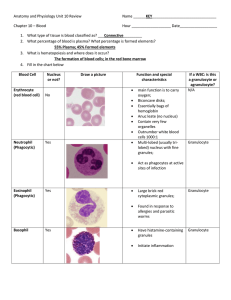
Function of Blood
advertisement
Blood Function of Blood Composition of Blood Blood Types Function of Blood Transport of: Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Nutrients Wastes Immunity Composition Of Blood 55 % Plasma 45% Cells and Cell Parts Plasma composed of: – clear golden fluid and Water – dissoved substances – proteins Has several functions: – Transports small molecules and ions – contains proteins involved in blood clotting – contains antibodies that are involved in disease fighting Blood Cells and Cell Parts There are 3 Cellular components to blood Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Blood Platelets Red Blood Cells Also called Erythrocytes Main function is to carry Oxygen Structure: – Mature cells do not contain a nucleus – Cytoplasm contains a molecule called Hemoglobin The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen every R.B.C contains > 200 mil. hemoglobin molecules White Blood Cells also called Leucocytes Function: protect the body from infection There are Two main types of W.B.C. s macrophages – move out of capp. and digest foriegn materials by phagocytosis Lymphocytes – manufacture antibobies that fight infection Platelets Cell fragments 250 million per cubic centimetre Function: Trigger the Blood Clotting Process Review of Blood Components Blood Plasma Blood Cells and Blood Parts White Blood Cells(W.B.C) -Leucocytes Macrophages Lymphocytes Platelets Red Blood Cells (R.B.C) -Erththrocytes Important Terms Antigen Molecules that cause the synthesis of antibodies when injected into another organism Antibody Proteins found in blood that attack and neutralize substances that are foreign to the body Major Blood Groups Discovered by Karl Landsteiner Different blood groups are due to differing antigens present on red cell membranes 4 Major Blood Types – – – – A B AB O BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS Not all blood types can be mixed together If the wrong Blood types are mixed a process called Agglutination will occur Agglutination - the clumping of blood Examine the next chart to see compatible blood groups Blood Compatibilities Blood Type Antigen Antibody A A Anti B B B Anti A AB A and B None O None Anti A and Anti B Rh Factors Other antigens that may be present on R. B C. s Most people have these antigens they are said to be Rh Positive Those without the antigen are said to be Rh Negative Rh Factors and Pregancy Problems may occur if Rh negative mother gives birth to Rh positive baby Mother may develop anti-Rh antibodies Future pregnancies may result in these antibodies causing agglutination of babies blood However injections have been developed that correct this problem Blood Clotting Platelets broken open by damaged blood vessels Platelets release chemicals that convert prothrombrin into thrombrin Thrombrin causes fibrinogen molecules to join together to form strands called Fibrin Many strands of Fibrin form amesh or clot that stops the bleeding Blood Clotting Blood Problems Anemia - occurs when there is a shortage of hemoglobin ib blood Leukemia - Cancer of the white blood cells A.I.D.S - the H.I.V. virus attacks and destroys an important type of WBC Sickle Cell Disease - abnormal hemoglobin causes RBC s to have irregular shape