follow along sheet
advertisement

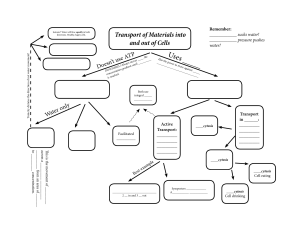
Membrane Structure and Transport Plasma Membrane A membrane that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell the contents of the cell from the outside environment Regulates what and the cell. Fluid Mosaic Model A model that describes the cell membrane as a flexible mosaic composed of embedded dispersed in a fluid of Think of how many mosaic tiles make a complete picture. Membrane Structure Composed of: Made of amphiphatic molecules, meaning the molecules have both a and non-polar portion Helps phospholipids and affects fluidity Used for recognition (communication/”name tag”) Membrane Function To transport and of the cell: Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport, Endocytosis/Exocytosis Adhesion Cell Communication Simple Diffusion “down the concentration gradient” The movement of molecules from an area of their concentration to an area of their concentration. At Equilibrium: Particles are in motion, there is just no NET movement Passive Transport Diffusion across a biological membrane with expenditure of energy by the cell Osmosis A kind of passive transport Diffusion of through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of the H2O concentration to an area of the H2O concentration Ex: Dialysis, Kidney Filtration Tonicity The relative concentration of one solution compared to another solution Hypotonic: solute concentration Hypertonic: solute concentration Isotonic: Solutions with solute concentrations (it does not necessarily mean that there is no solute) Osmosis and Tonicity In osmosis, the “Salt sucks” , typically H2O, moves from the: solution to the solution. Cell Physiology and Tonicity Lysed: In a solution, the blood cell to intake of water. Shriveled: In a solution, the blood cell will shrivel due to loss of water. or burst due or Cell Physiology and Tonicity : When placed in a solution, the plant cell’s vacuoles with water and develop a pressure. : When placed in an solution, the cell will neither gain nor lose water. : When placed in a solution, the cell’s vacuoles will water and the cytoplasm will shrink ( ). Selective Permeability Simple Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion ( ) Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Passive Transport: expenditure of energy Movement of particles (ions and polar molecules) a concentration gradient via a that is embedded in a plasma membrane Active Transport Requires expenditure of energy in the form of Typically, involves movement of solutes gradient, but not always Requires a transport protein The sodium/potassium pump is an example ( ) the concentration Endocytosis An process for the movement of materials cell via membranous vesicles. 2 Types: cytosis Cell “ ” cytosis Cell “ ” Exocytosis An process for the movement of materials of a cell via membranous vesicles (example: hormones) a