Notes on Reproduction Reproduction: All living things come from
advertisement

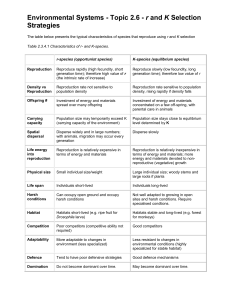
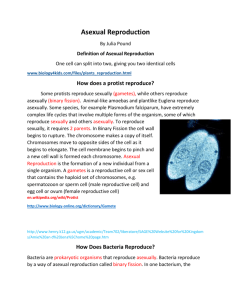
Notes on Reproduction Reproduction: All living things come from _____________________________________. An organism comes from a parent organism through _______________________. Reproduction: Sexual reproductionAsexual reproduction Fertilization is the process where a sperm _________ from a male and an egg _______ from a female join into a single _________. Any characteristic of a living thing is a ____________. In asexual reproduction, the offspring is __________ to the parent. All six kingdoms have organisms that reproduce asexually. Kingdoms that reproduce asexually: o Bacteria o o Most fungi o Plants Animals that can reproduce asexually: o Jellyfish o Corals o o Echinoderms Splitting: unicellular protists and bacteria reproduce by ________ into two cells. Budding: a small part of the parent’s body grows into a tiny and complete version of the ____________. Vegetative propagation- produces new plants from leaves, roots, or _________. Sexual Reproduction Embryo- the beginning of a new ______________. Inside the________ of a flower, fertilization takes place. The inside of the seed is where the _________ grows. This seeds contains all the food supply for the growing embryo. Eventually the embryo will develop enough to make its own food. Fruit develops from the ovary and it protects the seed inside. Another form of protection comes from the seed coat which is tough outer covering. Notes on Reproduction Plants that use _____ for reproduction are called conifers and fertilization takes place inside the cone. After _____________, the developing egg matures into a seed inside the cone. Seed dispersal: o They can be carried by water or by the wind. o _____________ can move seeds from place to place. o Animals can eat seeds and as the seeds pass through their ______________ system they deposit them in a new location. __________ reproduce sexually. Fish and _______ lay their eggs in water. The water keeps the eggs moist and a jellylike layer protects the embryos. Food is provided for the embryo from the ________ of the eggs. Most mammals develop inside their __________. They get nutrients from their mothers’ bodies as they develop. Monotremes are the only mammals that lay eggs. All other mammals give birth to live young. Yeast are _________ that reproduce through budding. Other fungi can reproduce _____________ by producing spores. Some fungi also reproduce sexually. Budding: o ____________ begins when a small growth, called a bud, forms on the parent cell. o As the bud grows, the nucleus in the parent cell ________ in two. o Each nuclei has identical genetic information. o On of the nuclei becomes part of the developing bud and eventually the bud breaks off and lives as a new ________________. Multicellular fungi reproduce asexually. Fruiting body: fungal structure that produces spores. Most fungi can also reproduce ___________. Sexual reproduction occurs when two hyphae fuse and form a new spore-producing structure. Asexual reproduction is convenient. An organism does not have to depend on another ___________ to reproduce. It can live in isolation. Sexual reproduction promotes variety in a _________. It can give rise to offspring better suited to environmental changes. Offspring are ______ identical to either parent. Some are smaller, larger, or faster.