young Develop and share ideas Pass ideas to the next generations Some anthropologists believe that it is the human capacity for language that separates humans from all other species HOW DID WE BECOME HUMAN? - the development of our complex brain resulting from a combination of: - development and use of tools and hunting in groups - development and use of language More likely..... - social skills required to get along in groups resulted in more complex brain functioning - learning to share ACTIVITY: OPPOSABLE THUMBS • Get into groups of two • Take a copy of the instructions • Each member needs a copy of the worksheet to complete • Do all activities with thumbs free • Repeat all activities with thumbs taped down HUMAN VARIATION Study of genetic differences between people and populations to understand differences between people how and why human beings are different understand differences from evolutionary perspective Why are we different? (Charles Darwin and Natural Selection) 1. Variation 2. Heritability (traits passed to offspring) 3. Environmental fitness (individuals who are better adapted to their environment will produce more offspring and pass their traits to the next generation) The Leakey Family (Louis and Mary) Rejected theory of Asian human origin and traveled to Africa where they (Louis and Mary) discovered fossilized human remains 2 million yrs BP Reconstructed a series of human civilizations from 100 000 yrs BP to over 2 million years BP Experimented with Stone Age tools to discover how our ancestors hunted for food Raymond Dart Discovered a skull in South Africa in 1924 Skull represented the transitional stage between apes and humans Donald Johanson Discovered Lucy in 1974 in Ethiopia Humans walked upright 3.2 million years ago Jane Goodall Worked with Leakey’s in Tanzania recording life of chimpanzees Discovered chimps used tools to bore holes in trees to get ants to feed on; chimps have a highly developed social structure Dian Fossey Studied Rwanda’s mountain gorilla community Learned to imitate their habits and sounds in order to gain acceptance by community Observed them demonstrating affection toward family and aggression toward outsiders Birute Galdikas Employed by Louis Leakey to study orangutans (who share98% of its genetic material with humans) 1968 set up camp in Borneo, Indonesia Became a foster parent to Surgito, a male 1 year old orangutan that was kept in cage