Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam 2 PRIMATES Reasons
advertisement

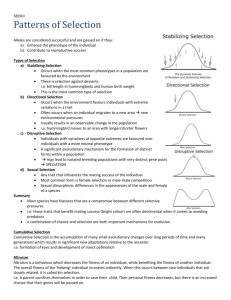
Physical Anthropology Study Guide for Exam 2 PRIMATES Reasons to study Shared anatomical characteristics Evolutionary trends Ecology Why primate ecology important Key components: food & predation Metabolic rates Energy requirements Distribution of food Activity patterns Home range Territoriality Resource defense Defense against predation: alarm calls/social groups Mating Systems Reproductive strategies; male and female Multimale, multifemale groups Single male, multifemale groups Monogamy Parental investment Reproductive success Dominance hierarchies Social Groups Sexual selection Male mating strategies Female mating strategies Intrasexual selection Intersexual selection Sexual dimorphism Sperm production/testicle size Competition Infanticide Social Behavior Social interactions Altruistic behavior Selfish behavior Mutualistic behavior Spiteful behavior Increasing fitness Inclusive fitness Group selection Individual selection Kin selection Transmission of rank from mothers to offspring Grooming Food sharing Reciprocal altruism Primate intelligence: why are primates smart? Ecological knowledge Social knowledge POSSIBLE ESSAY QUESTIONS Diet, extractive foraging, and social challenges have all been suggested as influencing the evolution of cognitive abilities of primates. What is the rationale for each of these models? What evidence do we have that monkeys have a concept of kinship? There are relatively few good examples of reciprocal altruism in nature. Why is reciprocal altruism uncommon? Why would it be more common among primates than other animals? Why is the VARIANCE in male reproductive fitness greater than the variance for females among mammals? What effect does this have on sexual selection? Infanticide by male primates is generally limited to species that form one-male groups. Why wouldn't males in multi-male groups benefit from infanticide? Why do males in one-male groups benefit? Territoriality is linked to group size, day range, and diet. Explain each correlation. Territoriality reduces access of outside individuals to food, sleeping sites, mates, and other resources. Why aren't ALL primates territorial?